AI winters were not due to imagination traps, but due to lack of imagination. Imaginations bring order out of chaos. Deep learning with deep imagination is the road map to AI springs and AI autumns.
AI的冬天不是由于想象力的陷阱,而是由于缺乏想象力。 想象力使秩序摆脱混乱。 具有深层想象力的深度学习是通往AISpring和AI秋季的路线图。
The advancements in the field of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have helped us achieve many milestones over the period of time. DNNs have brought machines closer to human performance.
深度神经网络(DNN)领域的进步帮助我们在一段时间内实现了许多里程碑。 DNN使机器更接近人类性能。
With many advantages of the usage of DNNs, there have also been some issues that are being addressed and will also be in the future. DNNs usually have a large number of input features, as the consideration of more parameters usually improves the accuracy of the prediction. The size of the first hidden layer is critical. A small first hidden layer fails to propagate all input features properly while a large first hidden layer increases the number of weight drastically. Another limitation of the traditional DNNs is the vanishing gradient. When the number of layers is more, the gradient is high at neurons near output, and it becomes negligible at neurons near inputs. DNN training becomes difficult due to the vanishing gradient problem.
利用DNN的许多优点,已经解决了一些问题,并且将来也会出现。 DNN通常具有大量的输入功能,因为更多参数的考虑通常会提高预测的准确性。 第一隐藏层的大小至关重要。 较小的第一隐藏层无法正确传播所有输入特征,而较大的第一隐藏层会急剧增加权重数量。 传统DNN的另一个局限性是消失的梯度。 当层数更多时,梯度在输出附近的神经元处较高,而在输入附近的神经元处可忽略不计。 由于逐渐消失的梯度问题,DNN训练变得困难。
目录 (Table Of Contents)
- Introduction 介绍
- Theoretical Background 理论背景
- Proposed SpinalNet 拟议的SpinalNet
- Universal Approximation of Proposed SpinalNet 拟议的SpinalNet的通用逼近
- Results 结果
- Future Prospects of SpinalNet SpinalNet的未来前景
- Conclusion 结论
1.简介 (1. Introduction)
- The human brain receives a lot of information from different parts of the body. The brain senses pressure, heat, vibrations, complex textures, hardness, state of matter, etc. 人脑从身体的不同部位接收很多信息。 大脑感知压力,热量,振动,复杂的纹理,硬度,物质状态等。
- The human spinal cord receives senses of touch from different locations in different parts of it. 人体脊髓从其不同部位的不同位置接收触觉。
The next figure presents simplified rough connections between
下图显示了简化的粗略连接
human touch-sensors and the spinal cord.
人类的触摸传感器和脊髓。

The new proposed SpinalNet architecture works on the principle of gradual inputs, and this way a similar behavior experienced in the spinal cord and human brain can be achieved by neural networks.
提出的新的SpinalNet体系结构是基于逐步输入的原理工作的,这样,通过神经网络就可以实现在脊髓和人脑中经历的类似行为。
SpinalNet tries to overcome issues like more computation, vanishing gradient, number of connections, and number of layers are too high in deep neural networks, such problems can be solved with the use of SpinalNet.
