毕业设计:2023-2024年计算机专业毕业设计选题汇总(建议收藏)
毕业设计:2023-2024年最新最全计算机专业毕设选题推荐汇总
🍅感兴趣的可以先收藏起来,点赞、关注不迷路,大家在毕设选题,项目以及论文编写等相关问题都可以给我留言咨询,希望帮助同学们顺利毕业 。🍅
1、项目介绍
技术栈:
Python语言、MySQL数据库、Flask框架、Echarts可视化、Dlib库、刷脸签到、多角色登录
课堂考勤签到是教育教学中的重要环节,可以实现学生出勤情况的管理,同时也是学生学习过程中的重要参考。传统的课堂签到方式存在着效率低、易产生作弊等问题。因此,基于人脸识别技术的课堂签到系统应运而生,其可以实现自动化签到,提高签到效率,同时也能减少作弊现象的发生。本文将介绍一种基于Flask框架开发的课堂人脸签到系统。
该系统主要分为前端和后端两个部分,前端负责人脸采集、人脸识别以及签到信息的展示,后
2、项目界面
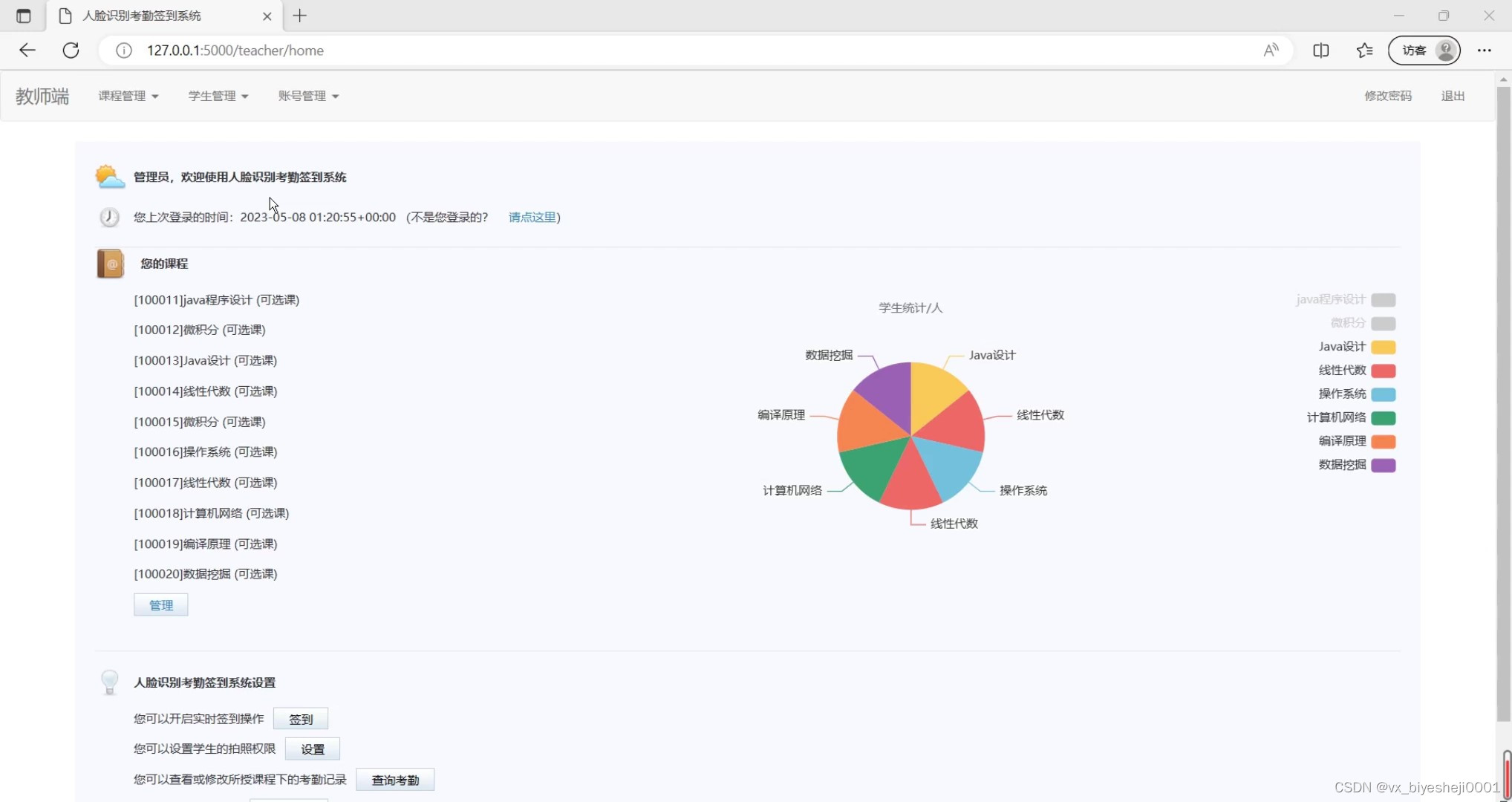
(1)管理员端界面
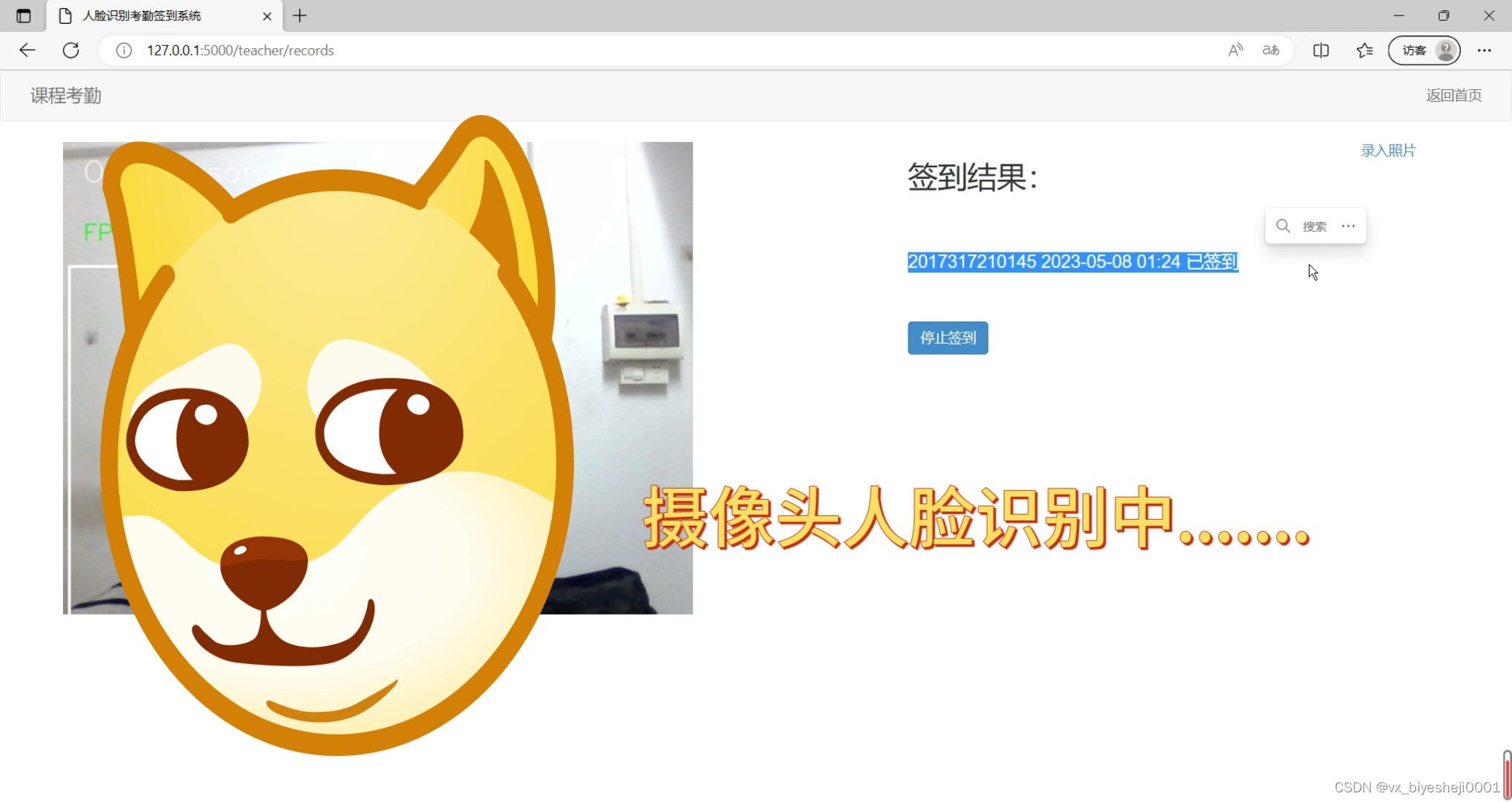
(2)摄像头人脸识别考勤签到界面
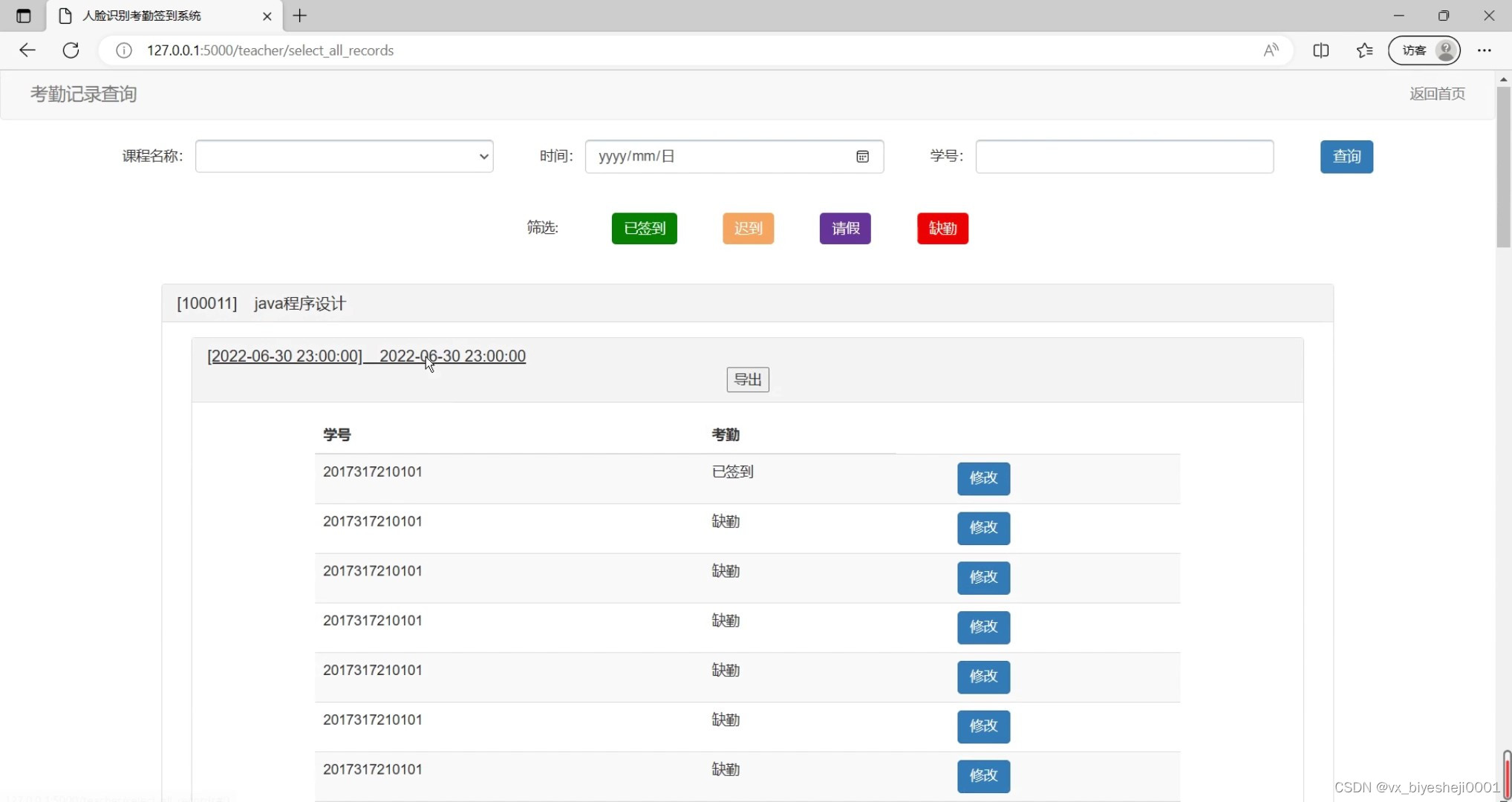
(3)课程考勤情况
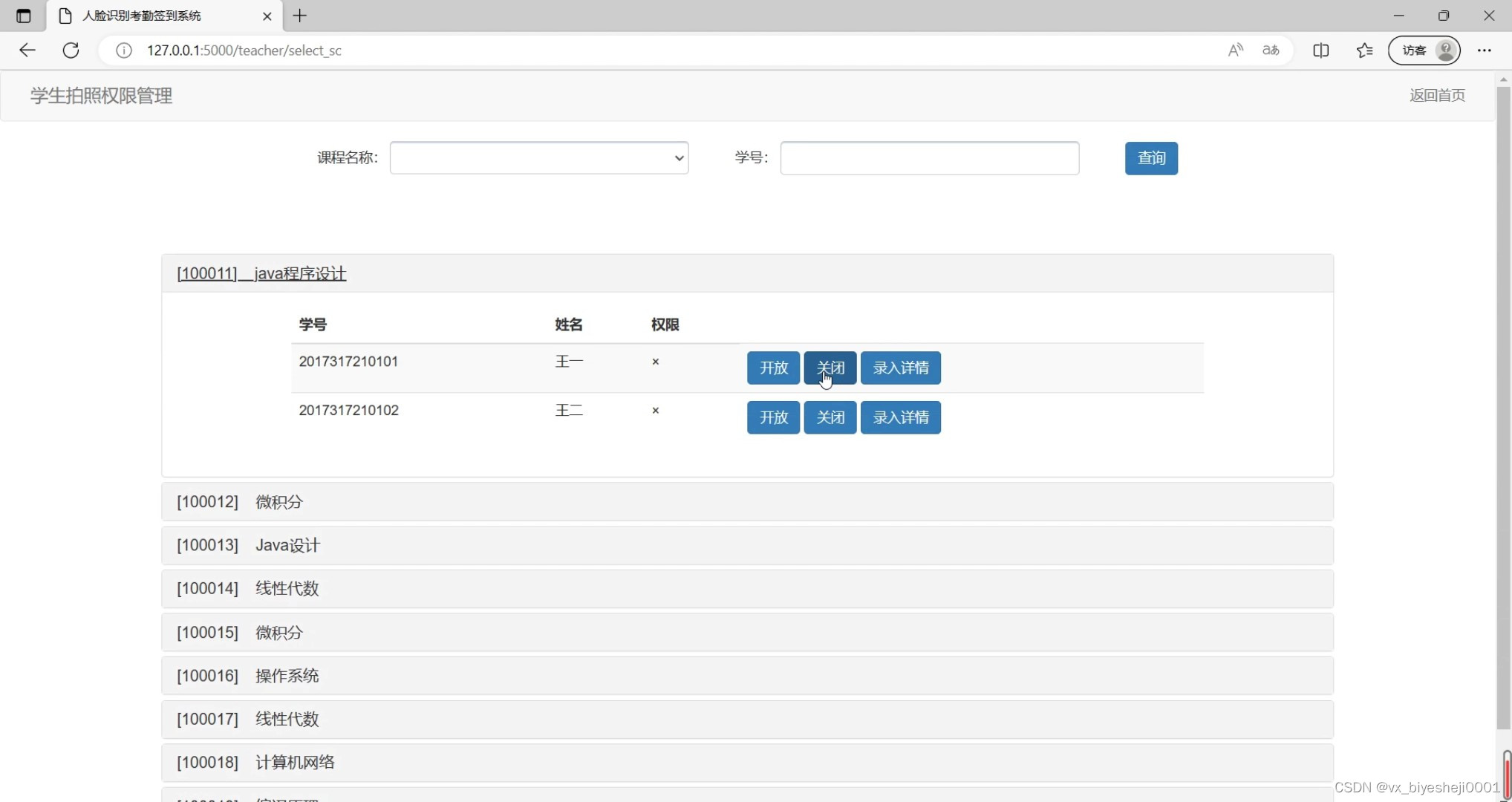
(4)学生考勤权限设置
(5)学生信息
(6)系统登录界面
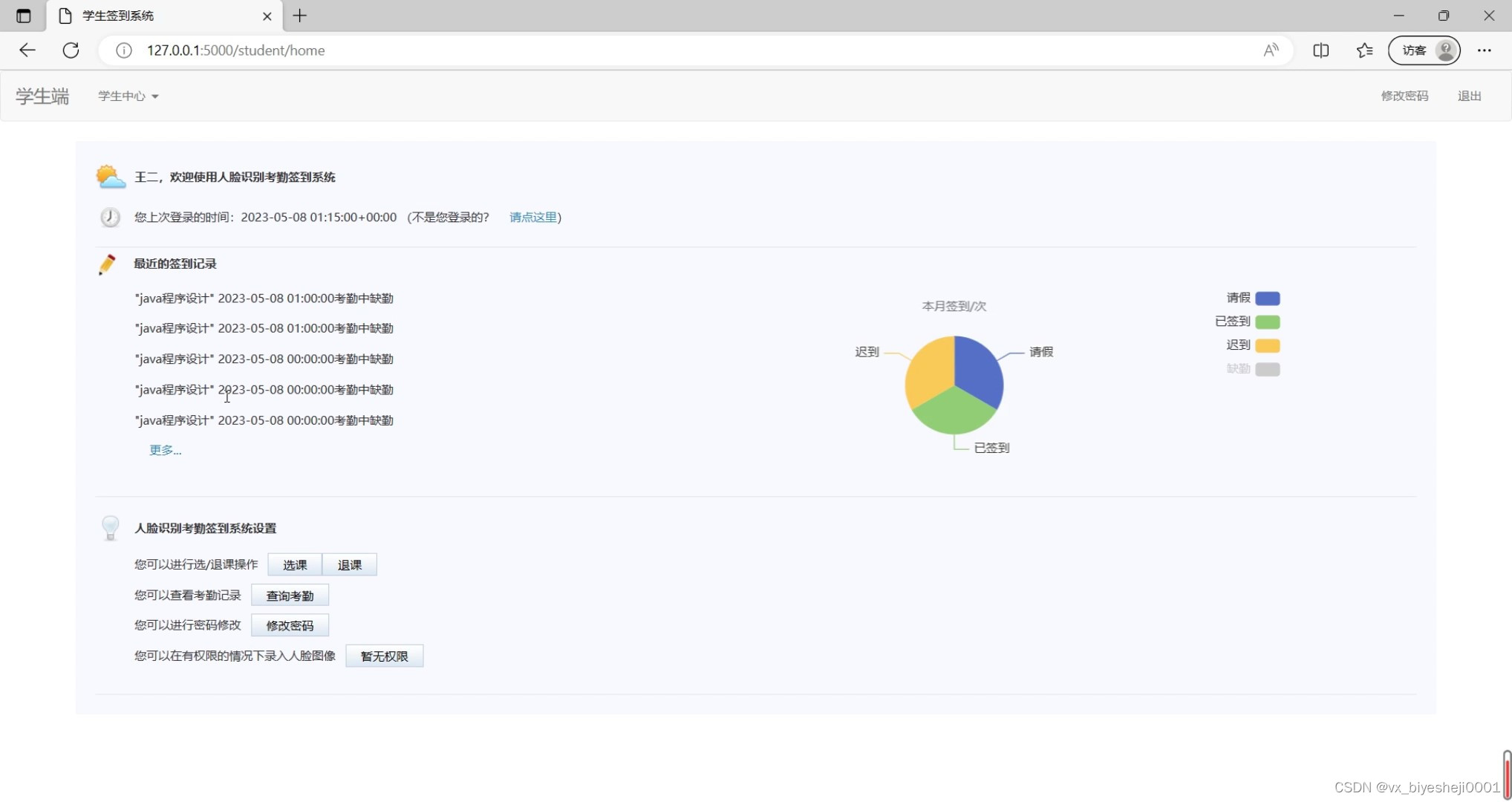
(7)学生端界面
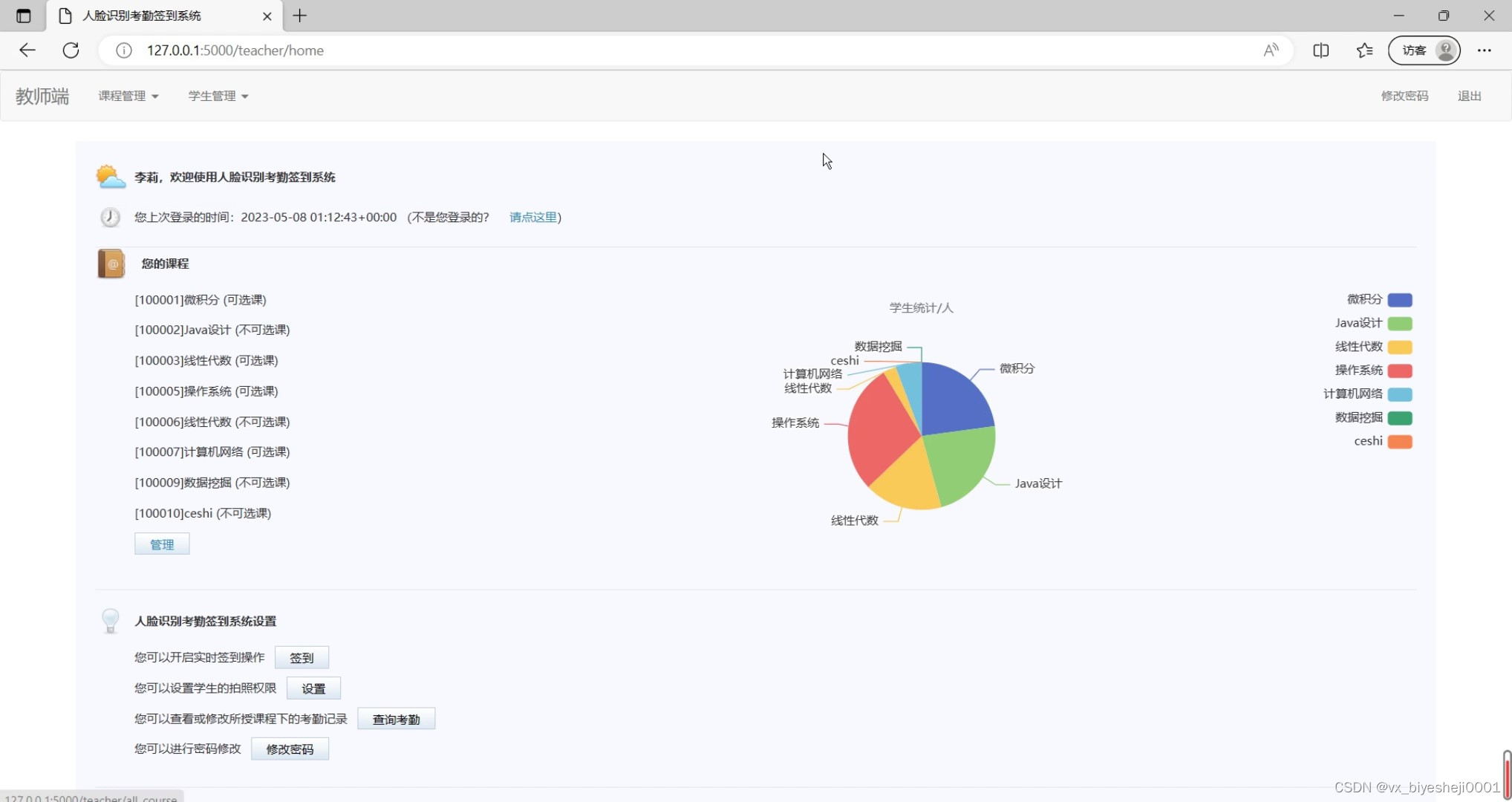
(8)教师端界面
3、项目说明
课堂考勤签到是教育教学中的重要环节,可以实现学生出勤情况的管理,同时也是学生学习过程中的重要参考。传统的课堂签到方式存在着效率低、易产生作弊等问题。因此,基于人脸识别技术的课堂签到系统应运而生,其可以实现自动化签到,提高签到效率,同时也能减少作弊现象的发生。本文将介绍一种基于Flask框架开发的课堂人脸签到系统。
该系统主要分为前端和后端两个部分,前端负责人脸采集、人脸识别以及签到信息的展示,后端则负责存储学生信息和签到记录,并进行相关的逻辑处理。
系统的前端采用HTML、CSS和JavaScript等技术进行开发,主要包括人脸采集页面、签到页面和签到记录页面。人脸采集页面提供了学生人脸的采集功能,签到页面则用于展示学生签到状态,签到记录页面用于展示历史签到记录。在人脸采集和签到页面中,系统使用了摄像头进行拍摄,并利用OpenCV库进行人脸识别。
系统的后端采用了Python语言和Flask框架进行开发。后端主要包括学生信息管理模块、签到记录管理模块和人脸识别模块。在学生信息管理模块中,系统管理员可以对学生信息进行增删改查操作。签到记录管理模块则用于存储学生签到记录,并提供了签到统计和查询功能。人脸识别模块则是整个系统的核心,其利用已经训练好的人脸识别模型进行签到信息的验证和识别。
总体来说,该系统可以提高课堂签到效率,降低作弊率,同时也能够减轻教师的工作负担。未来,可以考虑引入更多的功能和技术,如人脸特征提取、人脸活体检测等,进一步提升系统的精度和安全性。
关键字:人脸识别;人脸考勤;python;flask;opencv;Dlib;
4、核心代码
from flask import Blueprint, render_template, redirect, request, Response, session, flash, jsonify, url_for
import app
from app import db
from .models import Teacher, Faces, Course, SC, Attendance, Time_id, Student
from sqlalchemy.sql import exists
import base64
import os
from app import get_faces_from_camera as gf
