1项目3
1.1项目3设计要求
要求学生改进GeekOS的调度程序,实现基于4级反馈队列的调度算法(初始GeekOS系统仅提供了FIFO进程调度算法),并实现信号量,支持进程间通信。
即完成以下几项:
(1)实现src/geekos/syscall.c文件中的Sys_SetSchedulingPolicy系统调用,它的功能是设置系统采用的何种进程调度策略;
(2)实现src/geekos/syscall.c文件中的Sys_GetTimeOfDay系统调用,它的功能是获取全局变量g_numTicks的值;
(3)实现函数Change_Scheduling_Policy(),具体实现不同调度算法的转换。
(4)实现syscall.c中信号量有关的四个系统调用:sys_createsemaphore( )、sys_P( )、sys_V( )和sys_destroysemaphore( )。
1.2 项目3设计原理和分析
1)Set_Scheduling_Policy(policy,quantum),policy是设置的调度策略,quantum是设置的时间片。例如policy为1说明设置的是多级反馈队列调度算法,g_schedulingPolicy设置为1(g_schedulingPolicy为系统添加的标识算法的变量,初始化为0)。如果policy为0,则说明设置的是轮转调度, g_schedulingPolicy设置为0,把4个队列变成一个队列,即所有的线程都在队列0上了。
2)在系统调用Sys_GetTimeOfDay()中,只需要返回g_numTicks就可以了。在Sys_SetSchedulingPolicy()中,如果state->ebx是1,则设置的是MLF算法,为0则是RR算法。如果state->ebx为其他值,则返回-1。
3)在Init_Thread()中都是把队列放在0队列上的,并且blocked变量为false。
4)在Get_Next_Runnable()中,从最高级的队列开始,调用Find_Best()来找线程优先级最大的线程,直到在某级队列中找到符合条件可以运行的线程。
5)在Wait()函数中,线程被阻塞,所以blocked变量被设置为true,并且如果是MLF算法,则该进程的currentReadyQueue加一,下次运行的时候进入高一级的线程队列。
6)信号量定义
GveekOS定义了信号量的结构体:
structSemaphore{
int semaphoreID; /*信号量的ID*/
char *semaphoreName; /*信号量的名字*/
int value; /*信号量的值*/
int registeredThreadCount; /*注册该信号量的线程数量*/
struct Kernel_Thread*registeredThreads[MAX_REGISTERED_THREADS];
/*注册的线程*/
struct Thread_Queue waitingThreads; /*等待该信号的线程队列*/
DEFINE_LINK(Semaphore_List,Semaphore); /*连接信号链表的域*/
}
7)信号量PV操作
信号量操作:
Semaphore_Create()
Semaphore_Acquire(P操作)
Semaphore_Release(V操作)
Semaphore_Destroy()
Create_Semaphore()函数首先检查请求创建的这个信号量的名字是否存在,如果存在,那么就把这个线程加入到这个信号量所注册的线程链表上;如果不存在,则分配内存给新的信号量,清空它的线程队列,把当前的这个线程加入到它的线程队列中,设置注册线程数量为1,初始化信号量的名字,值和信号量的ID,并把这个信号量添加到信号量链表上,最后返回信号量的ID。
P操作Semaphore_Acquire()中,首先检查传入的信号量ID是否存在,如果存在,接着检查当前线程是否注册使用了这个信号量,如果这两项检查任意一项失败了,那么就返回-1。如果成功了,就把信号量的值减去1,如果减去1后信号量的值小于0,那么就把当前线程放入这个信号量的等待队列上。
V操作Semaphore_Release()中,首先也是检查传入的信号量ID是否存在,如果存在,接着检查当前线程是否注册使用了这个信号量,如果这两项检查任意一项失败了,那么就返回-1。如果成功了,那就把信号量的值加上1,如果加上1后信号量的值小于或等于0,则要把该信号量里等待队列上的一个线程唤醒。
Semaphore_Destroy()中,首先也是检查传入的信号量ID是否存在,如果存在,接着检查当前线程是否注册使用了这个信号量,如果这两项检查任意一项失败了,那么就返回-1。如果成功了,就把该线程从这个信号量的注册的线程数组中删除,并把注册的线程数量减去1。如果这个信号量的注册线程为0了,则把这个信号量从信号量链表中删除,并释放它的内存。
8)多级反馈队列调度队列模型
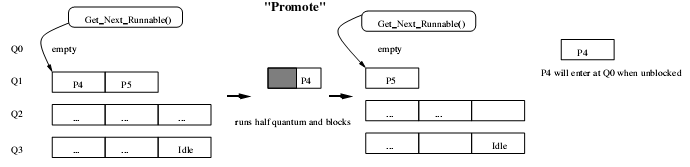