SpinalNet试图克服诸如深度神经网络中更多的计算,梯度消失,连接数以及层数过高等问题,可以使用SpinalNet解决这些问题。
2.理论背景 (2. Theoretical Background)
2.1人体体感系统与脊髓 (2.1 Human Somatosensory System and the Spinal Cord)
- The authors of SpinalNet try to mimic a few attributes of the human Somatosensory system as this system is still not well understood. SpinalNet的作者试图模仿人类体感系统的一些属性,因为该系统仍未被很好地理解。
- The SpinalNet tries to mimic the following SpinalNet试图模仿以下内容
— Gradual input and nerve plexus
—逐步输入和神经丛
— Voluntary and involuntary actions
-自愿和非自愿行动
— Attention to pain intensity
—注意疼痛强度
- Sensory neurons reach the spinal cord through a complex network, known as nerve plexus. 感觉神经元通过称为神经丛的复杂网络到达脊髓。
- The following figure shows a part of the nerve plexus. 下图显示了神经丛的一部分。
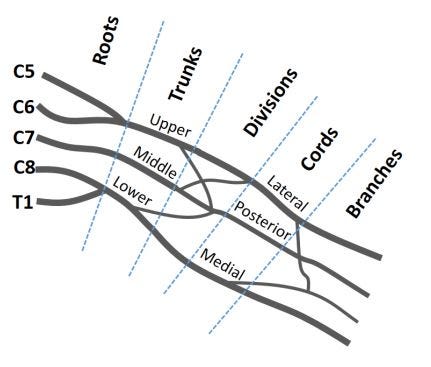
- Single vertebrae do not receive all the information. The tactile sensory network consists of millions of sensors. 单椎骨不能接收所有信息。 触觉感官网络由数百万个传感器组成。
- Moreover, our tactile system is more stable compared to the vision or the auditory system, as there is a much fewer number of ‘touch-blind’ patients than the number of blindness. 此外,与视觉或听觉系统相比,我们的触觉系统更稳定,因为“盲人”患者的数量要少于失明患者的数量。
- The nerve plexus network sends all tactile signals to the spinal cord gradually. Different locations of a spinal cord receive the pain of leg and the pain of hand. 神经丛网络逐渐将所有触觉信号发送到脊髓。 脊髓的不同位置会承受腿部疼痛和手部疼痛。
- Neurons in vertebrae transfer the sense of touch to the brain and may take some actions. 椎骨中的神经元将触觉转移到大脑,并可能会采取一些行动。
- Our brain can control the spinal neurons, to increase or decrease the pain intensity. 我们的大脑可以控制脊髓神经元,以增加或减少疼痛强度。
- Sensory neurons may also convey information to the lower-motor before getting instruction from the brain. That is called involuntary movements, or reflex movements. 感觉神经元也可能在从大脑获得指令之前将信息传递到下运动。 这称为非自愿运动或反射运动。
3.拟议的SpinalNet (3. Proposed SpinalNet)
- The SpinalNet is created to have commonalities with the working of the human spinal cord. SpinalNet的创建与人类脊髓的工作具有共同点。
- The similarities are as follows: 相似之处如下:
— Gradual Input
—逐步输入
— Local output and probable global influence
-当地产出和可能的全球影响力
— Weights reconfigured during training
—在训练过程中重新配置了重量
- Similar to the functioning of the brain, SpinalNet takes inputs gradually. 类似于大脑的功能,SpinalNet逐渐接受输入。
- All layers of the proposed model contribute towards the local output that can be compared to reflex, and a modulated portion of the input is sent to the global output and that can be compared to the brain. 所提出模型的所有层都对局部输出做出贡献,可以将其与反射相比较,并将输入的调制部分发送到全局输出,并且可以与大脑相比较。
- The following figure is the proposed SpinalNet architecture. 下图是建议的SpinalNet体系结构。

In the proposed architecture consists of an input row, an intermediate row, and an output row.
