亚马逊 ai 解雇
新成果 /使用AI的节约环境/哈佛 AI促进社会公益 / IEEE SMC 2020 接受 (New results / Saving Environment using AI / Harvard AI for Social Good / Accepted at IEEE SMC 2020)
(Accepted) Satyam Mohla, Sidharth Mohla, Anupam Guha, Biplab Banerjee; IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, & Cybernetics (IEEE SMC’20)
(接受) 萨蒂扬·莫拉 ( Satyam Mohla) ,西达斯· 莫拉 (Sidharth Mohla),阿努帕姆·古哈(Anupam Guha),比帕拉·班纳吉(Biplab Banerjee) IEEE系统,人与控制论国际会议(IEEE SMC'20)
Detection of burn marks due to wildfires in inaccessible rain forests is important for various disaster management and ecological studies. The fragmented nature of arable landscapes and diverse cropping patterns often thwart the precise mapping of burn scars. Recent advances in remote-sensing and availability of multimodal data offer a viable solution to this mapping problem. However, the task to segment burn marks is difficult because of its indistinguishably with similar looking land patterns, severe fragmented nature of burn marks and partially labelled noisy datasets. In this work we present AmazonNET — a convolutional based network that allows extracting of burn patters from multimodal remote sensing images. The network consists of UNet- a well-known encoder decoder type of architecture with skip connections. The proposed framework utilises stacked RGB-NIR channels to segment burn scars from the pastures by training on a new weakly labelled noisy dataset from Amazonia. Our model illustrates superior performance by correctly identifying partially labelled burn scars and rejecting incorrectly labelled samples, demonstrating our approach as one of the first to effectively utilise deep learning based segmentation models in multimodal burn scar identification.
在无法访问的雨林中检测由野火引起的燃烧痕迹对于各种灾难管理和生态研究都很重要。 耕地景观的零散性质和多样化的种植方式常常阻碍了烧伤疤痕的精确绘制。 遥感和多模式数据可用性方面的最新进展为解决这种映射问题提供了可行的解决方案。 但是,分割燃烧痕迹的任务很困难,因为它很难与相似的土地格局,燃烧痕迹的严重碎片性质和部分标记的噪声数据集区分开。 在这项工作中,我们介绍了AmazonNET-一个基于卷积的网络,该网络允许从多模式遥感影像中提取烧伤图案。 该网络由UNet组成,UNet是一种具有跳过连接的著名编码器解码器类型的体系结构。 拟议的框架利用堆叠的RGB-NIR通道,通过对来自Amazonia的新的弱标签噪声数据集进行训练,来分割牧场的烧伤疤痕。 我们的模型通过正确识别部分标记的烧伤疤痕并拒绝不正确标记的样品来说明卓越的性能,这表明我们的方法是在多模式烧伤疤痕识别中有效利用基于深度学习的分割模型的第一种方法。
In Amazonia, fire is associated with several land-practices. Slash-and-Burn is one of the most used practices in Brazilian agriculture (as part of a seasonal cycle called “queimada”). Whether for opening and cleaning agricultural areas or renewing pastures, its importance in the agricultural chain is undeniable. Unfortunately, this is often the cause of wildfires in forests.
在亚马孙地区,火灾与几种土地惯例有关。 刀耕火种是巴西农业中最常用的做法之一(作为季节性循环的一部分,称为“ queimada”)。 无论是开放和清洁农业区还是更新牧场,其在农业链中的重要性都是不可否认的。 不幸的是,这通常是森林大火的原因。
Amazon rainforests are a major reservoir for flora and billions of tons of carbon, release of which can cause a major increase in temperatures. Recent news of wildfires in Amazon therefore, caused major uproar and concern.
亚马逊雨林是植物群和数十亿吨碳的主要储库,其释放会导致温度大幅上升。 因此,最近有关亚马逊山火的消息引起了轩然大波和令人担忧。
Uncontrollable fires, especially in dry season, have major local & regional impacts, leading to destruction of natural biomes, extinction of animal & plant species, pollution, erosion and an imbalance in the carbon cycle. Such disturbances affect agricultural production as well. Thus, many environmental studies & resources management activities require accurate identification of burned areas for monitoring the affected regions (the so-called scars from burning) spatially and temporally in order to understand and assess the vulnerability of these areas and to promote sustainable development.