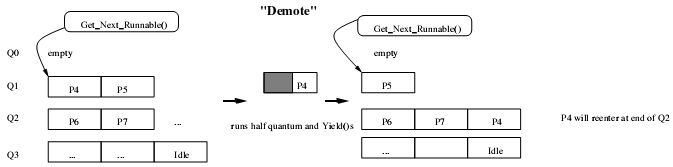
9)多级反馈队列与分时调度进程队列的转换
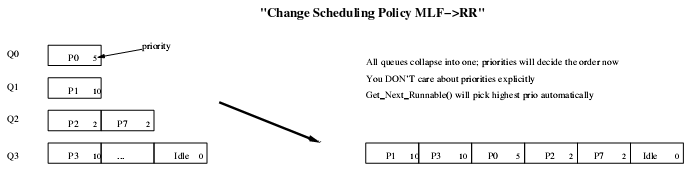
1..3项目3实现
实现信号量需要在synch.h文件中添加信号量结构体的定义和信号量队列的的定义
/*
*define Semaphore
*/
struct Semaphore;
DEFINE_LIST(Semaphore_List,Semaphore);
struct Semaphore{
intsemaphoreID;
char*semaphoreName;
intvalue;
intregisteredThreadCount;
#defineMAX_REGISTERED_THREADS 60
structKernel_Thread *registeredThreads[MAX_REGISTERED_THREADS];
structThread_Queue waitingThreads;
DEFINE_LINK(Semaphore_List,Semaphore);
};
IMPLEMENT_LIST(Semaphore_List,Semaphore);
static __inline__ void Enqueue_Semaphore(structSemaphore_List *list, struct Semaphore *sem) {
Add_To_Back_Of_Semaphore_List(list, sem);
}
static __inline__ void Remove_Semaphore(structSemaphore_List *list, struct Semaphore *sem) {
Remove_From_Semaphore_List(list, sem);
}
在syscall.c文件中添加:
static structSemaphore_List s_sphlist;//如果定义为指针类型易导致13号页保护中断
static intsemnub=1;
并完成如下函数:
/*
* Create asemaphore.
* Params:
* state->ebx - user address of name ofsemaphore
* state->ecx - length of semaphore name
* state->edx - initial semaphore count
* Returns: theglobal semaphore id
*/
static int Sys_CreateSemaphore(struct Interrupt_State*state)
{
// TODO("CreateSemaphoresystem call");
int rc;
char*name = 0;
//intexit, id_sem;
structSemaphore *s=s_sphlist.head;
if ((rc =Copy_User_String(state->ebx, state->ecx, VFS_MAX_PATH_LEN, &name)) !=0 )
goto fail;
//Print("Copy_User_String_Name=%s\n",name);
while(s!=0)
{
//Print("whiles->semaphoreName=%s\n",s->semaphoreName);
if(strcmp(s->semaphoreName,name)==0)
{
s->registeredThreads[s->registeredThreadCount]=g_currentThread;
s->registeredThreadCount+=1;
returns->semaphoreID;
}
s=Get_Next_In_Semaphore_List(s);
}
s=(structSemaphore *)Malloc(sizeof(struct Semaphore));
s->registeredThreads[0]=g_currentThread;
s->registeredThreadCount=1;
//strcpy(s->semaphoreName,name);
s->semaphoreName=name;
//Print("s->semaphoreName=name===%s\n",s->semaphoreName);
Clear_Thread_Queue(&s->waitingThreads);
s->value=state->edx;
s->semaphoreID=semnub;
semnub++;
Add_To_Back_Of_Semaphore_List(&s_sphlist,s);
returns->semaphoreID;
fail:
Print("CreateSemaphorefailed!");
return -1;
}
/*
* Acquire asemaphore.