from datetime import timedelta
import cv2
import pandas as pd
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
import numpy as np
import dlib
import time
import pandas as pd
import xlsxwriter
import xlwt
from io import BytesIO
from urllib.parse import quote
from flask import send_file
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
teacher = Blueprint('teacher', __name__, static_folder="static")
# 本次签到的所有人员信息
attend_records = []
# 本次签到的开启时间
the_now_time = ''
@teacher.route('/home')
def home():
flag = session['id'][0]
print(flag)
courses = {}
course = db.session.query(Course).filter(Course.t_id == session['id']).all()
for c in course:
num = db.session.query(SC).filter(SC.c_id == c.c_id).count()
courses[c] = num
return render_template('teacher/teacher_home.html', before=session['time'], flag=flag, name=session['name'],
courses=courses)
# Dlib 正向人脸检测器
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
# Dlib 人脸 landmark 特征点检测器
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor('app/static/data_dlib/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat')
# Dlib Resnet 人脸识别模型,提取 128D 的特征矢量
face_reco_model = dlib.face_recognition_model_v1("app/static/data_dlib/dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat")
#人脸识别类
class VideoCamera(object):
def __init__(self):
self.font = cv2.FONT_ITALIC
# 通过opencv获取实时视频流
self.video = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 统计 FPS
self.frame_time = 0
self.frame_start_time = 0
self.fps = 0
# 统计帧数
self.frame_cnt = 0
# 用来存储所有录入人脸特征的数组
self.features_known_list = []
# 用来存储录入人脸名字
self.name_known_list = []
# 用来存储上一帧和当前帧 ROI 的质心坐标
self.last_frame_centroid_list = []
self.current_frame_centroid_list = []
# 用来存储当前帧检测出目标的名字
self.current_frame_name_list = []
