day07
一.找出10000以内能被5或6整除,但不能被两者同时整除的数(函数)
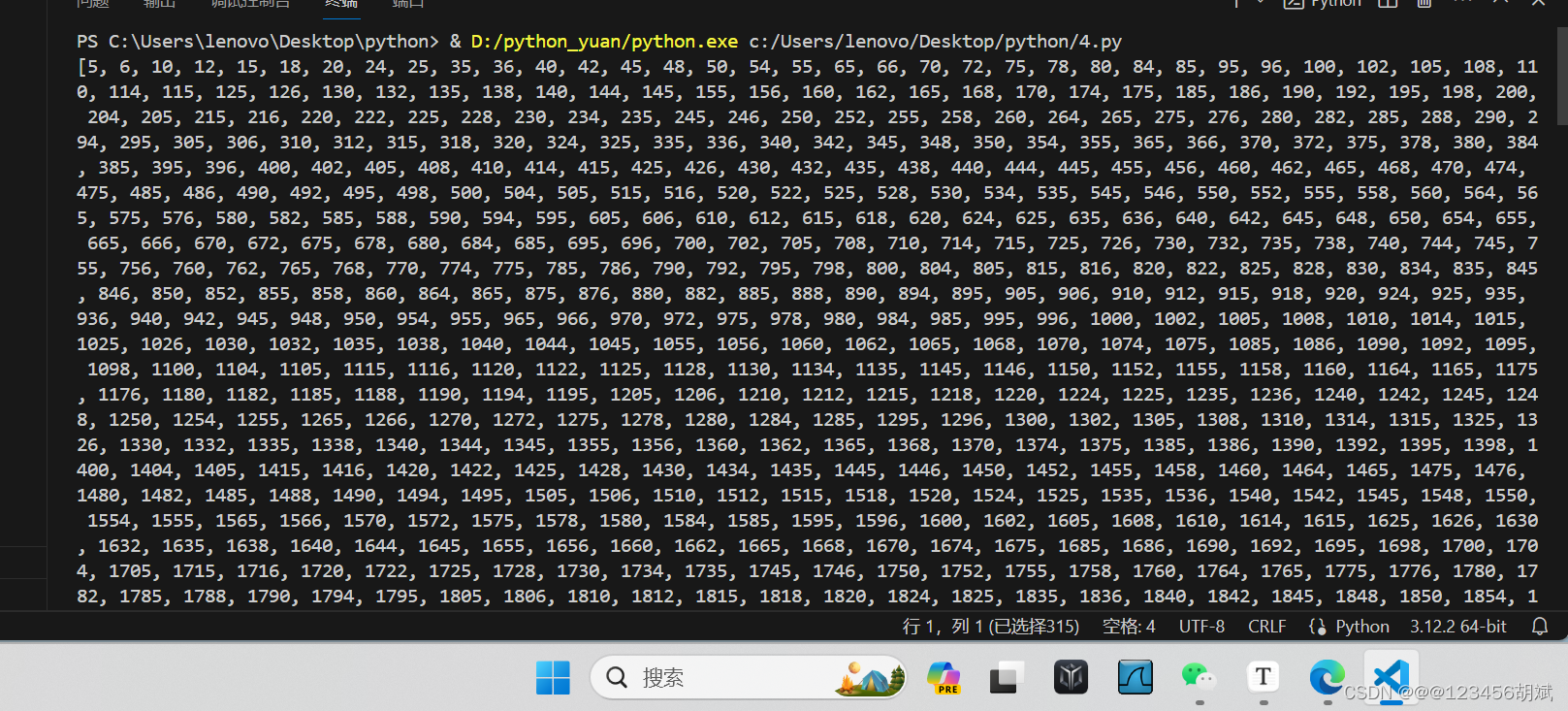
# 找出10000以内能被5或6整除,但不能被两者同时整除的数:
def find_special_numbers(upper_limit=10000):
special_numbers = []
for i in range(1, upper_limit):
if (i % 5 == 0 or i % 6 == 0) and not (i % 5 == 0 and i % 6 == 0):
special_numbers.append(i)
return special_numbers
print(find_special_numbers())运行截图:
二.写一个方法,计算列表所有偶数下标元素的和(注意返回值)
def sum_even_index_elements(lst):