不可控制的大火,特别是在旱季,对当地和地区造成重大影响,导致自然生物群落遭到破坏,动植物物种灭绝,污染,侵蚀和碳循环失衡。 这些干扰也影响农业生产。 因此,许多环境研究和资源管理活动都需要准确地确定烧伤区域,以便在空间和时间上监测受影响的区域(所谓的烧伤疤痕),以便了解和评估这些区域的脆弱性并促进可持续发展。
Due to the large geographical extent of fires at regional and global scales and the limited accessibility of the areas affected by fire, remote sensing approaches have become cost effective alternatives in the last few years, capable of collecting burned area information at adequate spatial and temporal resolutions. Remote sensing technologies can provide useful data for fire management, estimation & detection, fuel mapping, to post wildfire monitoring, including burn area and severity estimation.
由于区域和全球范围内大范围的火灾发生以及受火灾影响的地区的可达性有限,近几年来,遥感方法已成为具有成本效益的替代方案,能够以足够的时空分辨率收集燃烧的区域信息。 遥感技术可以为火灾管理,估计和检测,燃料映射提供有用的数据,以进行野火监视,包括燃烧面积和严重性估计。
问题陈述 (Problem Statement)

Current non-deep learning methods heavily rely on domain knowledge and manual input from the user and are unable to extract the abstract representations from the data. Deep learning attempts to resolve these problems however, they remain largely neglected in burn scar prediction due to general lack of any labelled data.
当前的非深度学习方法严重依赖领域知识和来自用户的手动输入,并且无法从数据中提取抽象表示。 深度学习试图解决这些问题,但是由于普遍缺乏任何标记数据,它们在烧伤疤痕预测中仍然被很大程度上忽略。
