一、三大组件
1.Channel & Buffer
channel有一点类似于stream,它就是读写数据的双向通道,可以从channel将数据读入buffer,也可以将buffer中的数据写入channel,而之前的stream要么是输入,要么是输出,channel要比stream更底层。
常见的channel有
- FileChannel
- DatagramChannel
- SocketChannel
- ServerSocketChannel
buffer则是用来缓冲读写数据,常见的buffer有
- ByteBuffer
(实现类)
MappedBuffer
DirectByteBuffer
HeapByteBuffer
- ShortBuffer
- IntBuffer
- LongBuffer
- FloatBuffer
- DoubleBuffer
- CharBuffer
2.Selector
Selector(选择器)是一个特殊的组件,用于采集各个通道的状态(或者说事件)。 我们先将通道注册到选择器,并设置好关心的事件,然后就可以通过调用select()方法,静静地等待事件发生。
多线程版本设计:

多线程版本设计缺点:
- 内存占用高
- 线程上下文切换成本高
- 只适合连接数较少的场景
线程池版本设计
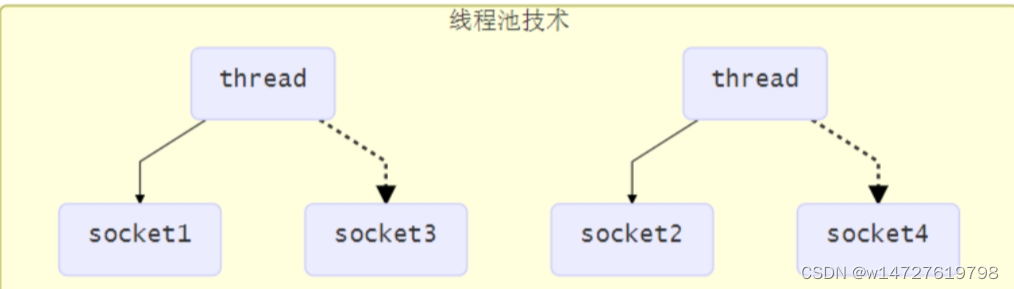
线程池版缺点:
- 阻塞模式下,线程仅能处理一个socket连接
- 仅适合短连接场景
selector版设计
selector的作用就是配合一个线程来管理多个channel,获取这些channel上发生的事件,这些channel工作在非阻塞模式下,不会让一个线程吊死在一个channel上。适合连接数特别多,但流量低的场景(low traffic)

调用selector的select()会阻塞直到channel发生读写就绪事件,这些事件发生,select方法 就会返回这些事件给Thread线程。
二、ByteBuffer
1.channel的基本使用
1.1.建立工程导入依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.2.3</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.wang</groupId>
<artifactId>NettySummary</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.39.Final</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.projectlombok/lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.30</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId>
<artifactId>gson</artifactId>
<version>2.8.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>19.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-simple</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0-beta4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0-beta4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0-beta4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
1.2.在resource目录下导入logback.xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration scan="true"
scanPeriod="60 seconds"
debug="false">
<!-- 应用名称:和统一配置中的项目代码保持一致(小写) -->
<property name="APP_NAME" value="app"/>
<contextName>${APP_NAME}</contextName>
<!--日志文件保留天数 -->
<property name="LOG_MAX_HISTORY" value="30"/>
<!--定义日志文件的存储地址 勿在 LogBack 的配置中使用相对路径 -->
<!--应用日志文件保存路径 -->
<!--在没有定义${LOG_HOME}系统变量的时候,可以设置此本地变量。 -->
<property name="LOG_HOME" value="logs"/>
<property name="INFO_PATH" value="${LOG_HOME}/info"/>
<property name="DEBUG_PATH" value="${LOG_HOME}/debug"/>
<property name="ERROR_PATH" value="${LOG_HOME}/error"/>
<!--<property name="LOG_HOME" msg="/home/logs/${APP_NAME}" />-->
<!--=========================== 按照每天生成日志文件:默认配置=================================== -->
<!-- 控制台输出 -->
<appender name="console" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%c类名,%t表示线程名,%L行, %p日志级别 %msg:日志消息,%n是换行符 -->
