1.Executor 主体结构
Executor是MyBatis执行者接口,执行器的功能包括:
- 基本功能:改、查,没有增删的原因是,所有的增删操作都可以归结到改。
- 缓存维护:这里的缓存主要是为一级缓存服务,功能包括创建缓存Key、清理缓存、判断缓存是否存在。
- 事物管理:提交、回滚、关闭、批处理刷新。
Executor 的生命周期和 SqlSession 是一样的,之所以要明确的指出这一点是因为 Executor 中包含了缓存的处理,并且因为 SqlSession 是线程不安全的。
对于这个接口MyBatis是有三个实现子类。分别是
-
SimpleExecutor(简单执行器)
-
ReuseExecutor(重用执行器)
-
BatchExecutor(批处理执行器)。
public interface Executor { ResultHandler NO_RESULT_HANDLER = null; int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException; <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException; <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException; <E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException; List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException; void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException; void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException; CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql); boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key); void clearLocalCache(); void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType); Transaction getTransaction(); void close(boolean forceRollback); boolean isClosed(); void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor); }
1.1Executor类结构
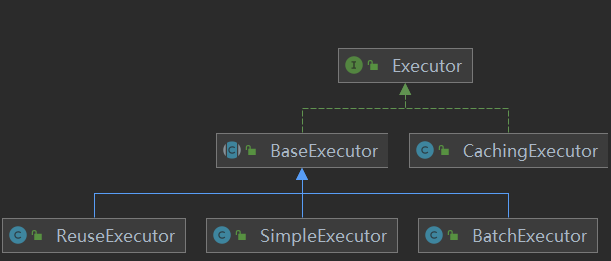
其各自的功能:
- BaseExecutor:基础执行器,封装了子类的公共方法,包括一级缓存、延迟加载、回滚、关闭等功能;
- SimpleExecutor:简单执行器,每执行一条 sql,都会打开一个 Statement,执行完成后关闭;
- ReuseExecutor:重用执行器,相较于 SimpleExecutor 多了 Statement 的缓存功能,并使用SQL语句作为Key,其内部维护一个
Map<String, Statement>,每次编译完成的 Statement 都会进行缓存,不会关闭; - BatchExecutor:批量执行器,基于 JDBC 的
addBatch、executeBatch功能,并且在当前 sql 和上一条 sql 完全一样的时候,重用 Statement,在调用doFlushStatements的时候,将数据刷新到数据库; - CachingExecutor:缓存执行器,装饰器模式,在开启二级缓存的时候。会在上面三种执行器的外面包上 CachingExecutor;
1.2创建Executor
Executor会根据ExecutorType的类型进行创建,如果mybatis的config配置文件开启了二级缓存(cacheEnabled=true)则会使用装饰器模式创建一个CachingExecutor来维护二级缓存。后面会详细介绍
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 开启二级缓存,使用装饰器模式
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// mybatis插件相关
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
2.BaseExecutor
BaseExecutor 基础执行器主要是用于维护一级缓存和事物。事物是通过会话中调用commit、rollback进行管理。
重点在于一级缓存这块它是如何处理的?
