Android applications, as previously established, run within instances of the Dalvik virtual machine with each virtual machine being viewed by the operating system as a separate process. If the system identifies that resources on the device are reaching capacity it will take steps to terminate processes to free up memory.
When making a determination as to which process to terminate in order to free up memory, the system takes into consideration both the priority and state of all currently running processes, combining these factors to create what is referred to by Google as an importance hierarchy. Processes are then terminated starting with the lowest priority and working up the hierarchy until sufficient resources have been liberated for the system to function.
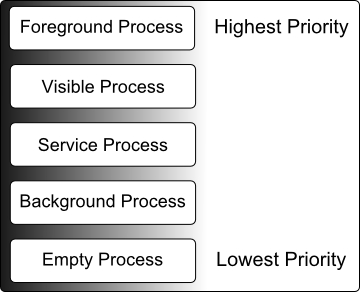
Android Process States
Processes host applications and applications are made up of components. Within an Android system, the current state of a process is defined by the highest ranking active component within application that it hosts. As outlined in Figure 8-1, a process can be in one of the following five states at any given time:
Figure 8-1
Foreground Process
These processes are assigned the highest level of priority. At any one time there are unlikely to be more than one or two foreground process active and these are usually the last to be terminated by the system. A process must meet one or more of the following criteria to qualify for foreground status:
- Hosts an activity with which the user is currently interacting.
- Hosts a Service connected to the activity with which the user is interacting.
- Hosts a Service that has indicated, via a call to startForeground(), that termination would be disruptive to the user experience.
- Hosts a Service executing either its onCreate(), onResume() or onStart() callbacks.
- Hosts a Broadcast Receiver that is currently executing its onReceive() method.
Visible Process
Service Process
Processes that contain a Service that has already been started and is currently executing.
Background Process
A process that contains one or more activities that are not currently visible to the user, and does not host a Service that qualifies for Service Process status. Processes that fall into this category are at high risk of termination in the event that additional memory needs to be freed for higher priority processes. Android maintains a dynamic list of background processes, terminating processes in chronological order such that processes that were the least recently in the foreground are killed first.
Empty Process
Empty processes no longer contain any active applications and are held in memory ready to serve as hosts for newly launched applications, somewhat analogous to keeping the doors open and the engine running on a bus in anticipation of passengers arriving. Such processes are, obviously, considered to be the lowest priority and are the first to be killed to free up resources.
Inter-Process Dependencies
The situation with regard to determining the highest priority process is slightly more complex than outlined in the preceding section for the simple reason that processes can often be inter-dependent. As such, when making a determination as to the priority of a process, the Android system will also take into consideration whether the process is in some way serving another process of higher priority (for example a service process acting as the content provider for a foreground process). As a basic rule, the Android documentation states that a process can never be ranked lower than another process that it is currently serving.
The Activity Lifecycle
As we have previously determined, the state of an Android process is determined to a large extent by the status of the activities and components that make up the application that it hosts. It is important to understand, therefore, that these activities also transition through different states during the execution lifetime of an application. The current state of an activity is determined, in part, by its position in something called the Activity Stack.
The Activity Stack
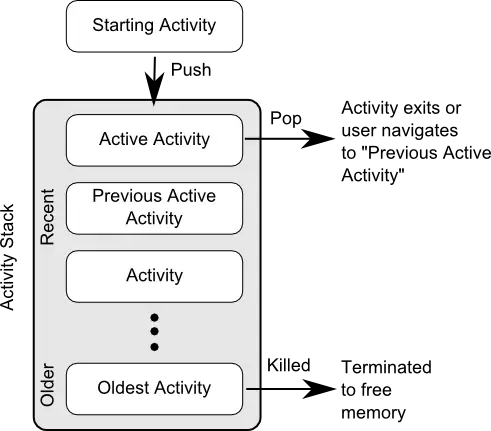
For each application that is running on an Android device, the runtime system maintains an Activity Stack. When an application is launched, the first of the application’s activities to be started is placed onto the stack. When a second activity is started, it is placed on the top of the stack and the previous activity is pushed down. The activity at the top of the stack is referred to as the active (or running) activity. When the active activity exits, it is popped off the stack by the runtime and the activity located immediately beneath it in the stack becomes the current active activity. The activity at the top of the stack might, for example, simply exit because the task for which it is responsible has been completed. Alternatively, the user may have selected a “Back” button on the screen to return to the previous activity, causing the current activity to be popped off the stack by the runtime system and therefore destroyed. A visual representation of the Android Activity Stack is illustrated in Figure 8-2:
Figure 8-2
As shown in the diagram, new activities are pushed on to the top of the stack when they are started. The current active activity is located at the top of the stack until it is either pushed down the stack by a new activity, or popped off the stack when it exits or the user navigates to the previous activity. In the event that resources become constrained, the runtime will kill activities, starting with those at the bottom of the stack.
The Activity Stack is what is referred to in programming terminology as a Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) stack in that the last item to be pushed onto the stack is the first to be popped off.
Activity States
An activity can be in one of a number of different states during the course of its execution within an application:
- Active / Running – The activity is at the top of the Activity Stack, is the foreground task visible on the device screen, has focus and is currently interacting with the user. This is the least likely activity to be terminated in the event of a resource shortage.
- Paused – The activity is visible to the user but does not currently have focus (typically because this activity is partially obscured by the current active activity). Paused activities are held in memory, remain attached to the window manager, retain all state information and can quickly be restored to active status when moved to the top of the Activity Stack.
- Stopped – The activity is currently not visible to the user (in other words it is totally obscured on the device display by other activities). As with paused activities, it retains all state and member information, but is at higher risk of termination in low memory situations.
- Killed – The Activity has been terminated by the runtime system in order to free up memory and is no longer present on the Activity Stack. Such activities must be restarted if required by the application.
Handling State Change
If nothing else, it should be clear from this chapter that an application and, by definition, the components contained therein will transition through many states during the course of its lifespan. Of particular importance is the fact that these state changes (up to and including complete termination) are imposed upon the application by the Android runtime subject to the actions of the user and the availability of resources on the device.
In practice, however, these state changes are not imposed entirely without notice and an application will, in most circumstances, be notified by the runtime system of the changes and given the opportunity to react accordingly. This will typically involve saving or restoring both internal data structures and user interface state, thereby allowing the user to switch seamlessly between applications and providing at least the appearance of multiple, concurrently running applications. The steps involved in gracefully handling state changes will be covered in detail in the next chapter entitled Handling Android Activity State Changes.
Summary
Mobile devices are typically considered to be resource constrained, particularly in terms of onboard memory capacity. Consequently, a prime responsibility of the Android operating system is to ensure that applications, and the operating system in general, remain responsive to the user.
Applications are hosted on Android within processes (essentially instances of the Dalvik virtual machine). Each application, in turn, is made up of components in the form of activities and Services.
The Android runtime system has the power to terminate both processes and individual activities in order to free up memory. Process state is taken into consideration by the runtime system when deciding whether a process is a suitable candidate for termination. The state of a process is, to a large extent, dependent upon the status of the activities hosted by that process.
The key message of this chapter is that an application moves through a variety of states during its execution lifespan and has very little control over its destiny within the Android runtime environment. Those processes and activities that are not directly interacting with the user run a higher risk of termination by the runtime system. An essential element of Android application development, therefore, involves the ability of an application to respond to state change notifications from the operating system, a topic that is covered in the next chapter.





















 1252
1252

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