<pattern>%black(%contextName - %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}) %green([%c][%t][%L]) %highlight(%-5level) - %gray(%msg%n)</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- 按照每天生成日志文件:主项目日志 -->
<appender name="APP_DEBUG" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!--日志文件输出的文件名 -->
<FileNamePattern>${DEBUG_PATH}/debug-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</FileNamePattern>
<!--日志文件保留天数 -->
<MaxHistory>${LOG_MAX_HISTORY}</MaxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%c类名,%t表示线程名,%L行, %p日志级别 %msg:日志消息,%n是换行符 -->
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%c][%t][%L][%p] - %msg%n</pattern>
<charset>UTF-8</charset>
</encoder>
<!-- 此日志文件只记录debug级别的 -->
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.LevelFilter">
<level>debug</level>
<onMatch>ACCEPT</onMatch>
<onMismatch>DENY</onMismatch>
</filter>
</appender>
<!-- 按照每天生成日志文件:主项目日志 -->
<appender name="APP_INFO" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!--日志文件输出的文件名 -->
<FileNamePattern>${INFO_PATH}/info-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</FileNamePattern>
<!--日志文件保留天数 -->
<MaxHistory>${LOG_MAX_HISTORY}</MaxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%c类名,%t表示线程名,%L行, %p日志级别 %msg:日志消息,%n是换行符 -->
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%c][%t][%L][%p] - %msg%n</pattern>
<charset>UTF-8</charset>
</encoder>
<!-- 此日志文件只记录info级别的 -->
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.LevelFilter">
<level>info</level>
<onMatch>ACCEPT</onMatch>
<onMismatch>DENY</onMismatch>
</filter>
</appender>
<!-- 按照每天生成日志文件:主项目日志 -->
<appender name="APP_ERROR" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!--日志文件输出的文件名 -->
<FileNamePattern>${ERROR_PATH}/error-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</FileNamePattern>
<!--日志文件保留天数 -->
<MaxHistory>${LOG_MAX_HISTORY}</MaxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%c类名,%t表示线程名,%L行, %p日志级别 %msg:日志消息,%n是换行符 -->
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%c][%t][%L][%p] - %msg%n</pattern>
<charset>UTF-8</charset>
</encoder>
<!-- 此日志文件只记录error级别的 -->
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.LevelFilter">
<level>error</level>
<onMatch>ACCEPT</onMatch>
<onMismatch>DENY</onMismatch>
</filter>
</appender>
<!--日志输出到文件-->
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="APP_DEBUG"/>
<appender-ref ref="APP_INFO"/>
<appender-ref ref="APP_ERROR"/>
<appender-ref ref="console"/>
</root>
<!-- mybatis 日志级别 -->
<logger name="com.wang" level="debug">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</logger>
</configuration>