total = 0
for i in range(0, len(lst), 2):
total += lst[i]
return total
lst = [8, 2, 3, 6, 5,9, 7, 8, 10]
print(sum_even_index_elements(lst))运行截图
三.根据完整的路径从路径中分离文件路径、文件名及扩展名
四.根据标点符号对字符串进行分行,去掉字符串数组中每个字符串的空格
import re
def split_string_by_punctuation(text):
return re.split(r'(?<=[.,;!?])', text)
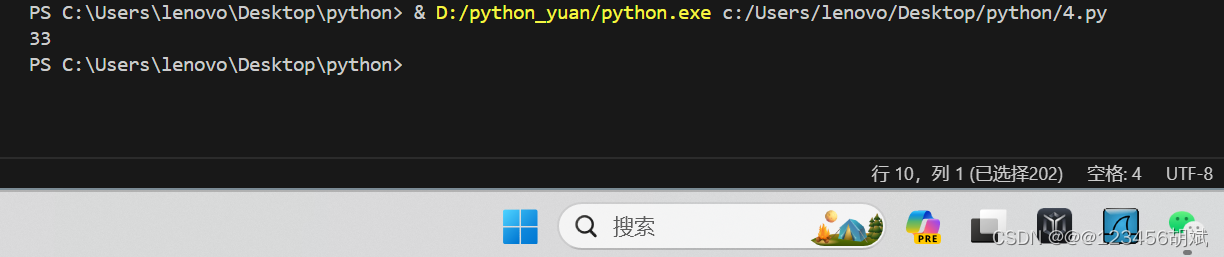
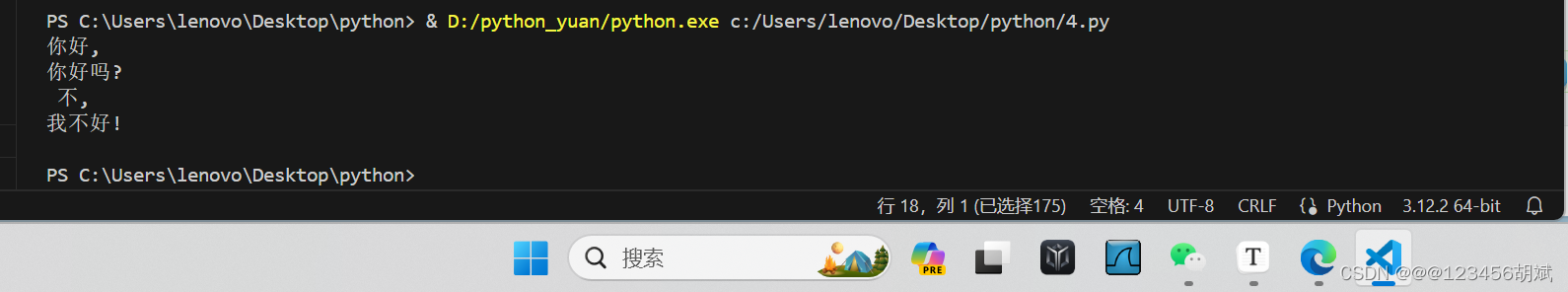
text = "你好,你好吗? 不,我不好!"
