直接上干货。。。。。
链表常见题型:
- 找到单链表的倒数第k个节点。
- 删除单链表中的某个结点(O(1))。
- 反转链表。
- 两个链表的第一个公共结点。
- 有环链表返回环路的开头节点(及判断是否有环)。
- 合并两个排序的链表。
- 删除链表中重复的结点。
先给出链表的定义:
/**
* 单链表定义
*/
public static class Node<E>{
private E element;//节点保存的元素
private Node<E> next;//指向下一个节点的引用
public Node(){}
public Node(E element){
this.element = element;
}
public Node(E element,Node<E> next){
this.element = element;
this.next = next;
}
public E getElement(){
return element;
}
public Node<E> getNext(){
return next;
}
public void setElement(E element){
this.element = element;
}
public void setNext(Node<E> next){
this.next = next;
}
}
关于鲁棒性:
鲁棒性也称为健壮性,是指程序能够判断输入是否合乎规范要求,并对不合要求的输入予以合理的处理。容错性是鲁棒性的一个重要体现。提高代码鲁棒性的有效途径是进行防御性编程,防御性编程是一种编程习惯,是指预见在什么地方可能会出现问题,并为这些可能出现问题制定处理方式。在面试时,最常用也是最有效的防御性编程是在函数入口添加代码以验证用户输入是否符合要求。
1. 找到单链表的倒数第k个节点。
这里假设最后一个节点为倒数第一个。思想:快慢指针。实现代码如下:
public static Node<Integer> solution(Node<Integer> head,int k){
// 判断k是否非法
if(k < 1){return null;}
// 判断是否为空
if(head == null) return null;
// 快指针
Node<Integer> nAhead = head;
// 慢指针
Node<Integer> nBehind = head;
// 快指针先走k-1步
for(int i = 0;i<k-1;i++){
// 判断是否存在倒数第k个节点
if(nAhead.getNext() != null)
nAhead = nAhead.getNext();
else
return null;
}
// 同时向后移动
while(nAhead.getNext() != null){
nAhead = nAhead.getNext();
nBehind = nBehind.getNext();
}
return nBehind;
}
- 功能测试:第k个节点在中间,在头节点,在尾节点
- 特殊测试:头节点为null,k为0,节点个数小于k个
- 时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度为:O(1)
2. 删除单链表中的某个结点(O(1))。
假定你只能访问该节点。思想:互换位置。实现代码如下:
// 不知道头节点,并且无法删除尾节点。
public static boolean solution(Node<Integer> node){
// 节点为空判断
if(node == null) return false;
// 节点为最后一个节点
if(node.getNext() == null) return false;
Node<Integer> temp = node.getNext();
// 交换节点存储数据
node.setElement(temp.getElement());
node.setNext(temp.getNext());
return true;
}
注意:若知道头节点的话,能够保证平均时间复杂度为O(1)。若不知道头节点想删除尾节点的话,只能标记一下尾节点。
3. 反转链表
代码如下:
public static Node<Integer> solution(Node<Integer> head){
//头节点为空
if(head == null) return head;
//只有一个节点
if(head.getNext() == null) return head;
//记录最后被反转的节点
Node<Integer> temp1 = head;
//记录将要反转的节点
Node<Integer> temp2 = head;
//记录将要反转的节点的下一个节点
Node<Integer> temp3 = head.getNext();
while(temp3 != null){
temp2 = temp3;
temp3 = temp2.getNext();
temp2.setNext(temp1);
temp1 = temp2;
}
head.setNext(null);
head = temp1;
/*while(temp1 != null){
System.out.print(temp1.getElement() + ",");
temp1 = temp1.getNext();
}*/
return head;
}
注意:在调用方法的时候当时我没反应过来,直接solution(head);然后打印head指向的链表。。。其实,你懂的,俺是菜鸟。。。。。
好吧这里solution(head)方法中传递的是head的引用,因此执行完该方法后,head还是指向原来的第一个节点,也就是现在的最后一个节点。。。因此这样的话打印head的话只会输出一个节点。
两个无环链表的第一个公共结点。