1.3.写一个data.txt测试文件,这里面写一些文字
1234567890abc1.4.在测试目录下编写测试类
package com.wang;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
@Slf4j
public class TestByteBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//FileChannel
//1.输入输出流。 2.RandomAccessFile
try (FileChannel channel = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel()){
//准备缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
while (true){
// 从channel读取数据,向buffer写入
int len = channel.read(buffer);
if (len == -1){//如果返回结果为-1,这说明文件内容已经全部读取完毕
break;
}
//打印buffer的内容
buffer.flip();//切换至读模式
while (buffer.hasRemaining()){// 是否还有剩余未读数据
byte b = buffer.get();
log.info("读取到字节:{}",(char) b);
}
//上面的buffer是读模式,读取完一次之后,需要切换
buffer.clear();//切换成写模式
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
1.5.测试结果

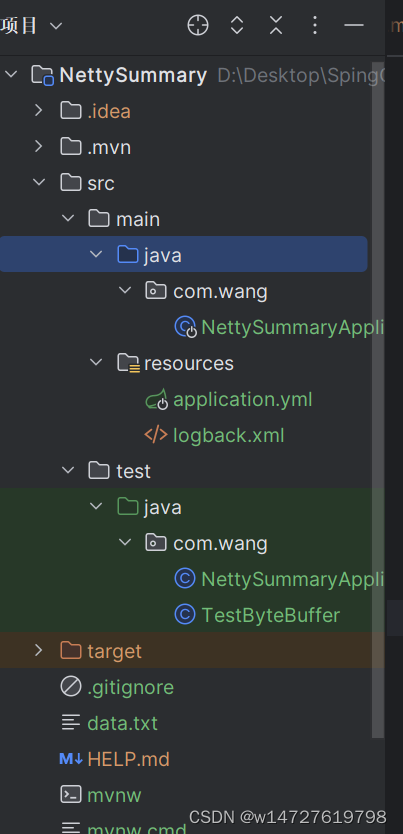
1.6.注意:工程目录结构:
1.7.ByteBuffer的正确使用姿势总结:
- 向buffer写入数据,例如调用channel。read(buffer)
- 调用flip()切换至读模式
- 从buffer读取数据,例如调用buffer.get()
- 调用clear()或compact()切换成写模式
- 重复1~4步骤
2.ByteBuffer结构
ByteBuffer有以下重要属性
- capacity
- position
- limit
2.1.图示
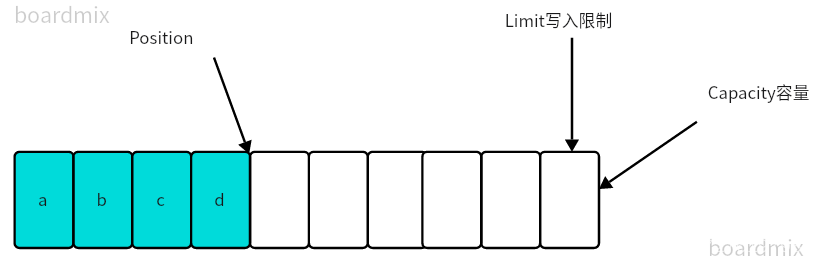
一开始

写模式下,position是写入位置,limit等于容量,下图表示写入了4个字节后的状态
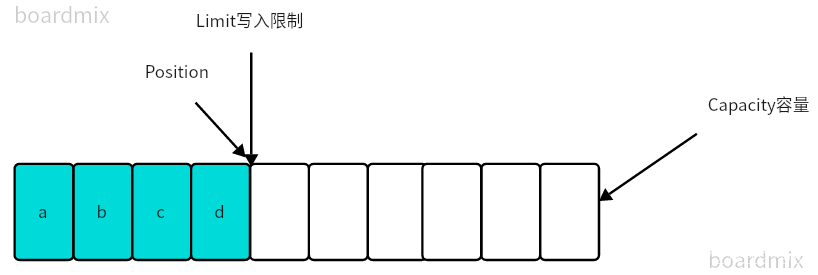
flip()动作发生之后,position切换为读取位置,limit切换为读取限制

读取四个字节后的状态:
clear动作发生后的状态:

compact方法,是把未读取的部分向前压缩,然后切换为写模式
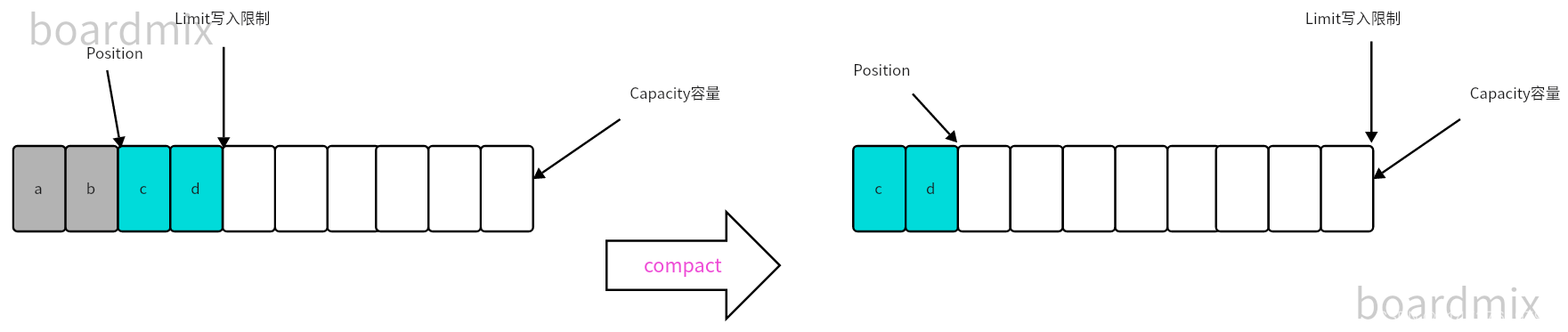
2.2.代码演示
导入工具类
package com.wang;
import io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import static io.netty.util.internal.MathUtil.isOutOfBounds;
import static io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil.NEWLINE;
public class ByteBufferUtil {
private static final char[] BYTE2CHAR = new char[256];
private static final char[] HEXDUMP_TABLE = new char[256 * 4];
private static final String[] HEXPADDING = new String[16];
private static final String[] HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES = new String[65536 >>> 4];
private static final String[] BYTE2HEX = new String[256];
private static final String[] BYTEPADDING = new String[16];
static {
final char[] DIGITS = "0123456789abcdef".toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
HEXDUMP_TABLE[i << 1] = DIGITS[i >>> 4 & 0x0F];
HEXDUMP_TABLE[(i << 1) + 1] = DIGITS[i & 0x0F];
}
int i;
// Generate the lookup table for hex dump paddings
for (i = 0; i < HEXPADDING.length; i++) {
int padding = HEXPADDING.length - i;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding * 3);
for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) {
buf.append(" ");
}
HEXPADDING[i] = buf.toString();
}
// Generate the lookup table for the start-offset header in each row (up to 64KiB).