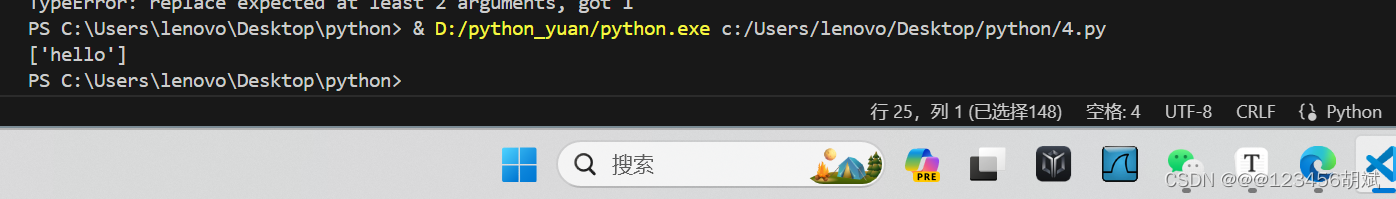
print('\n'.join(split_string_by_punctuation(text)))def remove_spaces(str_list):
return [s.replace(" ", "") for s in str_list]
# 示例
strings = ["h el lo"]
print(remove_spaces(strings))运行截图
五.两个学员输入各自最喜欢的游戏名称,判断是否一致,如 果相等,则输出你们俩喜欢相同的游戏;如果不相同,则输 出你们俩喜欢不相同的游戏。
def compare_game_names(name1, name2):
if name1.lower() == name2.lower():
print("你们俩喜欢相同的游戏")
else:
print("你们俩喜欢不相同的游戏")
# 示例
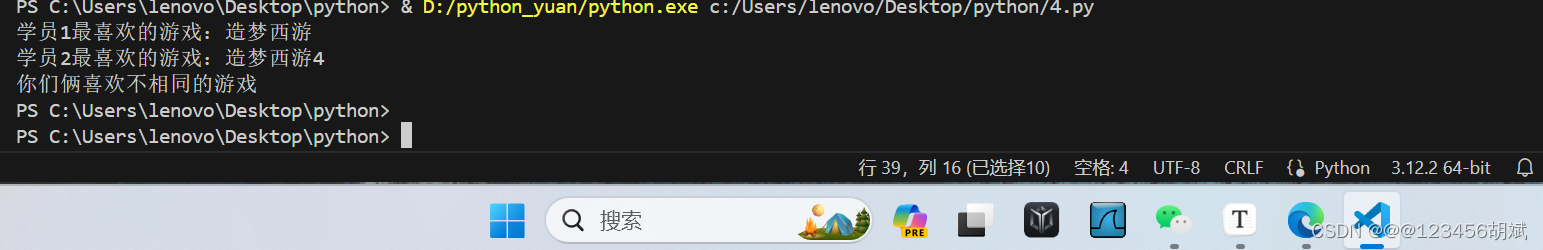
name1 = input("学员1最喜欢的游戏:")
name2 = input("学员2最喜欢的游戏:")
compare_game_names(name1, name2)运行截图
六.上题中两位同学输入 lol和 LOL代表同一游戏,怎么办?
def standardize_game_name(name):
return name.lower()
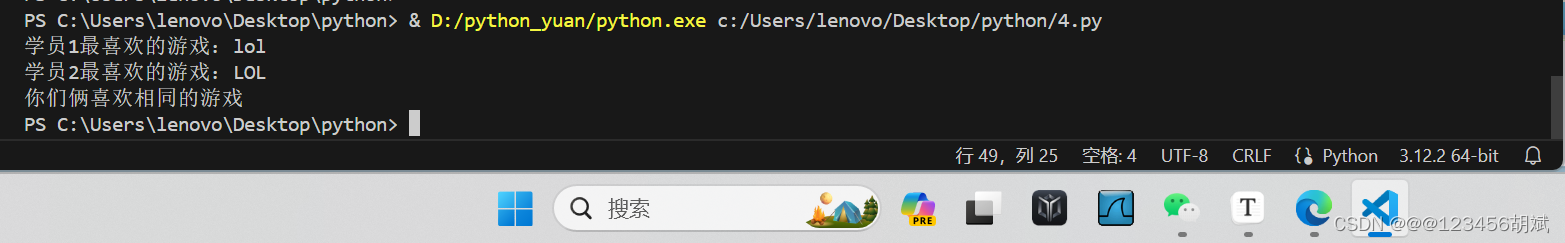
name1 = standardize_game_name(input("学员1最喜欢的游戏:").strip())
name2 = standardize_game_name(input("学员2最喜欢的游戏:").strip())
if name1 == name2:
print("你们俩喜欢相同的游戏")
else:
print("你们俩喜欢不相同的游戏")运行截图
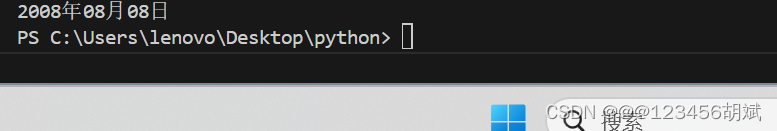
七.让用户输入一个日期格式如“2008/08/08”,将 输入的日 期格式转换为“2008年-8月-8日”。
def convert_date_format(date_str):
date_parts = date_str.split('/')
return f"{date_parts[0]}年{date_parts[1]}月{date_parts[2]}日"
date_str = "2008/08/08"
print(convert_date_format(date_str))运行截图