In this work, we leverage the recent advances in sensing leading to ubiquitous availability of multimodal data and computer vision in remote sensing to utilise noisy, weakly labelled data to identify fragmented burn scars using UNet, making our approach one of the first to utilise deep learning based segmentation models in multimodal burn scar identification.
在这项工作中,我们利用传感技术的最新进展,导致遥感中广泛使用多模式数据和计算机视觉,从而利用UNet利用嘈杂,弱标签数据识别碎片状的烧伤疤痕,使我们的方法成为最早利用深度学习的方法之一多模式烧伤疤痕识别的基于分割的模型。
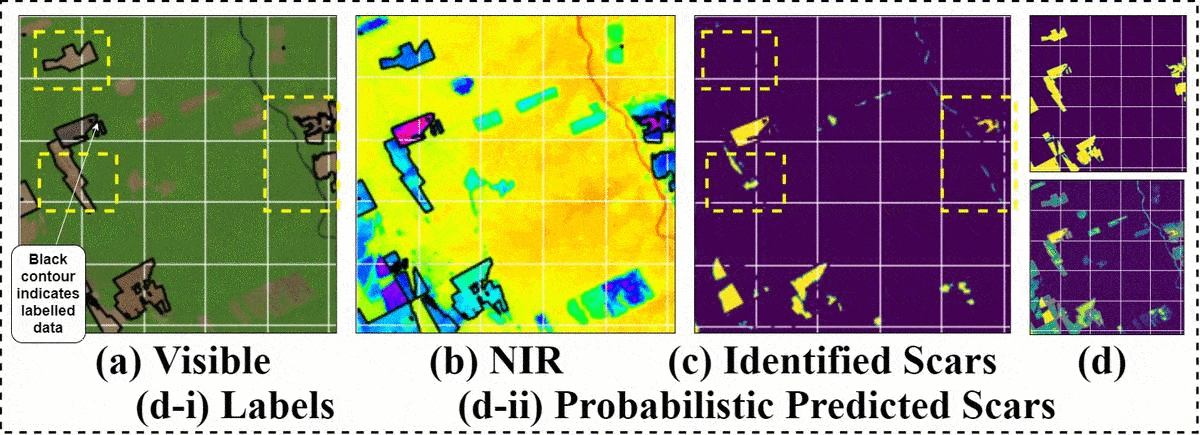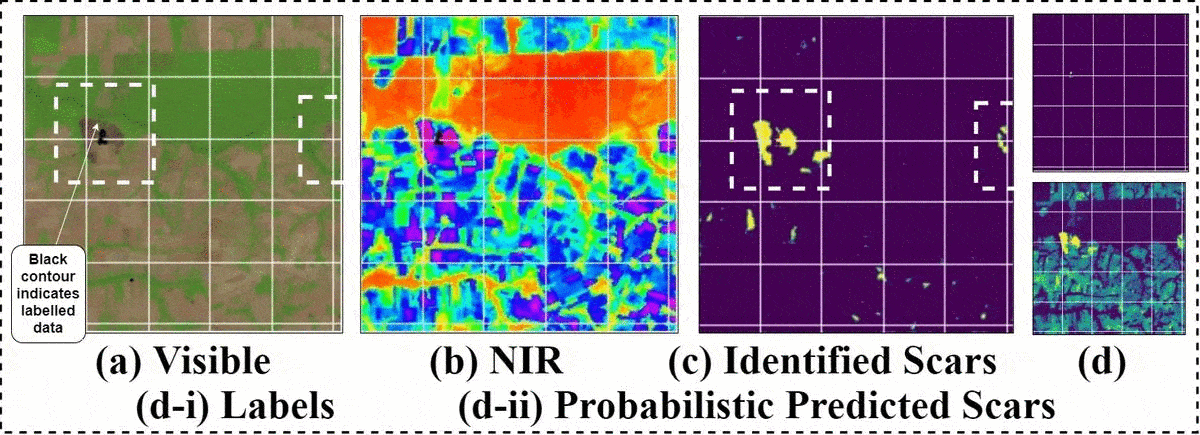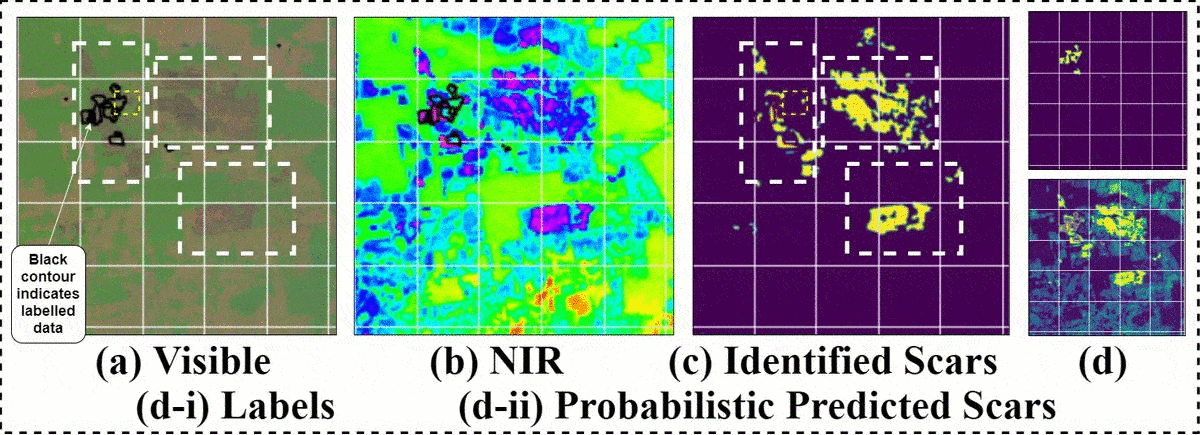
相关工作 (Related Work)
语义分割 (Semantic Segmentation)
Semantic Segmentation is an important problem in computer vision. It involves the clustering of various pixels together if they belong to the same object class. Due to their ability to capture semantic context with precise localisation, they have been used for various applications in autonomous driving, human-machine interaction, diagnosis, remote sensing etc.
语义分割是计算机视觉中的重要问题。 如果它们属于同一对象类,则涉及将各种像素聚在一起。 由于具有捕获精确定位的语义上下文的能力,它们已被用于自动驾驶,人机交互,诊断,遥感等各种应用。
Before the advent of DNNs, variety of features were used for semantic segmentation, such as K-means, Histogram of oriented gradients, Scale-invariant feature transform etc. Today, many encoder-decoder networks and their variants like SegNet, have been proposed. Specialized applications have led to novel improvements like UNet for Medical Image Segmentation, CRFs based networks for fine segmentation.