for (i = 0; i < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length; i++) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(12);
buf.append(NEWLINE);
buf.append(Long.toHexString(i << 4 & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L));
buf.setCharAt(buf.length() - 9, '|');
buf.append('|');
HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[i] = buf.toString();
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte-to-hex-dump conversion
for (i = 0; i < BYTE2HEX.length; i++) {
BYTE2HEX[i] = ' ' + StringUtil.byteToHexStringPadded(i);
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte dump paddings
for (i = 0; i < BYTEPADDING.length; i++) {
int padding = BYTEPADDING.length - i;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding);
for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) {
buf.append(' ');
}
BYTEPADDING[i] = buf.toString();
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte-to-char conversion
for (i = 0; i < BYTE2CHAR.length; i++) {
if (i <= 0x1f || i >= 0x7f) {
BYTE2CHAR[i] = '.';
} else {
BYTE2CHAR[i] = (char) i;
}
}
}
/**
* 打印所有内容
* @param buffer
*/
public static void debugAll(ByteBuffer buffer) {
int oldlimit = buffer.limit();
buffer.limit(buffer.capacity());
StringBuilder origin = new StringBuilder(256);
appendPrettyHexDump(origin, buffer, 0, buffer.capacity());
System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+");
System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\n", buffer.position(), oldlimit);
System.out.println(origin);
buffer.limit(oldlimit);
}
/**
* 打印可读取内容
* @param buffer
*/
public static void debugRead(ByteBuffer buffer) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(256);
appendPrettyHexDump(builder, buffer, buffer.position(), buffer.limit() - buffer.position());
System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- read -----------------------+----------------+");
System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\n", buffer.position(), buffer.limit());
System.out.println(builder);
}
private static void appendPrettyHexDump(StringBuilder dump, ByteBuffer buf, int offset, int length) {
if (isOutOfBounds(offset, length, buf.capacity())) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"expected: " + "0 <= offset(" + offset + ") <= offset + length(" + length
+ ") <= " + "buf.capacity(" + buf.capacity() + ')');
}
if (length == 0) {
return;
}
dump.append(
" +-------------------------------------------------+" +
NEWLINE + " | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |" +
NEWLINE + "+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+");
final int startIndex = offset;
final int fullRows = length >>> 4;
final int remainder = length & 0xF;
// Dump the rows which have 16 bytes.
for (int row = 0; row < fullRows; row++) {
int rowStartIndex = (row << 4) + startIndex;
// Per-row prefix.
appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, row, rowStartIndex);
// Hex dump
int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + 16;
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(" |");
// ASCII dump
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append('|');
}
// Dump the last row which has less than 16 bytes.