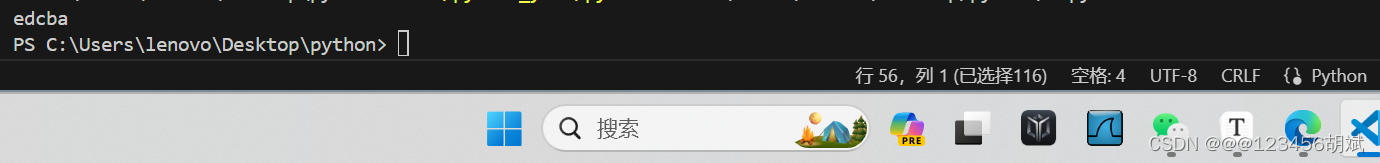
八.接收用户输入的字符串,将其中的字符进行排序(升 序),并以逆序的顺序输出,“cabed”→"abcde"→“edcba”
def sort_and_reverse(text):
return ''.join(sorted(text))[::-1]
text = "cabed"
print(sort_and_reverse(text))运行截图
九.接收用户输入的一句英文,将其中的单词以反序输 出,“hello c java python”→“python java c hello”。
def reverse_words(text):
return ' '.join(text.split()[::-1])
# 示例
text = "hello c java python"
print(reverse_words(text))运行截图
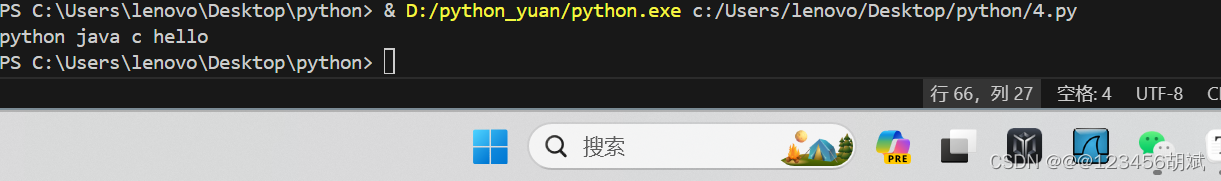
十.从请求地址中提取出用户名和域名 网易
from urllib.parse import urlparse, parse_qs
def extract_info_from_url(url):
parsed_url = urlparse(url)
query_params = parse_qs(parsed_url.query)
return query_params.get('userName', [])[0], parsed_url.netloc
# 示例
url = "http://www.163.com?userName=admin&pwd=123456"
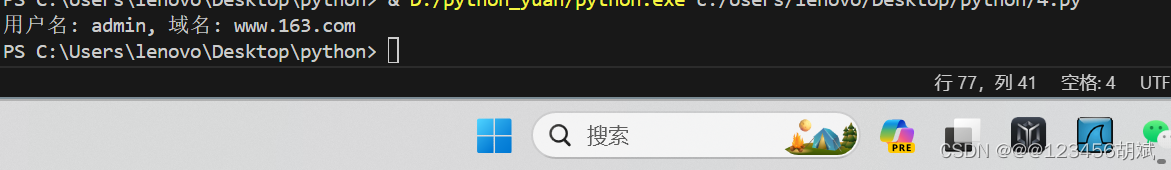
user_name, domain = extract_info_from_url(url)
print(f"用户名: {user_name}, 域名: {domain}")运行截图
十一.有个字符串数组,存储了10个书名,书名有长有短,现 在将他们统一处理,若书名长度大于10,则截取长度8的 子串并且最后添加“...”,加一个竖线后输出作者的名字。
def format_book_titles_with_author(titles_with_authors):
formatted_titles = []
for title_with_author in titles_with_authors:
title, author = title_with_author.split(' — ')
formatted_title = title if len(title) <= 10 else title[:8] + '...'