在所提出的体系结构中,由输入行 , 中间行和输出行组成 。
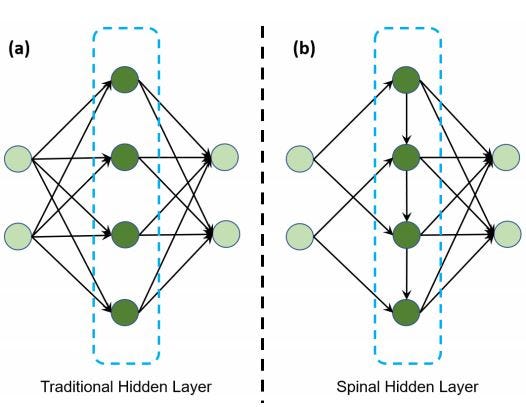
- Firstly, the input is separated and sent to the intermediate row. This intermediate row consists of different multiple hidden layers. 首先,将输入分离并发送到中间行。 此中间行由不同的多个隐藏层组成。
- In the above model, each intermediate row’s hidden layers consists of two neurons, and also the output row’s hidden layers consists of two neurons each. 在上面的模型中,每个中间行的隐藏层由两个神经元组成,并且输出行的隐藏层各由两个神经元组成。
- Both the number of intermediate neurons and the number of inputs per layer is usually kept small to reduce the number of multiplication. As the number of inputs and the number of intermediate hidden neurons per layer is usually low, the network may underfit. 通常将中间神经元的数量和每层输入的数量都保持较小,以减少乘法的数量。 由于每层的输入数量和中间隐藏神经元的数量通常很少,因此网络可能不适合。
- To overcome the above issue, each layer receives inputs from the previous layers. By repeating the input, if one important feature doesn’t affect the output in one hidden layer, it might affect the output by later hidden layers. 为了克服上述问题,每层都接收来自先前层的输入。 通过重复输入,如果一项重要功能不会影响一个隐藏层的输出,则可能会影响后面的隐藏层的输出。
- The intermediate row’s hidden layers have a non-linear activation function, and the output row’s hidden layer has a linear activation function. 中间行的隐藏层具有非线性激活函数,而输出行的隐藏层具有线性激活函数。
4.拟议的SpinalNet的通用近似 (4. Universal Approximation of Proposed SpinalNet)
Universal Approximation Theorem: The aim of a neural network is to map attributes(x) to output(y), and mathematically can be represented as a function y= f(x). The function f(x) can be any complex function, but should help map x to y. The Univeral Approximation Theorem poses that for any attributes(x) there is always a neural network that can map f(x) to output y, with any number of inputs and outputs.
通用逼近定理 :神经网络的目的是将属性(x)映射到输出(y),并且在数学上可以表示为函数y = f(x)。 函数f(x)可以是任何复数函数,但应有助于将x映射到y。 通用逼近定理提出,对于任何属性(x),总有一个神经网络可以将f(x)映射到输出y,并且输入和输出的数量不限。
- The universal approximation theorem can be proved for SpinalNet using the following approach. 可以使用以下方法为SpinalNet证明通用逼近定理。
1. Single hidden layer NN of large width is a universal approximator.
1.大宽度的单个隐藏层NN是通用逼近器。
2. If we can prove that, SpinalNet of a large depth can be equivalent to the single hidden layer NN of large width, the universal approximation is proved.
2.如果我们可以证明,大深度的SpinalNet可以等效于大宽度的单个隐藏层NN,则证明了通用逼近。

- The above figure is to show how a simpler version of SpinalNet can be converted to a single hidden layer NN. 上图显示了如何将更简单的SpinalNet版本转换为单个隐藏层NN。
In Fig- 4(a), the first layer neurons are simplified by making them as linear functions. So, the first layer only takes the weighted sum of x1 to x5 inputs.
在图4(a)中,通过使第一层神经元成为线性函数来简化它们。 因此,第一层仅取x1到x5输入的加权和。
- Now, from the first layer, the output only goes to the corresponding neuron in the second layer. All cross-connections between neurons of two layers and the connections with the output layer are disconnected by assigning weight zero. 现在,从第一层开始,输出仅到达第二层中的相应神经元。 通过分配权重零,可以断开两层神经元之间的所有交叉连接以及与输出层的连接。
The second layer receives the weighted sum of x6 to x10 as one input, and a weighted sum of x1 to x5 from the output of the first layer.
第二层接收x6到x10的加权和作为一个输入,并从第一层的输出中接收x1到x5的加权和。
So, the second layer will perform activation function equivalent on applying to x1 to x10 data points together. These two layers combined can be equivalent to a neural network containing a single hidden layer, with two neurons as shown in Fig- 4(b).
