A path in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence at most once. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
The path sum of a path is the sum of the node’s values in the path.
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum path sum of any non-empty path.
Example 1:
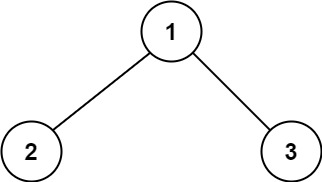
Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: 6
Explanation: The optimal path is 2 -> 1 -> 3 with a path sum of 2 + 1 + 3 = 6.
Example 2:
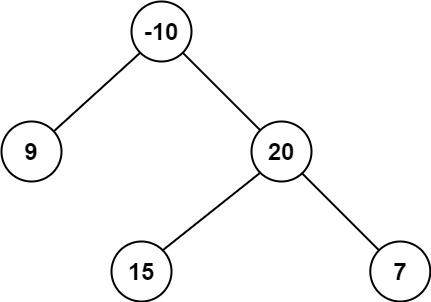
Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 42
Explanation: The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 3 * 104].
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
早期的题目还是很淳朴的, 放到今天,能给这个题一个 medium 都算是高估它了。
如果一个 path 经过一个 node, 那只有两种情况:
- path 只是路过, 从 node 的 left 或者 right 挑一条更优的向下延伸
- 该 node 是该 path 的顶点, path 从 left 和 right 分别向下延伸
面对情况 1, 我们能给上层节点的最优解就是 max(left + val, right + val, val), 面对情况 2, 我们能给答案贡献的最优解就是 max(left + right + val, left + val, right + val, val)
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
fn rc(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, ans: &mut i32) -> i32 {
if let Some(node) = root {
let val = node.borrow().val;
let left = Solution::rc(node.borrow_mut().left.take(), ans);
let right = Solution::rc(node.borrow_mut().right.take(), ans);
*ans = (*ans).max(left + right + val);
*ans = (*ans).max(left + val);
*ans = (*ans).max(right + val);
*ans = (*ans).max(val);
return (left + val).max(right + val).max(val);
}
0
}
pub fn max_path_sum(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
let mut ans = i32::MIN;
Solution::rc(root, &mut ans);
ans
}
}










 给定一棵二叉树,求解其中任一非空路径的最大路径和。本文通过两个例子解释如何找到这个最大路径和,并介绍了面对不同情况时的解决策略。
给定一棵二叉树,求解其中任一非空路径的最大路径和。本文通过两个例子解释如何找到这个最大路径和,并介绍了面对不同情况时的解决策略。
















 491
491

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