它实现了Executor中的Query与update方法。SqlSession会话中SQL请求,正是调用的这两个方法。Query方法中处理一级缓存逻辑,即根据SQL及参数判断缓存中是否存在数据,有就走缓存。否则就会调用子类的doQuery() 方法去查询数据库,然后在设置缓存。在doUpdate() 中主要是用于清空缓存。
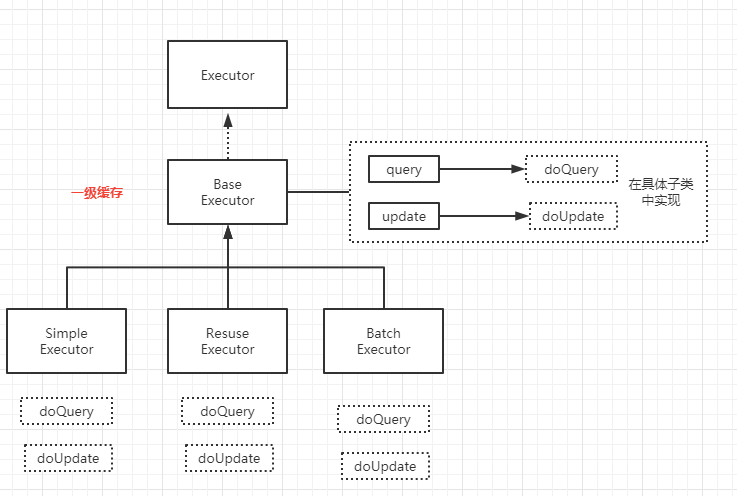
2.1query
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 获取绑定的sql
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 缓存key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// mapperxml文件FlushCache 配置为true,会清除缓存。不使用缓存
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
// 首先查看一级缓存
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 没有查到的时候直接到数据库查找
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
// 一级缓存本身不能关闭
// mybatis-config的setting节点设置一级缓存LocalCacheScope为STATEMENT也会清除缓存
// <setting name="localCacheScope" value="STATEMENT"/>
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 真正的去数据库查询数据
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
// 先清除缓存
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 查询结果加入到缓存中
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
2.2查询
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing an update").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// 清除缓存
clearLocalCache();
return doUpdate(ms, parameter);
}
2.3模板方法
这里就是一个典型的模版方法模式了,子类都会实现自己模版方法;
protected abstract int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException;
protected abstract List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException;
protected abstract <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException;
protected abstract <E> Cursor<E> doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException;
2.4事务相关
@Override
public void close(boolean forceRollback) {
try {
try {
// close之前,先回滚事务。
// connection没有设置自动提交,新增数据后没有commit。连接close之前,需要把数据回滚掉
rollback(forceRollback);
} finally {
if (transaction != null) {
transaction.close();
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// Ignore. There's nothing that can be done at this point.
log.warn("Unexpected exception on closing transaction. Cause: " + e);
} finally {
transaction = null;
deferredLoads = null;
localCache = null;
localOutputParameterCache = null;
closed = true;
}
}
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Cannot commit, transaction is already closed");
}
// 提交会清除一级缓存及刷新Statements
clearLocalCache();
flushStatements();
if (required) {
transaction.commit();
}
}
@Override
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
if (!closed) {
try {
// 回滚会清除一级缓存及刷新Statements
clearLocalCache();
flushStatements(true);
} finally {
if (required) {
transaction.rollback();
}
}
}
}
3.SimpleExecutor
SimpleExecutor是默认执行器,它的行为是每处理一次会话当中的SQl请求都会通过对应的StatementHandler 构建一个新个Statement,这就会导致即使是相同SQL语句也无法重用Statement。每次打开一个 Statement,使用完成以后关闭。后续的处理交由StatementHandler进行增删改查
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 构建StatementHandler
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
// 构建新的Statement
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.update(stmt);
} finally {
// 关闭Statement,同JDBC经典用法
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 获取连接,在Baseexecutor中,从Transaction中获取
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
4.ReuseExecutor