因此,第二层将执行等同于一起应用于x1至x10数据点的激活功能。 这两层的组合可以等效于一个包含单个隐藏层的神经网络,如图4(b)所示,具有两个神经元。
- A simplified version of SpinalNet of 4 hidden layers, containing 2 neurons in each layer is shown in Fig- 4(d). Similarly, SpinalNet is also equivalent to a neural network of one hidden layer, containing 4 neurons. 图4(d)显示了4个隐藏层的SpinalNet的简化版本,每层包含2个神经元。 同样,SpinalNet也等效于一个包含4个神经元的隐藏层的神经网络。
- From the above-discussed points, we can conclude that SpinalNet of large depth can be equivalent to a NN of a single hidden layer, containing a large number of neurons. 从上面讨论的观点,我们可以得出结论,大深度的SpinalNet可以等效于包含大量神经元的单个隐藏层的NN。
- Also, as a NN with a single hidden layer containing a large number of neurons achieves universal approximation, in a similar way SpinalNet with large depth achieves universal approximation. 另外,由于具有包含大量神经元的单个隐藏层的NN可以实现通用逼近,因此类似的方法是,深度较大的SpinalNet可以实现通用逼近。
5.结果 (5. Results)
The authors of [1], have effectively verified SpinalNet in both classification and regression problems.
[1]的作者有效地验证了SpinalNet的分类和回归问题。
Popular MNIST and CIFAR datasets are used for the classification problem.
流行的MNIST和CIFAR数据集用于分类问题。
A traditional NN has about 300 hidden neurons, SpinalNet also has 300 hidden neurons. But there is a drop in the number of multiplications by 35.5%.
传统的NN大约有300个隐藏的神经元 ,而SpinalNet也有300个隐藏的神经元。 但是乘法的次数却减少了35.5% 。
In a traditional NN 21,700 multiplications take place, while with the same number of neurons in SpinalNet it takes 14,000 multiplications.
在传统的NN中进行21,700次乘法 ,而在SpinalNet中具有相同数量的神经元时, 则需要进行14,000次乘法 。

- The above figure is the second proposed architecture that uses 3 SpinalNets, and this is used as a model for the classification problems. 上图是使用3个SpinalNets的第二个提议的体系结构,该体系结构用作分类问题的模型。
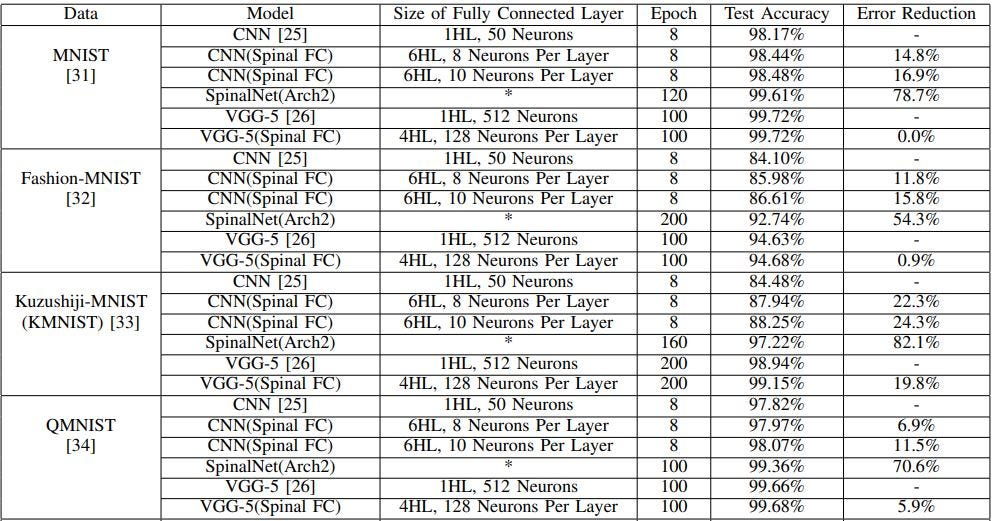
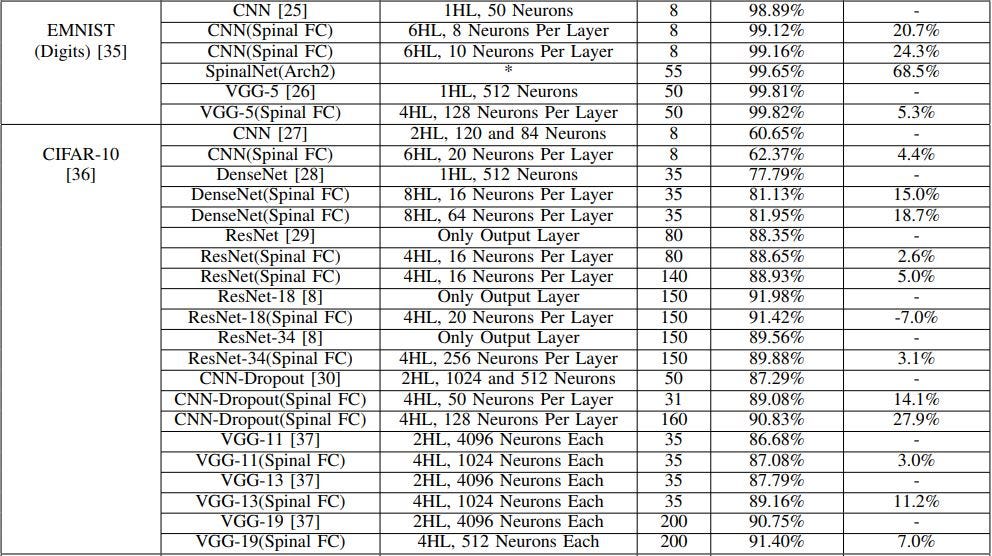
The above-presented table includes the dataset, Base Model, SpinalNet model specifications, epochs, accuracy, and increment or decrement of accuracy from the state-of-the-art models.