# 上一帧和当前帧中人脸数的计数器
self.last_frame_faces_cnt = 0
self.current_frame_face_cnt = 0
# 用来存放进行识别时候对比的欧氏距离
self.current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list = []
# 存储当前摄像头中捕获到的所有人脸的坐标名字
self.current_frame_face_position_list = []
# 存储当前摄像头中捕获到的人脸特征
self.current_frame_face_feature_list = []
# 控制再识别的后续帧数
# 如果识别出 "unknown" 的脸, 将在 reclassify_interval_cnt 计数到 reclassify_interval 后, 对于人脸进行重新识别
self.reclassify_interval_cnt = 0
self.reclassify_interval = 10
def __del__(self):
self.video.release()
# 从 "features_all.csv" 读取录入人脸特征 / Get known faces from "features_all.csv"
def get_face_database(self, cid):
# print(cid)
# course_sid = SC.query.filter(SC.c_id==cid).all()
# all_sid = []
# for sc in course_sid:
# all_sid.append(sc.s_id)
# from_db_all_features = Faces.query.filter(Faces.s_id.in_(all_sid)).all()
from_db_all_features = Faces.query.all()
if from_db_all_features:
for from_db_one_features in from_db_all_features:
someone_feature_str = str(from_db_one_features.feature).split(',')
self.name_known_list.append(from_db_one_features.s_id)
features_someone_arr = []
for one_feature in someone_feature_str:
if one_feature == '':
features_someone_arr.append('0')
else:
features_someone_arr.append(float(one_feature))
self.features_known_list.append(features_someone_arr)
# print("Faces in Database:", len(self.features_known_list))
return 1
else:
# print('##### Warning #####', '\n')
# print("'features' is empty")
# print('##### End Warning #####')
return 0
# 更新 FPS / Update FPS of video stream
def update_fps(self):
now = time.time()
self.frame_time = now - self.frame_start_time
self.fps = 1.0 / self.frame_time
self.frame_start_time = now
# 计算两个128D向量间的欧式距离
@staticmethod
def return_euclidean_distance(feature_1, feature_2):