formatted_titles.append(f"{formatted_title} -{author}")
return formatted_titles
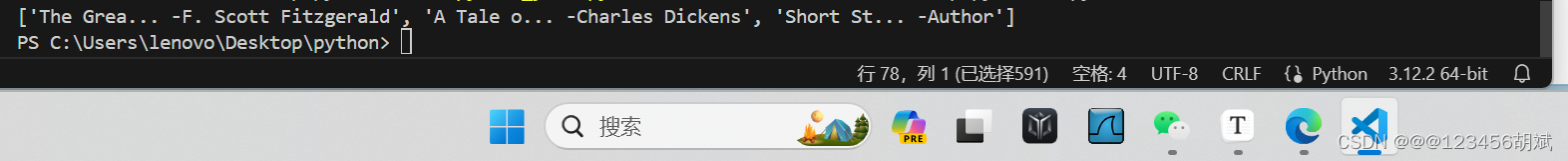
titles_with_authors = ["The Great Gatsby — F. Scott Fitzgerald", "A Tale of Two Cities — Charles Dickens", "Short Story — Author"]
formatted_titles = format_book_titles_with_author(titles_with_authors)
print(formatted_titles)运行截图
十二.让用户输入一句话,找出所有"呵"的位置。
def find_positions_of_word(text, word):
positions = [i for i, char in enumerate(text) if char == word]
return positions
# 示例
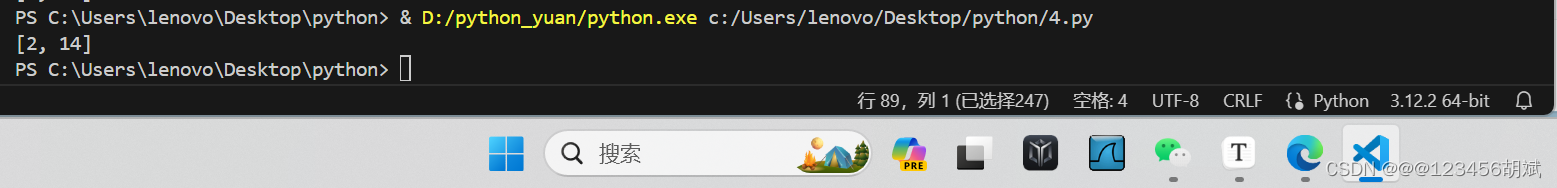
text = "你好呵,balbllbal。呵,这很重要。"
word = "呵"
positions = find_positions_of_word(text, word)
print(positions)运行截图
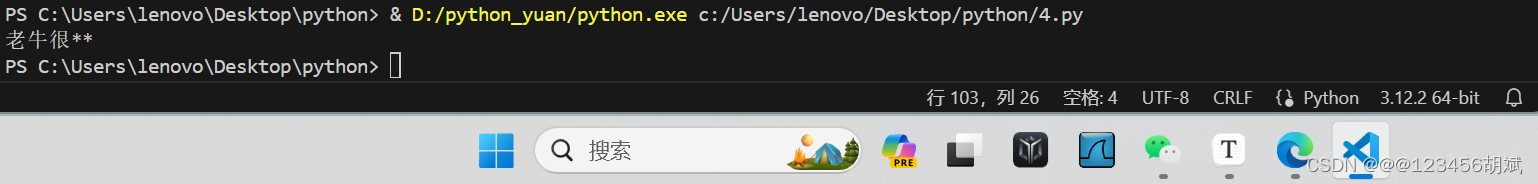
十三.让用户输入一句话,判断这句话中有没有邪恶,如果有邪 恶就替换成这种形式然后输出,如:“老牛很邪恶”,输出后变 成”老牛很**”;
def replace_evil(text):
return text.replace('邪恶', '**')
# 示例
text = "老牛很邪恶"
print(replace_evil(text))运行截图
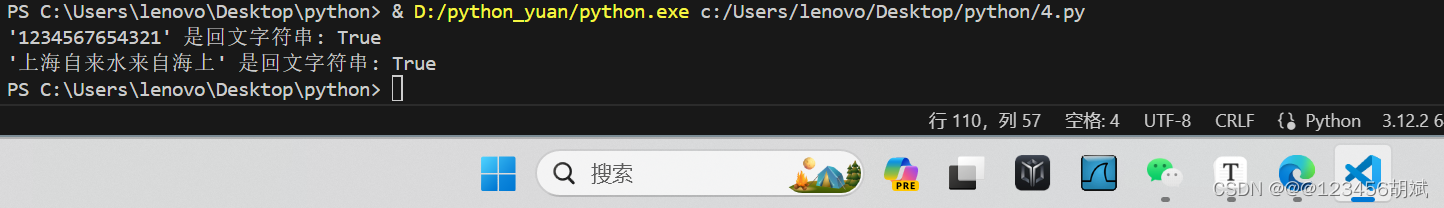
十四.判断一个字符是否是回文字符串 "1234567654321" "上海自来水来自海上"
def is_palindrome(s):
return s == s[::-1]
# 示例
strings = ["1234567654321", "上海自来水来自海上"]
for string in strings:
print(f"'{string}' 是回文字符串: {is_palindrome(string)}")运行截图