if (remainder != 0) {
int rowStartIndex = (fullRows << 4) + startIndex;
appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, fullRows, rowStartIndex);
// Hex dump
int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + remainder;
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(HEXPADDING[remainder]);
dump.append(" |");
// Ascii dump
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(BYTEPADDING[remainder]);
dump.append('|');
}
dump.append(NEWLINE +
"+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+");
}
private static void appendHexDumpRowPrefix(StringBuilder dump, int row, int rowStartIndex) {
if (row < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length) {
dump.append(HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[row]);
} else {
dump.append(NEWLINE);
dump.append(Long.toHexString(rowStartIndex & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L));
dump.setCharAt(dump.length() - 9, '|');
dump.append('|');
}
}
public static short getUnsignedByte(ByteBuffer buffer, int index) {
return (short) (buffer.get(index) & 0xFF);
}
}编写测试类
package com.wang;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
/**
* @BelongsProject: NettySummary
* @BelongsPackage: com.wang
* @Author: 王海鑫
* @CreateTime: 2024-03-05 09:41
* @Description: TODO
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class TestByteBufferReadWrite {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
//读取
buffer.put((byte) 0x61);
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);
buffer.put(new byte[]{0x62,0x63,0x64});
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);
//读取,未切换读取模式情况下,读取。他读取的是当前position位置的数
//System.out.println(buffer.get());
//切换成读模式
buffer.flip();
System.out.println(buffer.get());
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);
buffer.compact();
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);
buffer.put(new byte[]{0x65,0x6f});
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(buffer);
}
}
演示结果
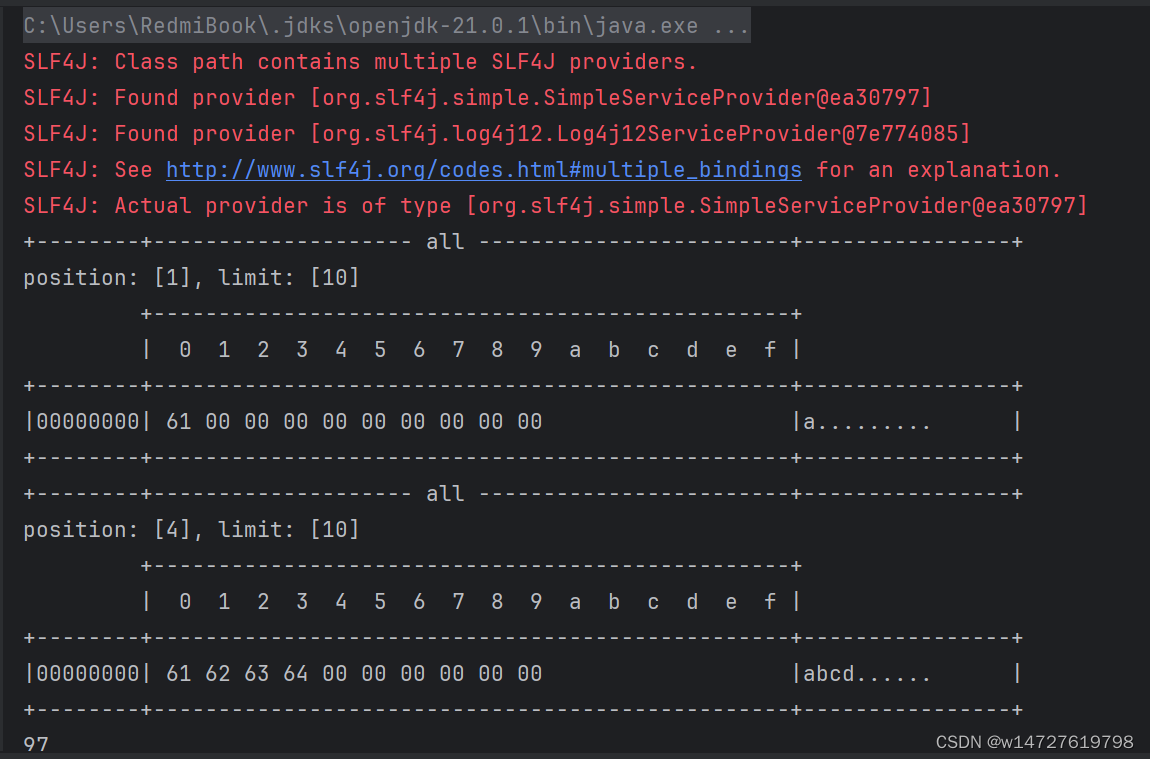

3.ByteBuffer常见方法
3.1.分配空间
可以使用allocate方法为ByteBuffer分配空间,其它buffer类也要该方法
Bytebuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
3.2.向 buffer 写入数据
同样有两种办法
-
调用 channel 的 read 方法
-
调用 buffer 自己的 put 方法
int readBytes = channel.read(buf);
和
buf.put((byte)127);
3.3 .从 buffer 读取数据
同样有两种办法
-
调用 channel 的 write 方法
-
调用 buffer 自己的 get 方法
int writeBytes = channel.write(buf);
和
byte b = buf.get();
get 方法会让 position 读指针向后走,如果想重复读取数据
-
可以调用 rewind 方法将 position 重新置为 0
-
或者调用 get(int i) 方法获取索引 i 的内容,它不会移动读指针
3.4.mark 和 reset
mark 是在读取时,做一个标记,即使 position 改变,只要调用 reset 就能回到 mark 的位置
注意
rewind 和 flip 都会清除 mark 位置
3.5.代码演示
package com.wang;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import static com.wang.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
/**
* @BelongsProject: NettySummary
* @BelongsPackage: com.wang
* @Author: 王海鑫
* @CreateTime: 2024-03-05 10:20
* @Description: TODO
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class TestByteBufferRead {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
buffer.put(new byte[]{'a','b','c','d'});
buffer.flip();//切换至读模式
buffer.get(new byte[4]);
debugAll(buffer);
//rewind从头开始读
buffer.rewind();
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
}
}
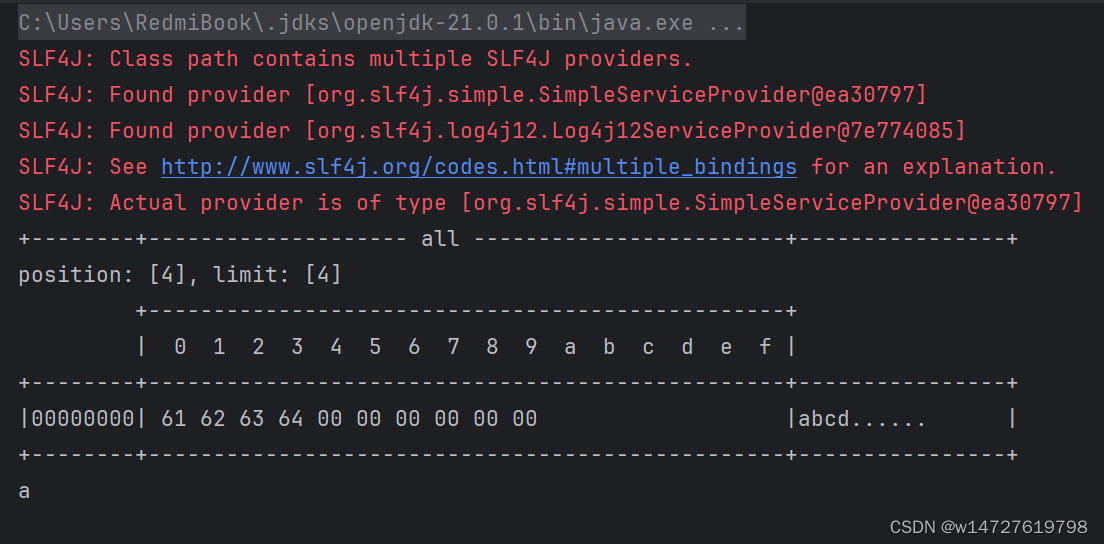
package com.wang;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import static com.wang.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
/**
* @BelongsProject: NettySummary
* @BelongsPackage: com.wang
* @Author: 王海鑫
* @CreateTime: 2024-03-05 10:20
* @Description: TODO
