LINUX多进程编程 简单实例
1.ps与top命令 查看进程状态
2.系统调用ping,并执行
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
int main()
{
char *exec_argv[4];
exec_argv[0] = "ping";
exec_argv[1] = "127.0.0.1";
exec_argv[2] = NULL;
exec_argv[3] = NULL;
if (execv("/bin/ping", exec_argv) == -1)
{
printf("execv error!\n");
}
return 0;
}
3.用户程序调用
父进程包含子进程的创建,父子进程都包含死循环。
【Crtl+C】终止进程
#include<signal.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int wait_flag;
void stop();
int main()
{
pid_t pid1,pid2;
signal(2, stop);
pause();
while((pid1=fork())==-1);
if(pid1>0)
{
while((pid2=fork())==-1);
if(pid2>0)
{
wait_flag=1;
sleep(5);
kill(pid1,16);
kill(pid2,17);
wait(0);
wait(0);
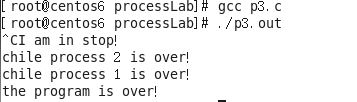
printf("the program is over!\n");
exit(0);
}
else{
wait_flag=1;
signal(17,stop);
printf("chile process 2 is over!\n");
exit(0);
}
}
else{
wait_flag=1;
signal(16,stop);
printf("chile process 1 is over!\n");
exit(0);
}
}
//Ctrl+C终止程序
void stop()
{
wait_flag=0;
printf("I am in stop!\n");
}
程序运行截图:
4.fork命令打印PID
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//print pid of fatherprocess and childprocess
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
if((pid = fork()) < 0 )
{
printf("erro");
exit(0);
}
else if(pid == 0)
{
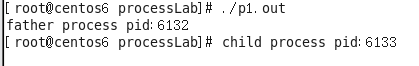
printf("child process pid:%d\n", getpid());
}
else
{
printf("father process pid:%d\n", getpid());
}
return 0;
}
运行截图:
5.利用fork和execv函数组创建一个多进程程序:
• 父进程创建子进程后,一直等待;
• 子进程显示当前运行的进程情况
• 父进程在子进程完成后,结束父进程
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//ping host ip
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
char *a[6];
a[0]="ping";
a[1]="-c";
a[2]="4"; //ping for 4
a[3]="127.0.0.1";
a[4]=NULL;
a[5]=NULL;
if((pid=fork()) < 0)
{
printf("error");
exit(0);
}
//child process
else if(pid==0)
{
printf("child process:\n");
execv("/bin/ping",a);
printf("command error\n");
}
else //father process
{
wait(NULL);
printf("Father process :child process is over.\n");
}
}
运行截图:
注: fork() 系统调用用于创建一个新进程,称为子进程,它与进程(称为系统调用fork的进程)同时运行,此进程称为父进程。创建新的子进程后,两个进程将执行fork()系统调用之后的下一条指令。
若成功调用一次则返回两个值,子进程返回0,父进程返回子进程ID;否则,出错返回-1。






















 171
171











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