* Assume thatthe process has permission to access the semaphore,
* the call willblock until the semaphore count is >= 0.
* Params:
* state->ebx - the semaphore id
*
* Returns: 0 ifsuccessful, error code (< 0) if unsuccessful
*/
static int Sys_P(struct Interrupt_State* state)
{
// TODO("P (semaphore acquire) system call");
structSemaphore *s=s_sphlist.head;
while(s!=0)
{
if(s->semaphoreID== state->ebx)
break;
s=Get_Next_In_Semaphore_List(s);
}
if(s==0)
return-1;
s->value-=1;
if(s->value<0)
Wait(&s->waitingThreads);
return 0;
}
/*
* Release asemaphore.
* Params:
* state->ebx - the semaphore id
*
* Returns: 0 ifsuccessful, error code (< 0) if unsuccessful
*/
static int Sys_V(struct Interrupt_State* state)
{
// TODO("V (semaphore release) system call");
structKernel_Thread *kthread;
structSemaphore *s=s_sphlist.head;
while(s!=0)
{
if(s->semaphoreID==state->ebx)
break;
s=Get_Next_In_Semaphore_List(s);
}
if(s==0)
return-1;
s->value+=1;
if(s->value>=0){
kthread =s->waitingThreads.head;
if(kthread !=0){
Wake_Up_One(&s->waitingThreads);
}
}
return 0;
}
/*
* Destroy asemaphore.
* Params:
* state->ebx - the semaphore id
*
* Returns: 0 ifsuccessful, error code (< 0) if unsuccessful
*/
static int Sys_DestroySemaphore(structInterrupt_State* state)
{
//TODO("DestroySemaphore system call");
structSemaphore *s = s_sphlist.head;
while (s) {
if(s->semaphoreID == state->ebx)
break;
s =Get_Next_In_Semaphore_List(s);
}
if (s == 0)
return-1;
s->registeredThreadCount--;
if(s->registeredThreadCount == 0) {
Free(s);
Remove_From_Semaphore_List(&s_sphlist,s);
}
return 0;
}
实现多队列的优先级调度要在kthread.h中定义调度方式的宏:
#define ROUND_ROBIN 0
#define MULTILEVEL_FEEDBACK 1
/* * Number ofscheduling policy. * 0 -> RoundRobin * 1 -> Multilevel feedback */
int g_schedulingPolicy;
在kthread.c中完成如下函数:
/*
* Get the nextrunnable thread from the run queue.
* This is thescheduler.
*/
struct Kernel_Thread* Get_Next_Runnable(void)
{
structKernel_Thread* best = 0;
int i,best_index_queue = -1;
if(g_schedulingPolicy == ROUND_ROBIN) {
structKernel_Thread* best_in_queue = NULL;
for (i =0; i < MAX_QUEUE_LEVEL; i++){
best_in_queue= Find_Best(&s_runQueue[i]);
if(best == NULL) {
best= best_in_queue;
best_index_queue= i;
}else if (best_in_queue != NULL){
if(best_in_queue->priority > best->priority) {
best= best_in_queue;
best_index_queue= i;
}
}
}
} else if(g_schedulingPolicy == MULTILEVEL_FEEDBACK) {
if (g_currentThread->priority != PRIORITY_IDLE ){
if (g_currentThread->blocked && g_currentThread->currentReadyQueue> 0 )
g_currentThread->currentReadyQueue--;
}
for (i =0; i < MAX_QUEUE_LEVEL; i++){
best= Find_Best(&s_runQueue[i]);
best_index_queue= i;
if(best != NULL)
break;
}
if (best->currentReadyQueue < MAX_QUEUE_LEVEL-1 )
best->currentReadyQueue++;
}
KASSERT(best!= NULL);
Remove_Thread(&s_runQueue[best_index_queue],best);
return best;
}
在syscall.c中完成如下函数:
/*
* Set the scheduling policy.