上面列出的表格包括数据集, 基本模型,SpinalNet模型规范,历元,准确性以及相对于最新模型的准确性增加或减少 。
A more detailed description of which model is being outperformed on which dataset by SpinalNet is presented in Section-3 Results of paper [1].
SpinalNet在哪个数据集上优于哪个模型的更详细描述,请参见论文的第3节 [1] 。
6. SpinalNet的未来前景 (6. Future Prospects of SpinalNet)
- The authors of [1] have proposed few prospects for SpinalNet as this is the first paper on SpinalNet. [1]的作者提出SpinalNet的前景很少,因为这是有关SpinalNet的第一篇论文。
The below given are the prospects of SpinalNet, for brief theory of these topics refer to Section-4 Prospects of SpinalNet [1].
下面给出的是SpinalNet的前景,有关这些主题的简要理论,请参见第4节SpinalNet的前景[1]。
Auto Dimension Reduction
自动缩小
Transfer Learning
转移学习
Ver Deep NN
Ver Deep NN
Spinal Hidden Layer
脊柱隐蔽层
Better Accuracy and New Datasets
更高的精度和新的数据集
NN Ensemble and Voting
NN合奏和投票
7.结论 (7. Conclusion)
- The nervous system and spinal cord in a human being have a unique way of sensing information and locating its source. 人类的神经系统和脊髓具有一种独特的感知信息和定位信息来源的方式。
- The SpinalNet is proposed in [1], with the idea of mimicking the functions of the brain and spinal cord that eventually help the deep neural networks to work with lesser computation and quicker response. SpinalNet是在[1]中提出的,其思想是模仿大脑和脊髓的功能,这些功能最终可以帮助深度神经网络以更少的计算和更快的响应来工作。
8.参考 (8. References)
[1] Dipu Kabir, H. M., et al. “SpinalNet: Deep Neural Network with Gradual Input.” arXiv e-prints (2020): arXiv-2007.
[1] Dipu Kabir,HM等。 “ SpinalNet:具有逐步输入的深度神经网络。” arXiv电子版 (2020年):arXiv-2007。
[2] Github Link for SpinalNet- https://github.com/dipuk0506/SpinalNet
[2]用于SpinalNet的Github链接-https ://github.com/dipuk0506/SpinalNet
翻译自: https://medium.com/visionwizard/spinalnet-deep-neural-network-with-gradual-input-20b901642eb9





















 581
581

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