ReuseExecutor 区别在于他会将在会话期间内的Statement进行缓存,并使用SQL语句作为Key。所以当执行下一请求的时候,不在重复构建Statement,而是从缓存中取出并设置参数,然后执行。
这也说明为啥执行器不能跨线程调用,这会导致两个线程给同一个Statement 设置不同场景参数。
// 缓存Statement的Map
private final Map<String, Statement> statementMap = new HashMap<>();
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 获取绑定的sql
BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql();
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
// 如果缓存中已经有了,直接得到Statement
if (hasStatementFor(sql)) {
// 从缓存中获取Statement
stmt = getStatement(sql);
applyTransactionTimeout(stmt);
} else {
// 如果缓存没有,就编译一个然后加入缓存
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 放入缓存中,下次使用
putStatement(sql, stmt);
}
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
private boolean hasStatementFor(String sql) {
try {
Statement statement = statementMap.get(sql);
// 缓存Statement存在且连接Connection没有关闭
return statement != null && !statement.getConnection().isClosed();
} catch (SQLException e) {
return false;
}
}
发现ReuseExecutor没有去手动关闭closeStatement。当没有设置connection为自动提交时,我们需要手动commit,close,rollback。会间接调用doFlushStatements来关闭Statements。
如果设置connection为AutoCommit时,我们需要自己调用doFlushStatements来关闭Statements。
public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) {
for (Statement stmt : statementMap.values()) {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
statementMap.clear();
return Collections.emptyList();
}
5.BatchExecutor
BatchExecutor 顾名思议,它就是用来作批处理的。但会将所 有SQL请求集中起来,最后调用Executor.flushStatements() 方法时一次性将所有请求发送至数据库。
BachExecutor 是基于 JDBC 的 addBatch、executeBatch 功能的执行器,所以 BachExecutor 只能用于更新(insert|delete|update),不能用于查询(select)。doQuery与SimpleExecutor一致。
// 待处理的 Statement
private final List<Statement> statementList = new ArrayList<>();
// 对应的结果集
private final List<BatchResult> batchResultList = new ArrayList<>();
// 上一次执行 sql
private String currentSql;
// 上次执行的 MappedStatement
private MappedStatement currentStatement;
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
final Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
final StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameterObject, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
final BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql();
// 本次执行的 sql
final String sql = boundSql.getSql();
final Statement stmt;
// 当本次执行的 sql 和 MappedStatement 与上次的相同时,直接复用上一次的 Statement
if (sql.equals(currentSql) && ms.equals(currentStatement)) {
int last = statementList.size() - 1;
stmt = statementList.get(last);
applyTransactionTimeout(stmt);
handler.parameterize(stmt);// fix Issues 322
BatchResult batchResult = batchResultList.get(last);
batchResult.addParameterObject(parameterObject);
} else {
// 不同时,新建 Statement,并加入缓存
Connection connection = getConnection(ms.getStatementLog());
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
handler.parameterize(stmt); // fix Issues 322
currentSql = sql;
currentStatement = ms;
statementList.add(stmt);
batchResultList.add(new BatchResult(ms, sql, parameterObject));
}
// 添加批处理任务
handler.batch(stmt);
// 注意这里返回的不再是更新的行数,而是一个常量
return BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE;
}
数据什么更新到数据库呢?
处理 update 的任何操作,包括 commit、close等任何操作,具体执行的方法就是 doFlushStatements;此外需要注意的是 Batch 方式插入使用 useGeneratedKeys 获取主键,在提交完任务之后,并不能马上取到,因为此时 sql 语句还在缓存中没有真正执行,当执行完 Flush 之后,会通过回调的方式反射设置主键;
