一直对AVL这个英文缩写比较困惑,原来一直以为是平衡二叉树的首字母缩写,但是又想不明白,哈!前段时间才明白原来是种这课树的三个人的名字的首字母的,哎,生活处处有惊喜,无知不可怕,现在我也知道了。废话不多说,下面我们说说,树形结构中的那些平衡二叉树。
| 二叉排序树 |
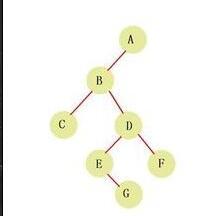
树的遍历顺序有3种,二叉排序树,顾名思义,就是一颗有序的二叉树,是一种按照中序遍历树中节点,而输出有序队列的一种树形结构,一种特殊的树形结构。
定义
对于二叉树,假设x为二叉树中的任意一个结点,x节点包含关键字key,节点x的key值记为key[x]。如果y是x的左子树中的一个结点,则key[y] <= key[x];如果y是x的右子树的一个结点,则key[y] >= key[x]。那么,这棵树就是二叉排序树。

二叉查找树是可以不平衡的!!!
杂谈:大多数人都称之为二叉查找树或者* 二叉搜索树*,从这一点,可以看出,其实并没有人用这种方式来进行数据的排序,而是在做查找或者是搜索的时候,常常使用,这也是它最为常见的应用场景。
性质
(01) 若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
(02) 任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
(03) 任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树;
(04) 没有键值相等的节点(no duplicate nodes);
建立
建立二叉查找树,就是要定义树形的结构,本文中的树形结构包括左右子树,父指针,节点权值,详细请见后面代码。
查找
按照左小右大的规则进行查找。
/*
* (递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点
*/
private BSTNode<T> search(BSTNode<T> x, T key) {
if (x==null)
return x;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
return search(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0)
return search(x.right, key);
else
return x;
}
public BSTNode<T> search(T key) {
return search(mRoot, key);
}/*
* (非递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点
*/
private BSTNode<T> iterativeSearch(BSTNode<T> x, T key) {
while (x!=null) {
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
x = x.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
x = x.right;
else
return x;
}
return x;
}
public BSTNode<T> iterativeSearch(T key) {
return iterativeSearch(mRoot, key);
}插入

整个插入的过程如上图所示,简单的一句话就是,先来的就是根节点,比根节点小的在左子树,比根节点大的在右子树,所以也就注定了,这种方式形成的树不是一颗二叉平衡树。
/*
* 将结点插入到二叉树中
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 二叉树的
* z 插入的结点
*/
private void insert(BSTree<T> bst, BSTNode<T> z) {
int cmp;
BSTNode<T> y = null;
BSTNode<T> x = bst.mRoot;
// 查找z的插入位置
while (x != null) {
y = x;
cmp = z.key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
x = x.left;
else
x = x.right;
}
z.parent = y;
if (y==null)
bst.mRoot = z;
else {
cmp = z.key.compareTo(y.key);
if (cmp < 0)
y.left = z;
else
y.right = z;
}
}
/*
* 新建结点(key),并将其插入到二叉树中
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 二叉树的根结点
* key 插入结点的键值
*/
public void insert(T key) {
BSTNode<T> z=new BSTNode<T>(key,null,null,null);
// 如果新建结点失败,则返回。
if (z != null)
insert(this, z);
}删除