feature_1 = np.array(feature_1)
feature_2 = np.array(feature_2)
dist = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(feature_1 - feature_2)))
return dist
# 生成的 cv2 window 上面添加说明文字 / putText on cv2 window
def draw_note(self, img_rd):
# 添加说明 (Add some statements
cv2.putText(img_rd, "One person at a time: ", (20, 40), self.font, 1, (255, 255, 255), 1,
cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(img_rd, "FPS: " + str(self.fps.__round__(2)), (20, 100), self.font, 0.8, (0, 255, 0), 1,
cv2.LINE_AA)
# cv2.putText(img_rd, "Q: Quit", (20, 450), self.font, 0.8, (255, 255, 255), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
def draw_name(self, img_rd):
# 在人脸框下面写人脸名字
# print(self.current_frame_name_list)
font = ImageFont.truetype("simsun.ttc", 30)
img = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(img_rd, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
draw.text(xy=self.current_frame_face_position_list[0], text=self.current_frame_name_list[0], font=font)
img_rd = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(img), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
return img_rd
# 处理获取的视频流,进行人脸识别
#进行人脸识别的方法
def get_frame(self, cid):
stream = self.video
# 1. 读取存放所有人脸特征的 csv / Get faces known from "features.all.csv"
#从数据库中获取Cid(studentid) 拿到人脸特征
if self.get_face_database(cid):
while stream.isOpened():
self.frame_cnt += 1
# print(">>> Frame " + str(self.frame_cnt) + " starts")
flag, img_rd = stream.read()
# 2. 检测人脸 / Detect faces for frame X
faces = detector(img_rd, 0) #人脸特征数组
# 3. 更新帧中的人脸数 / Update cnt for faces in frames
self.last_frame_faces_cnt = self.current_frame_face_cnt
self.current_frame_face_cnt = len(faces)
filename = 'attendacnce.txt'
with open(filename, 'a') as file:
