/** Spark SQL源码分析系列文章*/
接上一篇文章Spark SQL Catalyst源码分析之Physical Plan,本文将介绍Physical Plan的toRDD的具体实现细节:
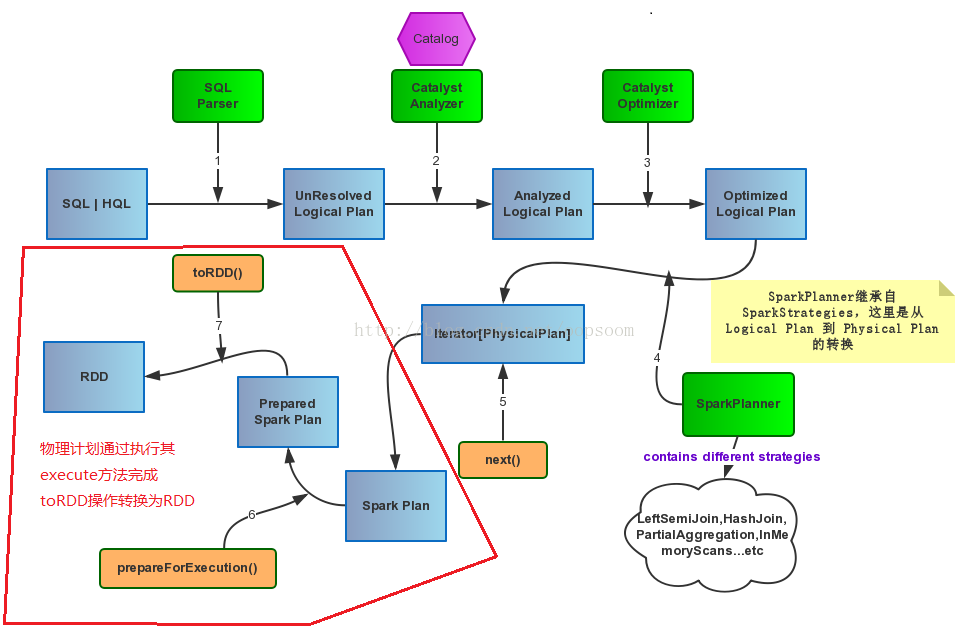
我们都知道一段sql,真正的执行是当你调用它的collect()方法才会执行Spark Job,最后计算得到RDD。 lazy val toRdd: RDD[Row] = executedPlan.execute()Spark Plan基本包含4种操作类型,即BasicOperator基本类型,还有就是Join、Aggregate和Sort这种稍复杂的。
如图:
一、BasicOperator
1.1、Project
Project 的大致含义是:传入一系列表达式Seq[NamedExpression],给定输入的Row,经过Convert(Expression的计算eval)操作,生成一个新的Row。
Project的实现是调用其child.execute()方法,然后调用mapPartitions对每一个Partition进行操作。
这个f函数其实是new了一个MutableProjection,然后循环的对每个partition进行Convert。
这个f函数其实是new了一个MutableProjection,然后循环的对每个partition进行Convert。
case class Project(projectList: Seq[NamedExpression], child: SparkPlan) extends UnaryNode {
override def output = projectList.map(_.toAttribute)
override def execute() = child.execute().mapPartitions { iter => //对每个分区进行f映射
@transient val reusableProjection = new MutableProjection(projectList)
iter.map(reusableProjection)
}
}
将一个Row转换为另一个已经定义好schema column的Row。
如果输入的Row已经有Schema了,则传入的Seq[Expression]也会bound到当前的Schema。
如果输入的Row已经有Schema了,则传入的Seq[Expression]也会bound到当前的Schema。
case class MutableProjection(expressions: Seq[Expression]) extends (Row => Row) {
def this(expressions: Seq[Expression], inputSchema: Seq[Attribute]) =
this(expressions.map(BindReferences.bindReference(_, inputSchema))) //bound schema
private[this] val exprArray = expressions.toArray
private[this] val mutableRow = new GenericMutableRow(exprArray.size) //新的Row
def currentValue: Row = mutableRow
def apply(input: Row): Row = {
var i = 0
while (i < exprArray.length) {
mutableRow(i) = exprArray(i).eval(input) //根据输入的input,即一个Row,计算生成的Row
i += 1
}
mutableRow //返回新的Row
}
}1.2、Filter
Filter的具体实现是传入的condition进行对input row的eval计算,最后返回的是一个Boolean类型,
如果表达式计算成功,返回true,则这个分区的这条数据就会保存下来,否则会过滤掉。
case class Filter(condition: Expression, child: SparkPlan) extends UnaryNode {
override def output = child.output
override def execute() = child.execute().mapPartitions { iter =>
iter.filter(condition.eval(_).asInstanceOf[Boolean]) //计算表达式 eval(input row)
}
}1.3、Sample
Sample取样操作其实是调用了child.execute()的结果后,返回的是一个RDD,对这个RDD调用其sample函数,原生方法。
case class Sample(fraction: Double, withReplacement: Boolean, seed: Long, child: SparkPlan)
extends UnaryNode
{
override def output = child.output
// TODO: How to pick seed?
override def execute() = child.execute().sample(withReplacement, fraction, seed)
}1.4、Union
Union操作支持多个子查询的Union,所以传入的child是一个Seq[SparkPlan]
execute()方法的实现是对其所有的children,每一个进行execute(),即select查询的结果集合RDD。
通过调用SparkContext的union方法,将所有子查询的结果合并起来。
case class Union(children: Seq[SparkPlan])(@transient sqlContext: SQLContext) extends SparkPlan {
// TODO: attributes output by union should be distinct for nullability purposes
override def output = children.head.output
override def execute() = sqlContext.sparkContext.union(children.map(_.execute())) //子查询的结果进行union
override def 







 本文深入探讨Spark SQL的Physical Plan,详细分析Project、Filter、Sample、Union、Limit、Sort等基本操作及其如何转化为RDD。同时,讨论了HashJoin,包括LeftSemiJoinHash、BroadcastHashJoin和ShuffleHashJoin等Join相关运算的实现细节。
本文深入探讨Spark SQL的Physical Plan,详细分析Project、Filter、Sample、Union、Limit、Sort等基本操作及其如何转化为RDD。同时,讨论了HashJoin,包括LeftSemiJoinHash、BroadcastHashJoin和ShuffleHashJoin等Join相关运算的实现细节。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 453
453

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