public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException {
try {
List<BatchResult> results = new ArrayList<>();
if (isRollback) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
// 循环处理statement的executeBatch
for (int i = 0, n = statementList.size(); i < n; i++) {
Statement stmt = statementList.get(i);
applyTransactionTimeout(stmt);
BatchResult batchResult = batchResultList.get(i);
try {
// 更新影响的结果数
batchResult.setUpdateCounts(stmt.executeBatch());
MappedStatement ms = batchResult.getMappedStatement();
List<Object> parameterObjects = batchResult.getParameterObjects();
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = ms.getKeyGenerator();
// insert返回主键,设置进实体对象中。会单独分析
if (Jdbc3KeyGenerator.class.equals(keyGenerator.getClass())) {
Jdbc3KeyGenerator jdbc3KeyGenerator = (Jdbc3KeyGenerator) keyGenerator;
jdbc3KeyGenerator.processBatch(ms, stmt, parameterObjects);
} else if (!NoKeyGenerator.class.equals(keyGenerator.getClass())) { //issue #141
for (Object parameter : parameterObjects) {
keyGenerator.processAfter(this, ms, stmt, parameter);
}
}
// Close statement to close cursor #1109
// 处理结束后关闭statement
closeStatement(stmt);
} catch (BatchUpdateException e) {
StringBuilder message = new StringBuilder();
message.append(batchResult.getMappedStatement().getId())
.append(" (batch index #")
.append(i + 1)
.append(")")
.append(" failed.");
if (i > 0) {
message.append(" ")
.append(i)
.append(" prior sub executor(s) completed successfully, but will be rolled back.");
}
throw new BatchExecutorException(message.toString(), e, results, batchResult);
}
results.add(batchResult);
}
// 返回处理结果,从BatchResult.updateCounts 获取更新的条数
return results;
} finally {
for (Statement stmt : statementList) {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
currentSql = null;
statementList.clear();
batchResultList.clear();
}
}
只有连续相同的SQL语句并且相同的SQL映射声明,才会重用Statement,并利用其批处理功能。否则会构建一个新的Satement然后在flushStatements() 时一次执行。这么做的原因是它要保证执行顺序,跟调用顺序一至。
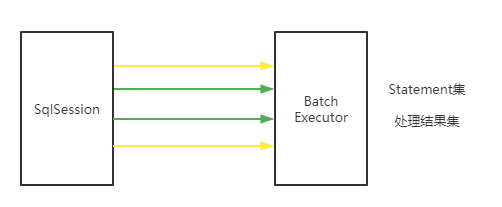
假设上图中相同的线条颜色,就是相同的SQL语句。为了保证执行顺序只有绿色线条合并成一个Statement而两条黄线不能,否则就会导致,后面的黄线先于中间的绿线执行,有违调用顺序。这中情况会创建3个Satement,两天sql语句之间有 其他的sql语句。
6.CachingExecutor
CachingExecutor缓存执行器,用于处理二级缓存的。二级缓存和一级缓存相对独立的逻辑,而且二级缓存可以通过参数控制关闭,而一级缓存是不可以的。综上原因把二级缓存单独抽出来处理。抽取的方式采用了装饰者设计模式,即在CachingExecutor 对原有的执行器进行包装,处理完二级缓存逻辑之后,把SQL执行相关的逻辑交给实至的Executor处理。
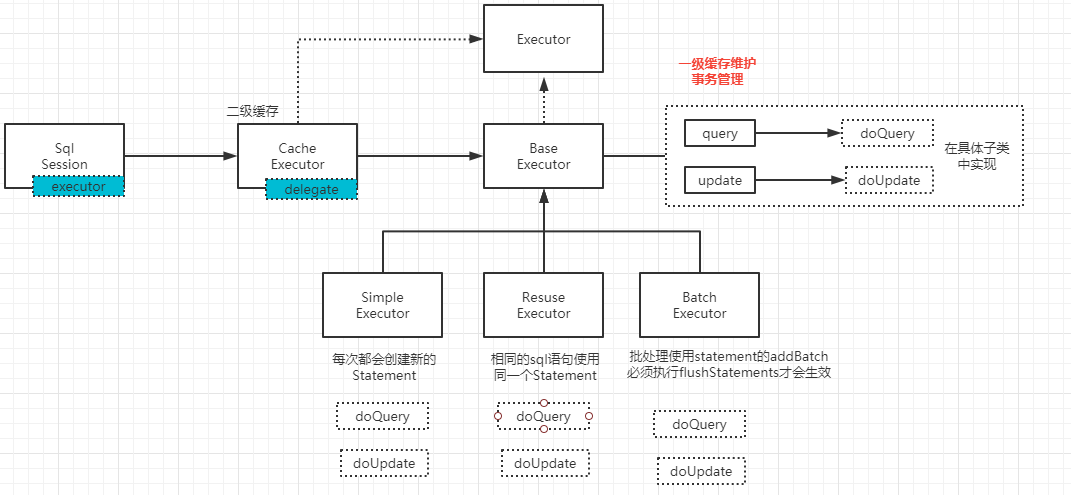
7.执行器总结
执行器的种类有:基础执行器、简单执行器、重用执行器和批处理执行器,此外通过装饰器形式添加了一个缓存执行器。对应功能包括缓存处理、事物处理、重用处理以及批处理,这些是多个SQL执行中有共性地方。执行器存在的意义就是去处理这些共性。 如果说每个SQL调用是独立的,不需要缓存,不需要事物也不需集中在一起进行批处理的话,Executor也就没有存在的必要。缓存的具体处理下面会详细分析
个Satement,两天sql语句之间有 其他的sql语句。
6.CachingExecutor
CachingExecutor缓存执行器,用于处理二级缓存的。二级缓存和一级缓存相对独立的逻辑,而且二级缓存可以通过参数控制关闭,而一级缓存是不可以的。综上原因把二级缓存单独抽出来处理。抽取的方式采用了装饰者设计模式,即在CachingExecutor 对原有的执行器进行包装,处理完二级缓存逻辑之后,把SQL执行相关的逻辑交给实至的Executor处理。
[外链图片转存中…(img-HJst6tnF-1630773787493)]
7.执行器总结
执行器的种类有:基础执行器、简单执行器、重用执行器和批处理执行器,此外通过装饰器形式添加了一个缓存执行器。对应功能包括缓存处理、事物处理、重用处理以及批处理,这些是多个SQL执行中有共性地方。执行器存在的意义就是去处理这些共性。 如果说每个SQL调用是独立的,不需要缓存,不需要事物也不需集中在一起进行批处理的话,Executor也就没有存在的必要。缓存的具体处理下面会详细分析






















 577
577











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