# 4.1 当前帧和上一帧相比没有发生人脸数变化 / If cnt not changes, 1->1 or 0->0
if self.current_frame_face_cnt == self.last_frame_faces_cnt:
# print(" >>> scene 1: 当前帧和上一帧相比没有发生人脸数变化 / No face cnt changes in this frame!!!")
if "unknown" in self.current_frame_name_list:
# print(" >>> 有未知人脸, 开始进行 reclassify_interval_cnt 计数")
self.reclassify_interval_cnt += 1
# 4.1.1 当前帧一张人脸 / One face in this frame
if self.current_frame_face_cnt == 1:
if self.reclassify_interval_cnt == self.reclassify_interval:
# print(" >>> scene 1.1 需要对于当前帧重新进行人脸识别 / Re-classify for current frame")
self.reclassify_interval_cnt = 0
self.current_frame_face_feature_list = []
self.current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list = []
self.current_frame_name_list = []
for i in range(len(faces)):
shape = predictor(img_rd, faces[i])
self.current_frame_face_feature_list.append(
face_reco_model.compute_face_descriptor(img_rd, shape))
# a. 遍历捕获到的图像中所有的人脸 / Traversal all the faces in the database
for k in range(len(faces)):
self.current_frame_name_list.append("unknown")
# b. 每个捕获人脸的名字坐标 / Positions of faces captured
self.current_frame_face_position_list.append(tuple(
[faces[k].left(),
int(faces[k].bottom() + (faces[k].bottom() - faces[k].top()) / 4)]))
# c. 对于某张人脸,遍历所有存储的人脸特征 / For every face detected, compare it with all the faces in the database
for i in range(len(self.features_known_list)):
# 如果 person_X 数据不为空 / If the data of person_X is not empty
if str(self.features_known_list[i][0]) != '0.0':
# print(" >>> with person", str(i + 1), "the e distance: ", end='')
e_distance_tmp = self.return_euclidean_distance(
self.current_frame_face_feature_list[k],
self.features_known_list[i])
# print(e_distance_tmp)
self.current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list.append(e_distance_tmp)
