138.随机链表的复制
题目
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
-
val:一个表示Node.val的整数。 -
random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从0到n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为null。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
示例 1:
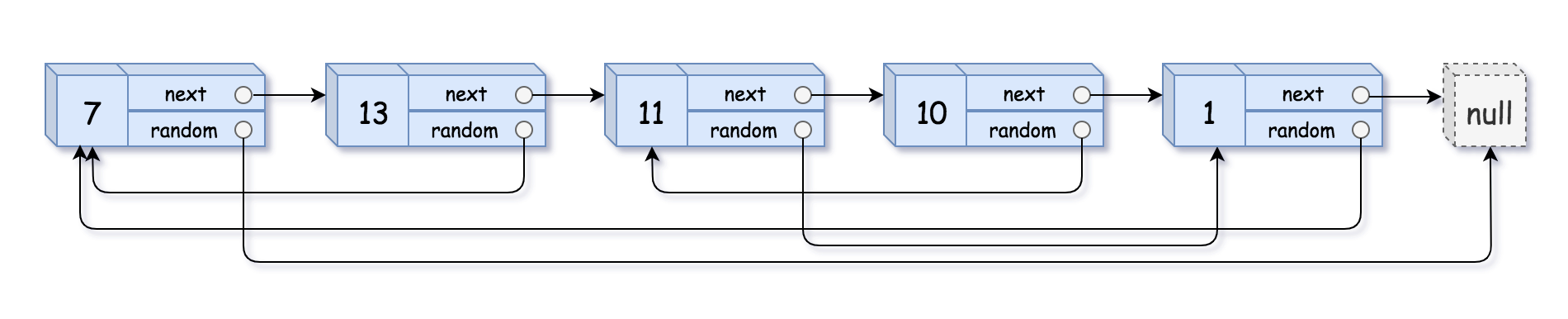
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] 输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
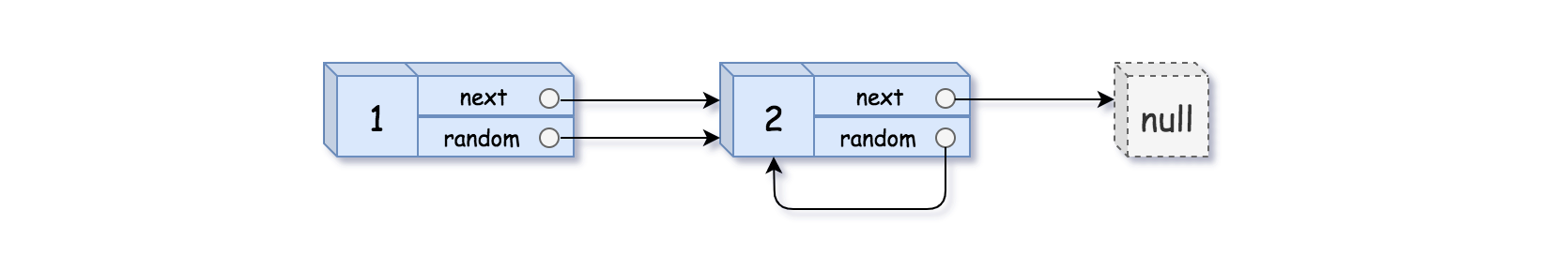
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]] 输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
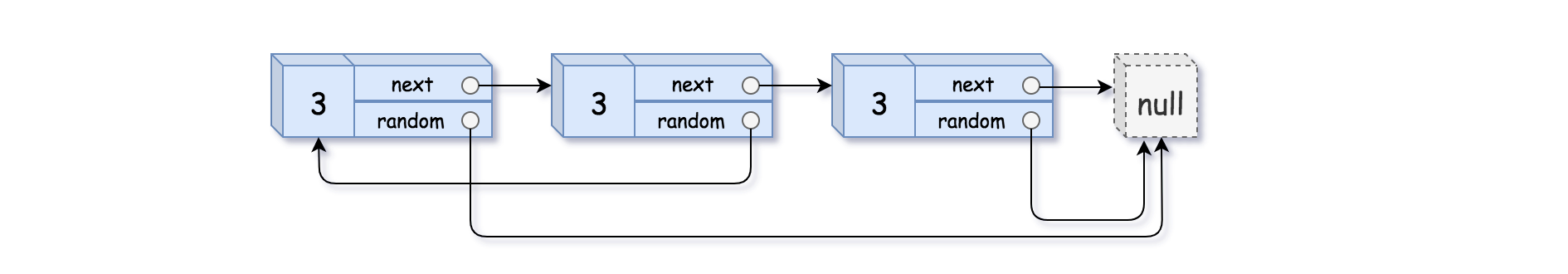
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] 输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
思路
这道题利用字典能够很快解决,字典一一对应后返回结果即可
代码:
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
unordered_map<Node*,Node*> map;
Node* cur = head;
while(cur){
map[cur] = new Node(cur->val);
cur = cur->next;
}
cur = head;
while(cur){
map[cur]->next = map[cur->next];
map[cur]->random = map[cur->random];
cur = cur->next;
}
return map[head];
}
};148.排序链表
题目
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
示例 1:
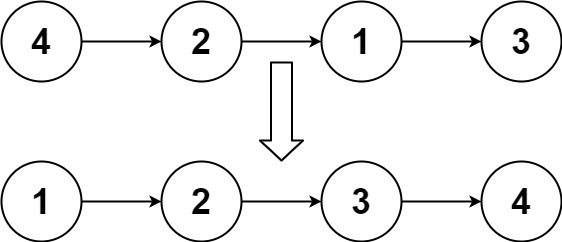
输入:head = [4,2,1,3] 输出:[1,2,3,4]
示例 2:
输入:head = [-1,5,3,4,0] 输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]
示例 3:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]
思路
我的思路比较朴素,将链表存成数组然后sort后改回来即可
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> tmp;
ListNode* node = head;
while(node){
tmp.emplace_back(node->val);
node = node->next;
}
sort(tmp.begin(),tmp.end());
node = head;
int i = 0;
while(node){
node->val = tmp[i++];
node = node->next;
}
return head;
}
};23.合并K个升序链表
题目
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6] 解释:链表数组如下: [ 1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6 ] 将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:
输入:lists = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:lists = [[]] 输出:[]
思路
考虑优先队列,每次都是最小的拿出来接在链表后面,最终完成合并K个升序链表
代码如下:
class Greater{
public:
bool operator()(ListNode* a,ListNode* b){
return a->val > b->val;
}
};
class Solution{
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
priority_queue<ListNode*,vector<ListNode*>,Greater> pq;
for(auto head:lists){
if(head){
pq.push(head);
}
}