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class TestByteBufferRead {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
buffer.put(new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'});
buffer.flip();//切换至读模式
// buffer.get(new byte[4]);
// debugAll(buffer);
// //rewind从头开始读
// buffer.rewind();
// System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
//mark & reset
//mark 做一个标记,记录position位置,reset是将position重置到mark位置
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
buffer.mark();//加标记,索引为2
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
buffer.reset();//将position重置到索引2
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
}
}

3.6.字符串与 ByteBuffer 互转
ByteBuffer buffer1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("你好");
ByteBuffer buffer2 = Charset.forName("utf-8").encode("你好");debug(buffer1);
debug(buffer2);CharBuffer buffer3 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer1);
System.out.println(buffer3.getClass());
System.out.println(buffer3.toString());
package com.wang;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import static com.wang.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
/**
* @BelongsProject: NettySummary
* @BelongsPackage: com.wang
* @Author: 王海鑫
* @CreateTime: 2024-03-05 10:39
* @Description: TODO
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class TestByteBufferString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.字符串转为ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
buffer.put("hello".getBytes());
debugAll(buffer);
//2.Charset
ByteBuffer buffer2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");
debugAll(buffer2);
//3.wrap
ByteBuffer buffer3 = ByteBuffer.wrap("hello".getBytes());
debugAll(buffer3);
}
}

3.7.Scattering Reads
分散读取,有一个文本文件 words.txt
onetwothree
package com.wang;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import static com.wang.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
/**
* @BelongsProject: NettySummary
* @BelongsPackage: com.wang
* @Author: 王海鑫
* @CreateTime: 2024-03-05 10:51
* @Description: TODO
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class TestScatteringReads {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("words.txt","r").getChannel()){
ByteBuffer b1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer b2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer b3 = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
channel.read(new ByteBuffer[]{b1,b2,b3});
b1.flip();
b2.flip();
b3.flip();
debugAll(b1);
debugAll(b2);
debugAll(b3);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
结果

3.8.Gathering Writes
package com.wang;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
/**
* @BelongsProject: NettySummary
* @BelongsPackage: com.wang
* @Author: 王海鑫
* @CreateTime: 2024-03-05 11:00
* @Description: TODO
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class TestGatheringWrites {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer b1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");
ByteBuffer b2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("world");
ByteBuffer b3 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("你好");
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("words2.txt","rw").getChannel()){
channel.write(new ByteBuffer[]{b1,b2,b3});
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
3.9.黏包半包
package com.wang;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import static com.wang.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
/**
* @BelongsProject: NettySummary
* @BelongsPackage: com.wang
* @Author: 王海鑫
* @CreateTime: 2024-03-05 16:05