else:
# 空数据 person_X / For empty data
self.current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list.append(999999999)
# print(" >>> current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list:",
# self.current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list)
# d. 寻找出最小的欧式距离匹配 / Find the one with minimum e distance
similar_person_num = self.current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list.index(
min(self.current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list))
# print(" >>> Minimum e distance with ", self.name_known_list[similar_person_num],
# ": ",
# min(self.current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list))
if min(self.current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list) < 0.4:
# 在这里更改显示的人名
# self.show_chinese_name()
self.current_frame_name_list[k] = self.name_known_list[similar_person_num]
# print(" >>> recognition result for face " + str(k + 1) + ": " +
# self.name_known_list[similar_person_num])
now = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M", time.localtime())
mm = self.name_known_list[similar_person_num] + ' ' + now + ' 已签到\n'
file.write(self.name_known_list[similar_person_num] + ' ' + now + ' 已签到\n')
attend_records.append(mm)
# session['attend'].append(mm)
else:
pass
# print(
# " >>> recognition result for face " + str(
# k + 1) + ": " + "unknown")
else:
# print(" >>> scene 1.2 不需要对于当前帧重新进行人脸识别 / No re-classification for current frame")
# 获取特征框坐标 / Get ROI positions
for k, d in enumerate(faces):
# 计算矩形框大小 / Compute the shape of ROI
height = (d.bottom() - d.top())
width = (d.right() - d.left())
hh = int(height / 2)
ww = int(width / 2)
cv2.rectangle(img_rd,
tuple([d.left() - ww, d.top() - hh]),