上图中,是比较简单的一种删除节点的情况,在二叉查找树中,删除的情况总共分为三种:
1、删除节点的左子树为null,直接用右子树进行替换删除节点;
2、删除节点的右子树为null,直接用左子树进行替换;
3、删除节点 z 的左右子树都不为null,则查找要删除节点右子树的最小元素,调整取走最小元素 y 的局部结构,用 y 节点的右节点代替y(其实右节点就是空,都是最小了,哪还有右节点),局部结构调整完毕;然后用 y 来代替 z 节点,完毕。需要注意的一点是,在这个操作中,会涉及到父指针的操作,千万不要忘记
/*
* 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* bst 二叉树
* z 删除的结点
*/
private BSTNode<T> remove(BSTree<T> bst, BSTNode<T> z) {
BSTNode<T> x=null;
BSTNode<T> y=null;
if ((z.left == null) || (z.right == null) )
y = z;
else
y = successor(z);
if (y.left != null)
x = y.left;
else
x = y.right;
if (x != null)
x.parent = y.parent;
if (y.parent == null)
bst.mRoot = x;
else if (y == y.parent.left)
y.parent.left = x;
else
y.parent.right = x;
if (y != z)
z.key = y.key;
return y;
}
/*
* 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 二叉树的根结点
* z 删除的结点
*/
public void remove(T key) {
BSTNode<T> z, node;
if ((z = search(mRoot, key)) != null)
if ( (node = remove(this, z)) != null)
node = null;
}完整的二叉搜索树代码如下 :
/**
* Java 语言: 二叉查找树
*
* @author skywang
* @date 2013/11/07
*/
public class BSTree<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private BSTNode<T> mRoot; // 根结点
public class BSTNode<T extends Comparable<T>> {
T key; // 关键字(键值)
BSTNode<T> left; // 左孩子
BSTNode<T> right; // 右孩子
BSTNode<T> parent; // 父结点
public BSTNode(T key, BSTNode<T> parent, BSTNode<T> left, BSTNode<T> right) {
this.key = key;
this.parent = parent;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public T getKey() {
return key;
}
public String toString() {
return "key:"+key;
}
}
public BSTree() {
mRoot=null;
}
/*
* 前序遍历"二叉树"
*/
private void preOrder(BSTNode<T> tree) {
if(tree != null) {
System.out.print(tree.key+" ");
preOrder(tree.left);
preOrder(tree.right);
}
}
public void preOrder() {
preOrder(mRoot);
}
/*
* 中序遍历"二叉树"
*/
private void inOrder(BSTNode<T> tree) {
if(tree != null) {
inOrder(tree.left);
System.out.print(tree.key+" ");
inOrder(tree.right);
}
}
public void inOrder() {
inOrder(mRoot);
}
/*
* 后序遍历"二叉树"
*/
private void postOrder(BSTNode<T> tree) {
if(tree != null)
{
postOrder(tree.left);
postOrder(tree.right);
System.out.print(tree.key+" ");
}
}
public void postOrder() {
postOrder(mRoot);
}
/*
* (递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点
*/
private BSTNode<T> search(BSTNode<T> x, T key) {
if (x==null)
return x;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
return search(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0)
return search(x.right, key);
else
return x;
}
public BSTNode<T> search(T key) {
return search(mRoot, key);
}
/*
* (非递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点
*/
private BSTNode<T> iterativeSearch(BSTNode<T> x, T key) {
while (x!=null) {
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
x = x.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
x = x.right;
else
return x;
}
return x;
}
public BSTNode<T> iterativeSearch(T key) {
return iterativeSearch(mRoot, key);
}
/*
* 查找最小结点:返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最小结点。
*/
private BSTNode<T> minimum(BSTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree == null)
return null;
while(tree.left != null)
tree = tree.left;
return tree;
}
public T minimum() {
BSTNode<T> p = minimum(mRoot);
if (p != null)
return p.key;
return null;
}
/*
* 查找最大结点:返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最大结点。
*/
private BSTNode<T> maximum(BSTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree == null)
return null;
while(tree.right != null)
tree = tree.right;
return tree;
}
public T maximum() {
BSTNode<T> p = maximum(mRoot);
if (p != null)
return p.key;
return null;
}
/*
* 找结点(x)的后继结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值大于该结点"的"最小结点"。
*/
public BSTNode<T> successor(BSTNode<T> x) {
// 如果x存在右孩子,则"x的后继结点"为 "以其右孩子为根的子树的最小结点"。
if (x.right != null)
return minimum(x.right);
// 如果x没有右孩子。则x有以下两种可能:
// (01) x是"一个左孩子",则"x的后继结点"为 "它的父结点"。
// (02) x是"一个右孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有左孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的后继结点"。
BSTNode<T> y = x.parent;
while ((y!=null) && (x==y.right)) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
/*
* 找结点(x)的前驱结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值小于该结点"的"最大结点"。
*/
public BSTNode<T> predecessor(BSTNode<T> x) {
// 如果x存在左孩子,则"x的前驱结点"为 "以其左孩子为根的子树的最大结点"。
if (x.left != null)
return maximum(x.left);
// 如果x没有左孩子。则x有以下两种可能:
// (01) x是"一个右孩子",则"x的前驱结点"为 "它的父结点"。
// (01) x是"一个左孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有右孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的前驱结点"。
BSTNode<T> y = x.parent;
while ((y!=null) && (x==y.left)) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
/*
* 将结点插入到二叉树中
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 二叉树的
* z 插入的结点
*/
private void insert(BSTree<T> bst, BSTNode<T> z) {
int cmp;
BSTNode<T> y = null;
BSTNode<T> x = bst.mRoot;
// 查找z的插入位置
while (x != null) {
y = x;
cmp = z.key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
x = x.left;
else
x = x.right;
}
z.parent = y;
if (y==null)
bst.mRoot = z;
else {
cmp = z.key.compareTo(y.key);
if (cmp < 0)
y.left = z;
else
y.right = z;
}
}
/*
* 新建结点(key),并将其插入到二叉树中
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 二叉树的根结点
* key 插入结点的键值
*/
public void insert(T key) {
BSTNode<T> z=new BSTNode<T>(key,null,null,null);
// 如果新建结点失败,则返回。
if (z != null)
insert(this, z);
}
/*
* 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* bst 二叉树
* z 删除的结点
*/
private BSTNode<T> remove(BSTree<T> bst, BSTNode<T> z) {
BSTNode<T> x=null;
BSTNode<T> y=null;
if ((z.left == null) || (z.right == null) )
y = z;
else
y = successor(z);
if (y.left != null)
x = y.left;
else
x = y.right;
if (x != null)
x.parent = y.parent;
if (y.parent == null)
bst.mRoot = x;
else if (y == y.parent.left)
y.parent.left = x;
else
y.parent.right = x;
if (y != z)
z.key = y.key;
return y;
}
/*
* 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 二叉树的根结点
* z 删除的结点
*/
public void remove(T key) {
BSTNode<T> z, node;
if ((z = search(mRoot, key)) != null)
if ( (node = remove(this, z)) != null)
node = null;
}
/*
* 销毁二叉树
*/
private void destroy(BSTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree==null)
return ;
if (tree.left != null)
destroy(tree.left);
if (tree.right != null)
destroy(tree.right);
tree=null;
}
public void clear() {
destroy(mRoot);
mRoot = null;
}
/*
* 打印"二叉查找树"
*
* key -- 节点的键值
* direction -- 0,表示该节点是根节点;
* -1,表示该节点是它的父结点的左孩子;
* 1,表示该节点是它的父结点的右孩子。
*/
private void print(BSTNode<T> tree, T key, int direction) {
if(tree != null) {
if(direction==0) // tree是根节点
System.out.printf("%2d is root\n", tree.key);
else // tree是分支节点
System.out.printf("%2d is %2d's %6s child\n", tree.key, key, direction==1?"right" : "left");
print(tree.left, tree.key, -1);
print(tree.right,tree.key, 1);
}
}
public void print() {
if (mRoot != null)
print(mRoot, mRoot.key, 0);
}
}文中代码和图参考自如果天空不死























 1199
1199

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