* Params:
* state->ebx - policy,
* state->ecx - number of ticks in quantum
* Returns: 0 if successful, -1otherwise
*/
static int Sys_SetSchedulingPolicy(struct Interrupt_State* state)
{
if (state->ebx != ROUND_ROBIN&& state->ebx != MULTILEVEL_FEEDBACK)
return -1;
g_schedulingPolicy =state->ebx;
g_Quantum = state->ecx;
return 0;
}
信号量测试结果如下图所示:
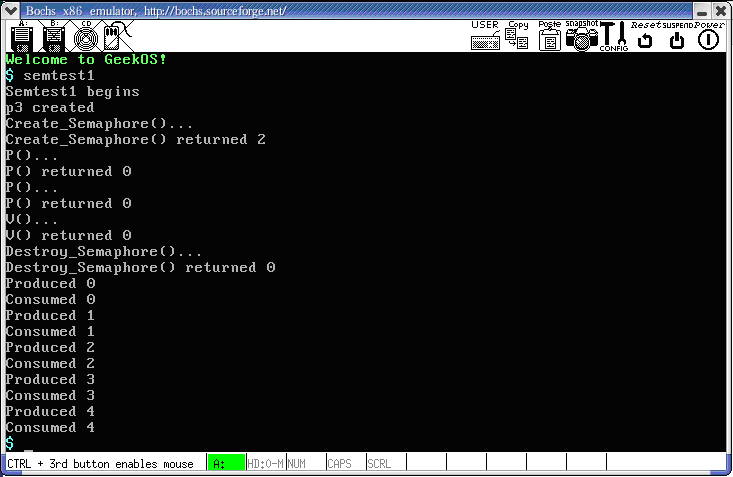
图1 项目3信号量测试界面
多队列优先级调度测试结果如下图所示:
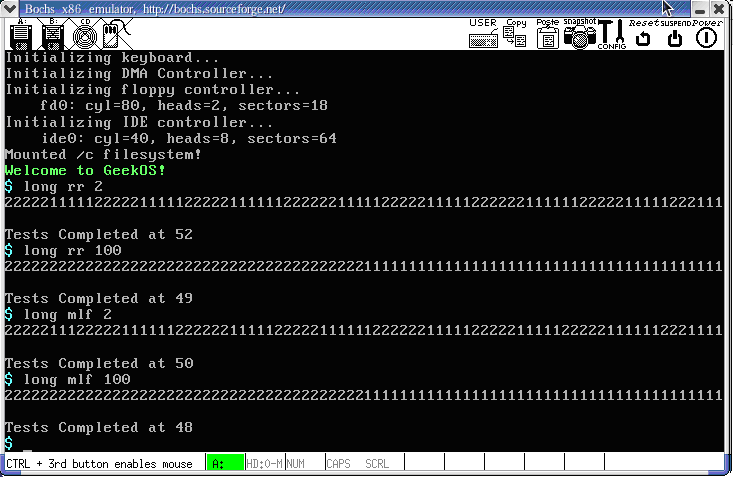
图2 项目3多队列优先级调度测试界面
1.4项目小结
从上面的测试结果来看,这两种调度算法都是基于时间片轮转,输出2和输出1的的数量基本一样多(多队列优先级调度算法的时间片都是一样的)。进程的周转时间还包括进程切换的时间。同样的调度算法,同样的时间片,程序执行的周转时间可能不一样(进程切换花费的时间可能不一样)。信号量测试程序测试的是生产者消费者的互斥操作,生产一个消费一个。
再分享一下我老师大神的人工智能教程吧。零基础!通俗易懂!风趣幽默!还带黄段子!希望你也加入到我们人工智能的队伍中来!https://blog.csdn.net/jiangjunshow





















 1187
1187

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