tuple([d.right() + ww, d.bottom() + hh]),
(255, 255, 255), 2)
self.current_frame_face_position_list[k] = tuple(
[faces[k].left(),
int(faces[k].bottom() + (faces[k].bottom() - faces[k].top()) / 4)])
# print(" >>> self.current_frame_name_list: ",
# self.current_frame_name_list[k])
# print(" >>> self.current_frame_face_position_list: ",
# self.current_frame_face_position_list[k])
img_rd = self.draw_name(img_rd)
# 4.2 当前帧和上一帧相比发生人脸数变化
else:
# print(" >>> scene 2: 当前帧和上一帧相比人脸数发生变化 / Faces cnt changes in this frame")
self.current_frame_face_position_list = []
self.current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list = []
self.current_frame_face_feature_list = []
# 4.2.1 人脸数从 0->1 / Face cnt 0->1
if self.current_frame_face_cnt == 1:
# print(" >>> scene 2.1 出现人脸,进行人脸识别
self.current_frame_name_list = []
for i in range(len(faces)):
shape = predictor(img_rd, faces[i])
self.current_frame_face_feature_list.append(
face_reco_model.compute_face_descriptor(img_rd, shape))
# a. 遍历捕获到的图像中所有的人脸
for k in range(len(faces)):
self.current_frame_name_list.append("unknown")
# b. 每个捕获人脸的名字坐标
self.current_frame_face_position_list.append(tuple(
[faces[k].left(),
int(faces[k].bottom() + (faces[k].bottom() - faces[k].top()) / 4)]))
# c. 对于某张人脸,遍历所有存储的人脸特征
# print(len(self.features_known_list))
for i in range(len(self.features_known_list)):
# 如果 person_X 数据不为空 / If data of person_X is not empty
if str(self.features_known_list[i][0]) != '0.0':
# print(" >>> with person", str(i + 1), "the e distance: ", end='')
e_distance_tmp = self.return_euclidean_distance(
self.current_frame_face_feature_list[k],
self.features_known_list[i])
# print(e_distance_tmp)
self.current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list.append(e_distance_tmp)