* @Description: TODO
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class TestByteBufferExam {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer source = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
source.put("Hello,world\nI'm zhangsan\nHo".getBytes());
split(source);
source.put("w are you\n".getBytes());
split(source);
}
public static void split(ByteBuffer source){
source.flip();//切换读模式
for (int i = 0; i < source.limit(); i++) {
//找到一条完整消息
if (source.get(i) == '\n') {
int length = i + 1 - source.position();
//把这条消息存入新的ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer target = ByteBuffer.allocate(length);
//从source读,向target写
for (int j = 0;j<length;j++){
target.put(source.get());
}
debugAll(target);
}
}
source.compact();
}
}
三、文件编程
1.FileChannel
FileChannel 工作模式
FileChannel 只能工作在阻塞模式下
1.1.获取
不能直接打开FileChannel,必须通过FileInputStream,FileOutputStream或者RandomAccessFile来获取FileChannel,他们都有getChannel方法。
- 通过FileInputStream获取的channel只能读
- 通过FileOutputStream获取的Channel只能写
- 通过RandomAccessFile是否能读写根据构造RandomAccessFile时候的读写模式决定
1.2.读取
会从channel中读取数据填充ByteBuffer,返回值表示读到了多少字节,-1表示达到了文件末尾。
int readBytes = channel.read(buffer);
1.3.写入
写入的正确姿势如下, SocketChannel
ByteBuffer buffer = ...;
buffer.put(...); // 存入数据
buffer.flip(); // 切换读模式while(buffer.hasRemaining()) {
channel.write(buffer);
}
在 while 中调用 channel.write 是因为 write 方法并不能保证一次将 buffer 中的内容全部写入 channel
1.4.关闭
channel 必须关闭,不过调用了 FileInputStream、FileOutputStream 或者 RandomAccessFile 的 close 方法会间接地调用 channel 的 close 方法
1.5.位置
获取当前位置
long pos = channel.position();
设置当前位置
long newPos = ...;
channel.position(newPos);
设置当前位置时,如果设置为文件的末尾
- 这时读取会返回 -1
- 这时写入,会追加内容,但要注意如果 position 超过了文件末尾,再写入时在新内容和原末尾之间会有空洞(00)
1.6.大小
使用 size 方法获取文件的大小
1.7.强制写入
操作系统出于性能的考虑,会将数据缓存,不是立刻写入磁盘。可以调用 force(true) 方法将文件内容和元数据(文件的权限等信息)立刻写入磁盘
2.两个Channel传输数据
package com.wang;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* @BelongsProject: NettySummary
* @BelongsPackage: com.wang
* @Author: 王海鑫
* @CreateTime: 2024-03-05 16:40
* @Description: TODO
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class TestFileChannelTransferTo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
FileChannel from = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel();
FileChannel to = new FileOutputStream("to.txt").getChannel();
){
//效率高,底层会利用操作系统的零拷贝进行优化
from.transferTo(0,from.size(),to);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
超过 2g 大小的文件传输
package com.wang;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* @BelongsProject: NettySummary
* @BelongsPackage: com.wang
* @Author: 王海鑫
* @CreateTime: 2024-03-05 16:40
* @Description: TODO
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class TestFileChannelTransferTo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
FileChannel from = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel();
FileChannel to = new FileOutputStream("to.txt").getChannel();
){
//效率高,底层会利用操作系统的零拷贝进行优化
//from.transferTo(0,from.size(),to);
long size = from.size();
//left 变量代表还剩余多少字节
for (long left = size;left>0;){
System.out.println("position:"+(size - left)+" left:"+left);
left -= from.transferTo((size - left),left,to);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.Path
jdk7 引入了 Path 和 Paths 类
-
Path 用来表示文件路径
-
Paths 是工具类,用来获取 Path 实例
Path source = Paths.get("1.txt"); // 相对路径 使用 user.dir 环境变量来定位 1.txt
Path source = Paths.get("d:\\1.txt"); // 绝对路径 代表了 d:\1.txt
Path source = Paths.get("d:/1.txt"); // 绝对路径 同样代表了 d:\1.txt
Path projects = Paths.get("d:\\data", "projects"); // 代表了 d:\data\projects
-
.代表了当前路径 -
..代表了上一级路径
d:
|- data
|- projects