十五.过滤某个文件夹下的所有"xx.py"python文件
import os
import glob
def filter_python_files(directory):
# 构建搜索模式
pattern = os.path.join(directory, "*.py")
# 使用glob模块查找所有匹配的文件
files = glob.glob(pattern)
return files
# 指定文件夹路径
directory_path = r"C:\Users\lenovo\Desktop"
python_files = filter_python_files(directory_path)
# 打印所有找到的.py文件
for file in python_files:
print(file)运行截图
day08
import hashlib
import random
import string
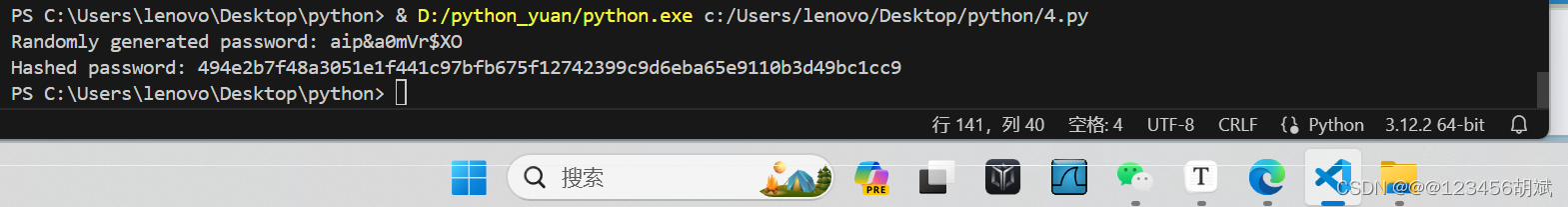
def generate_password(length=12):
"""Generate a random password"""
characters = string.ascii_letters + string.digits + string.punctuation
password = ''.join(random.choice(characters) for i in range(length))
return password
def hash_password(password):
"""Hash a password using SHA-256"""
hash_obj = hashlib.sha256(password.encode('utf-8'))
return hash_obj.hexdigest()
random_password = generate_password()
hashed_password = hash_password(random_password)
print(f"Randomly generated password: {random_password}")
print(f"Hashed password: {hashed_password}")运行截图





















 4993
4993











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