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode();
ListNode* cur = dummy;
while(!pq.empty()){
auto node = pq.top();
cur->next = node;
cur = cur->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};146.LRU缓存
题目
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现 LRUCache 类:
-
LRUCache(int capacity)以 正整数 作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存 -
int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。 -
void put(int key, int value)如果关键字key已经存在,则变更其数据值value;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组key-value。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过capacity,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
示例:
输入
["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
输出
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
解释
LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3
lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
思路
这道题是比较经典的腾讯爱考察的算法题了,,,为了实现查找O(1),那么需要哈希表,同时插入删除也得O(1),那么需要链表。故哈希表中需要建立key到节点的关系,而节点中保存value,同时为了能够O(1)删除某一项,那么需要是双向链表才行。代码如下:
struct Node{
int val;
int key;
Node* next;
Node* pre;
Node(): val(0),key(0),next(NULL),pre(NULL){}
Node(int key,int val):key(key),val(val),next(NULL),pre(NULL){}
};
class LRUCache {
private:
int capacity;
Node* head; //哨兵节点
Node* tail; //哨兵节点
unordered_map<int,Node*> map;
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) {
this->capacity = capacity;
head = new Node();
tail = new Node();
head->next = tail;
tail->pre = head;
}
void move_node_to_tail(int key){
Node* node = map[key];
node->pre->next = node->next;
node->next->pre = node->pre;
tail->pre->next = node;
node->next = tail;
node->pre = tail->pre;
tail->pre = node;
}
int get(int key) {
if(map.find(key) != map.end()){
move_node_to_tail(key);
return map[key]->val;
}
return -1;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if(map.find(key) != map.end()){
map[key]->val = value;
move_node_to_tail(key);
}
else{
if(capacity == map.size()){
map.erase(head->next->key);
head->next = head->next->next;
head->next->pre = NULL;
free(head->next->pre);
head->next->pre = head;
}
Node* tmp = new Node(key,value);
map[key] = tmp;
tmp->next = tail;
tmp->pre = tail->pre;
tail->pre->next = tmp;
tail->pre = tmp;
}
}
};





















 809
809

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