else:
# 空数据 person_X
self.current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list.append(999999999)
# d. 寻找出最小的欧式距离匹配
similar_person_num = self.current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list.index(
min(self.current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list))
if min(self.current_frame_face_X_e_distance_list) < 0.4:
# 在这里更改显示的人名
# self.show_chinese_name()
self.current_frame_name_list[k] = self.name_known_list[similar_person_num]
# print(" >>> recognition result for face " + str(k + 1) + ": " +
# self.name_known_list[similar_person_num])
now = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M", time.localtime())
mm = self.name_known_list[similar_person_num] + ' ' + now + ' 已签到\n'
file.write(self.name_known_list[similar_person_num] + ' ' + now + ' 已签到\n')
# session['attend'].append(mm)
attend_records.append(mm)
else:
pass
# print(
# " >>> recognition result for face " + str(k + 1) + ": " + "unknown")
if "unknown" in self.current_frame_name_list:
self.reclassify_interval_cnt += 1
# 4.2.1 人脸数从 1->0 / Face cnt 1->0
elif self.current_frame_face_cnt == 0:
# print(" >>> scene 2.2 人脸消失, 当前帧中没有人脸 / No face in this frame!!!")
self.reclassify_interval_cnt = 0
self.current_frame_name_list = []
self.current_frame_face_feature_list = []
# 5. 生成的窗口添加说明文字 / Add note on cv2 window
self.draw_note(img_rd)
self.update_fps()
# cv2.namedWindow("camera", 1)
# cv2.imshow("camera", img_rd)
# print(">>> Frame ends\n\n")
ret, jpeg = cv2.imencode('.jpg', img_rd)
return jpeg.tobytes()
5、源码获取方式
🍅由于篇幅限制,获取完整文章或源码、代做项目的,查看我的【用户名】、【专栏名称】、【顶部选题链接】就可以找到我啦🍅
感兴趣的可以先收藏起来,点赞、关注不迷路,下方查看👇🏻获取联系方式👇🏻

























 2818
2818











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