代码如下:
public static Node<Integer> solution(Node<Integer> head1,Node<Integer> head2){
// 判空
if(head1 == null || head2 == null) return null;
// 同一个链表,不用再计算长度
if(head1 == head2) return head1;
// 计算长度差
int length1 = 0;
int length2 = 0;
Node<Integer> temp1 = head1;
Node<Integer> temp2 = head2;
while(temp1.getNext() != null || temp2.getNext() != null){
if(temp1.getNext() != null)
temp1 = temp1.getNext();
else
length2++;
if(temp2.getNext() != null)
temp2 = temp2.getNext();
else
length1++;
}
temp1 = head1;
temp2 = head2;
// 链表1长,链表1先走length1步
if(length1 != 0){
// 先执行length1步
for(int i = 0;i<length1;i++){
temp1 = temp1.getNext();
}
while (temp1 != null){
// 相等即为第一个公共节点
if(temp1 == temp2){
return temp1;
}
else{
temp1 = temp1.getNext();
temp2 = temp2.getNext();
}
}
}
// 链表2长,链表2先走length2步
else if(length2 != 0){
// 先执行length2步
for(int i = 0;i<length2;i++){
temp2 = temp2.getNext();
}
while (temp1 != null){
// 相等即为第一个公共节点
if(temp1 == temp2){
return temp1;
}
else{
temp1 = temp1.getNext();
temp2 = temp2.getNext();
}
}
}
// 一样长
else{
while (temp1 != null){
if(temp1 == temp2){
return temp1;
}
else{
temp1 = temp1.getNext();
temp2 = temp2.getNext();
}
}
}
return null;
}
- 测试: 不相交,同一个,在中间相交,在结尾相交,null;
- 时间复杂度:O(max(m,n));
- 上面的代码复用不好,相同的部分可以写成另一个方法。
- 扩展为题:链表有环。
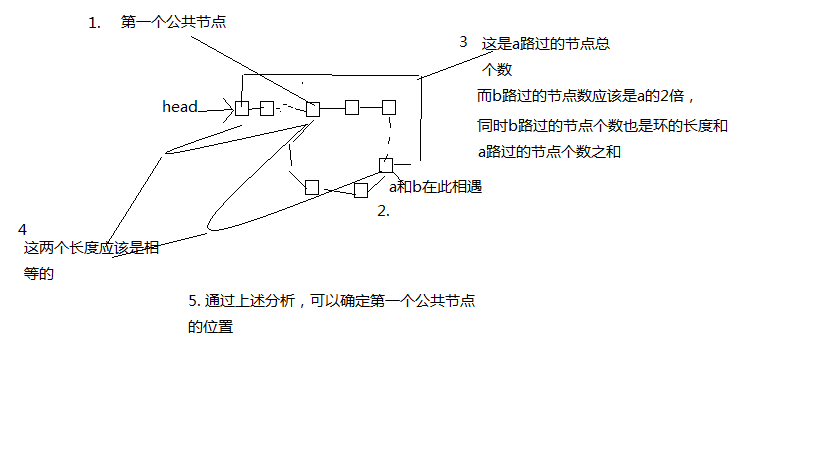
5. 有环链表返回环路的开头节点。
或求环的长度,或求节点总个数。代码如下:
public static Node<Integer> solution(Node<Integer> head){
// 定义两个节点变量,一个每次走两步,一个每次走一步
Node<Integer> aheadNode = head;
Node<Integer> behindNode = head;
// 找到第一次相遇的地方
while(aheadNode.getNext() != null){
aheadNode = aheadNode.getNext().getNext();
behindNode = behindNode.getNext();
if(behindNode == aheadNode) break;
}
// 慢节点指向head,然后两个指针每次走一步
behindNode = head;
while(behindNode != aheadNode){
behindNode = behindNode.getNext();
aheadNode = aheadNode.getNext();
}
return behindNode;
}
- 测试: 空,一个节点形成的环,中间节点形成的环,最后一个形成的环,没有环;
- 时间复杂度:O(n)。
衍生问题:
/**
* 判断链表是否有环
* 思路:快慢指针实现,若有环肯定会相交。
**/
public static boolean checkCircuit(Node<Integer> head){
// 判空
if(head == null) return false;
// 定义两个节点,一个快节点,一个慢节点
Node<Integer> aheadNode = head;
Node<Integer> behindNode = head;
// 绝对不能一次判断两个:behindNode.getNext().getNext()!= null
while(behindNode.getNext() != null){
behindNode = behindNode.getNext().getNext();
if(behindNode == null) return false;
aheadNode = aheadNode.getNext();
if(behindNode == aheadNode) return true;
}
return false;
}
- 测试: 空,一个节点形成的环,中间节点形成的环,最后一个形成的环,没有环。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
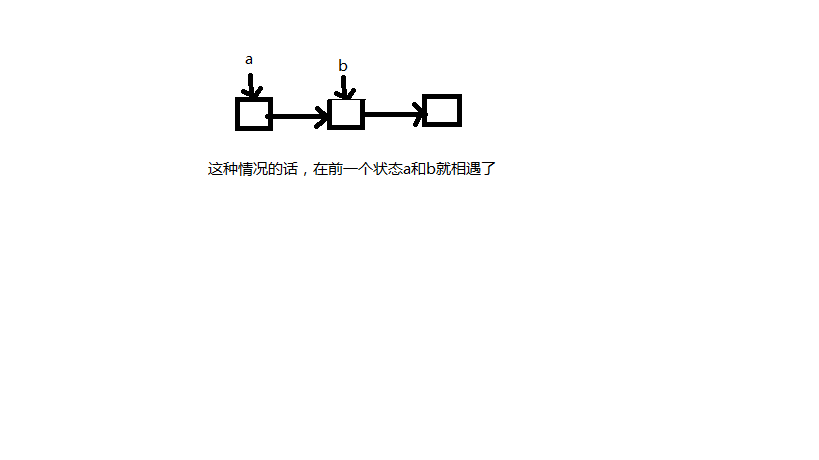
1. 为什么一个快慢指针能够判断是否相交?