|- a
|- b
代码
Path path = Paths.get("d:\\data\\projects\\a\\..\\b");
System.out.println(path);
System.out.println(path.normalize()); // 正常化路径
会输出
d:\data\projects\a\..\b d:\data\projects\b
4.Files
检查文件是否存在
Path path = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
System.out.println(Files.exists(path));
创建一级目录
Path path = Paths.get("helloword/d1");
Files.createDirectory(path);
-
如果目录已存在,会抛异常 FileAlreadyExistsException
-
不能一次创建多级目录,否则会抛异常 NoSuchFileException
创建多级目录用
Path path = Paths.get("helloword/d1/d2");
Files.createDirectories(path);
拷贝文件
Path source = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/target.txt");Files.copy(source, target);
-
如果文件已存在,会抛异常 FileAlreadyExistsException
如果希望用 source 覆盖掉 target,需要用 StandardCopyOption 来控制
Files.copy(source, target, StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING);
移动文件
Path source = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");Files.move(source, target, StandardCopyOption.ATOMIC_MOVE);
-
StandardCopyOption.ATOMIC_MOVE 保证文件移动的原子性
删除文件
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/target.txt");
Files.delete(target);
-
如果文件不存在,会抛异常 NoSuchFileException
删除目录
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/d1");
Files.delete(target);
-
如果目录还有内容,会抛异常 DirectoryNotEmptyException
遍历目录文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Path path = Paths.get("C:\\Program Files\\Java\\jdk1.8.0_91");
AtomicInteger dirCount = new AtomicInteger();
AtomicInteger fileCount = new AtomicInteger();
Files.walkFileTree(path, new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>(){
@Override
public FileVisitResult preVisitDirectory(Path dir, BasicFileAttributes attrs)
throws IOException {
System.out.println(dir);
dirCount.incrementAndGet();
return super.preVisitDirectory(dir, attrs);
}@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs)
throws IOException {
System.out.println(file);
fileCount.incrementAndGet();
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
});
System.out.println(dirCount); // 133
System.out.println(fileCount); // 1479
}
统计 jar 的数目
Path path = Paths.get("C:\\Program Files\\Java\\jdk1.8.0_91");
AtomicInteger fileCount = new AtomicInteger();
Files.walkFileTree(path, new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>(){
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs)
throws IOException {
if (file.toFile().getName().endsWith(".jar")) {
fileCount.incrementAndGet();
}
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
});
System.out.println(fileCount); // 724
删除多级目录
Path path = Paths.get("d:\\a");
Files.walkFileTree(path, new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>(){
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs)
throws IOException {
Files.delete(file);
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}@Override
public FileVisitResult postVisitDirectory(Path dir, IOException exc)
throws IOException {
Files.delete(dir);
return super.postVisitDirectory(dir, exc);
}
});
删除很危险
删除是危险操作,确保要递归删除的文件夹没有重要内容
拷贝多级目录
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String source = "D:\\Snipaste-1.16.2-x64";
String target = "D:\\Snipaste-1.16.2-x64aaa";Files.walk(Paths.get(source)).forEach(path -> {
try {
String targetName = path.toString().replace(source, target);
// 是目录
if (Files.isDirectory(path)) {
Files.createDirectory(Paths.get(targetName));
}
// 是普通文件
else if (Files.isRegularFile(path)) {
Files.copy(path, Paths.get(targetName));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);





















 259
259











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