一个指针a每次走1步,另一个指针b每次走两步。没有环肯定追不上。
现在考虑有环的情况,存在以下三种情况:
- a在b前一个节点;
- b在a前一个节点;
- a和b相遇。
显然,第三种情况自然证明了有环,第1和第2种情况见下图。
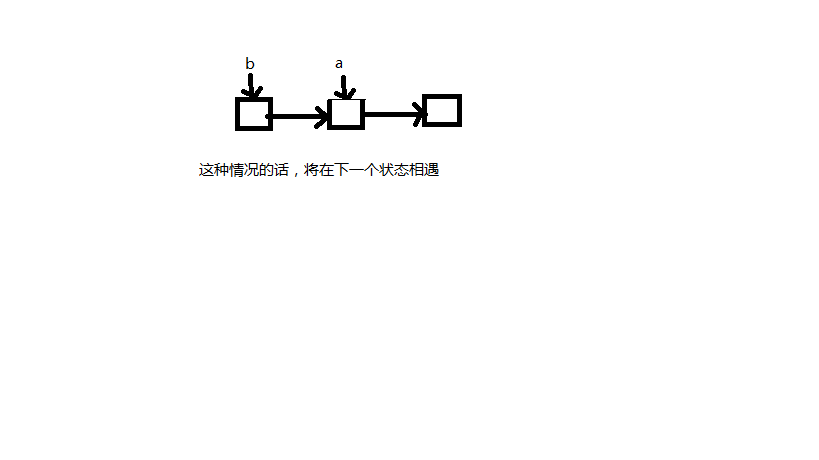
2. 为什么在相遇后a重新指向head,然后a和b每次走一步相遇时既是第一个公共节点?
具体见下图:
6. 合并两个排序的链表。
两种实现,递归和非递归。
7. 删除链表中重复的结点。
这题有两种,如下
重复的只保留一个
public static Node<Integer> solution(Node<Integer> head){
// 判空
if(head == null) return head;
Node<Integer> ahead = head;
Node<Integer> curr = head.getNext();
while(curr != null){
if(ahead.getElement() == curr.getElement()) //相同就删除
ahead.setNext(curr.getNext());
else
ahead = curr;//不同后移
curr = curr.getNext();//无论相同与否当前指针都后移
}
return head;
}
重复的一个不保留
public static Node<Integer> solution2(Node<Integer> head){
// 判空
if(head == null) return head;
// 即将判断的节点
Node<Integer> curr = head.getNext();
// curr的前一个节点
Node<Integer> ahead = head;
// 记录ahead的前一个节点
Node<Integer> preAhead = null;
// 记录ahead节点是否有重复
boolean needDelete = false;
while(curr != null){
// 相同就删除
if(ahead.getElement() == curr.getElement()){
ahead.setNext(curr.getNext());
needDelete = true;
}
else{
if(needDelete){
// ahead节点重复需要删除,用后一个节点替换前一个节点,后设置preAhead的后一个节点。
// 若直接设置preAhead的话,开始重复的就不能处理
ahead.setElement(curr.getElement());
ahead.setNext(curr.getNext());
needDelete = false;
}else{
// 不同后移
preAhead = ahead;
ahead = curr;
}
}
// 无论相同与否当前指针都后移
curr = curr.getNext();
}
if(needDelete){
// 若全都相等则返回空
if(preAhead == null){
return null;
}
// 否则就是最后一个节点需要删除
preAhead.setNext(null);
}
return head;
}
- 测试:全相等,开头相等,结尾相等,中间相等;
- 时间复杂度:O(n);
- 问题总结:在考虑问题时多注意起始条件,例如preAhead初始情况为null,若后面要操作它的话就要考虑清楚,前面是否有对它的赋值,否则就会出错。








 本文介绍了链表的一些经典题目,包括找到单链表的倒数第k个节点、删除单链表中的某个节点、反转链表、查找两个链表的第一个公共结点、检测并返回有环链表的起始节点,以及合并两个排序链表和删除链表中重复节点的方法。文章提供了详细的思想解析和Java代码实现,并讨论了快慢指针在解决链表问题中的应用。
本文介绍了链表的一些经典题目,包括找到单链表的倒数第k个节点、删除单链表中的某个节点、反转链表、查找两个链表的第一个公共结点、检测并返回有环链表的起始节点,以及合并两个排序链表和删除链表中重复节点的方法。文章提供了详细的思想解析和Java代码实现,并讨论了快慢指针在解决链表问题中的应用。














 429
429

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