在DNN出现之前,各种特征用于语义分割,例如K均值,定向梯度直方图,尺度不变特征变换等。今天,提出了许多编码器-解码器网络及其变体,例如SegNet。 特殊的应用带来了新颖的改进,例如用于医学图像分割的UNet,用于精细分割的基于CRF的网络。
遥感中的多模式数据 (Multimodal data in remote sensing)
Multimodal segmentation in remote sensing involves utilising various strategies to efficiently combine information contained in multiple modalities to generate a single, rich, fused representation beneficial for accurate land use classification. Common methods involve concatenation channels at input stage, concatenation of features extracted from unimodal networks like CNNs to generate land mapping segmentation. Recent works involve more sophisticated ideas like ‘cross-attention’ to fuse multiple modalities and generate attentive spectral and spatial representations.
遥感中的多模式分割涉及利用各种策略来有效地组合多种模式中包含的信息,以生成单个,丰富,融合的表示形式,这有利于准确的土地利用分类。 常见的方法包括在输入阶段连接通道,从诸如CNN的单峰网络提取的要素进行串联以生成土地制图分割。 最近的工作涉及更复杂的想法,例如“交叉注意”,以融合多种形式并产生细心的光谱和空间表示。
烧伤疤痕鉴定 (Burn Scar Identification)
Simultaneous availability of multimodal data has led to recent advances in locating fires and in quantifying the area burned. Each modality provides discriminating information about the same geographical region, helping in mapping amidst adverse conditions like spectral confusion (like due to cloud shadowing) & variability in burn scars making distinguishing between vegetation difficult. Majority of work done in this domain involves methods like auto-correlation , self-organizing maps, linear spectral mixture model, SVM , random forests . However, no recent works seem to utilise current deep learning methods like CNN or encoder-decoder models like SegNet or UNet, presumably due to lack of labelled data.
同时提供多模式数据已导致在定位火灾和量化燃烧面积方面的最新进展。 每个模式都提供有关同一地理区域的区分信息,有助于在不利条件下进行映射,例如频谱混乱(如由于云影所致)和烧伤疤痕的变化,从而难以区分植被。 在这一领域完成的大部分工作涉及诸如自相关,自组织图,线性光谱混合模型,SVM,随机森林之类的方法。 然而,大概是由于缺少标记数据,最近的工作似乎没有利用诸如CNN之类的当前深度学习方法或诸如SegNet或UNet之类的编码器-解码器模型。
拟议方法 (Proposed Method)
The objective of this work is to perform semantic segmentation and identify burn scars by harnessing the spatio-spectral information constituted in visible and near infrared.
这项工作的目的是通过利用可见光和近红外光中构成的时空光谱信息执行语义分割并识别烧伤疤痕。
建筑 (Architecture)
In remote sensing, computer vision based methods are difficult to apply, due to lack of good labelled datasets, because the required data processing and labelling can only be done by field experts, making labelled data rare or unavailable. Similar problems arise in medical image segmentation, and so common approaches in remote sensing are sometimes inspired from medical segmentation domain. For burn scar segmentation task, we base our network on the UNet architecture, where the feature activations from encoder were stored and transferred to corresponding decoder layer for concatenation.
在遥感中,基于计算机视觉的方法由于缺乏良好的标记数据集而难以应用,因为所需的数据处理和标记只能由现场专家完成,这使得标记的数据很少或不可用。 在医学图像分割中也会出现类似的问题,因此有时会从医学分割领域中激发遥感中的常用方法。 对于烧伤疤痕分割任务,我们基于UNet架构构建网络,在该架构中,存储了来自编码器的特征激活,并将其转移到相应的解码器层以进行级联。
Encoder: The encoder network consists of 3x3 convolution layers along with batch normalization layers, ReLU nonlinear activation layers, and 2x2 max-pooling layers.Decoder: The decoder network consists of UpSampling layers named as UpPool block, which performs 3x3 Conv2DTranspose, 3x3 Convolution along with batch normalization layers and Dropout2D layers with a dropout value of 0.1. The output results are thresholded to obtain a binary output map denoting the burn scars.
编码器:编码器网络由3x3卷积层,批处理归一化层,ReLU非线性激活层和2x2最大池化层组成。 解码器:解码器网络由名为UpPool块的UpSampling层组成,该层执行3x3 Conv2DTranspose,3x3卷积以及批处理归一化层和Dropout2D层,且其dropout值为0.1。 对输出结果进行阈值处理以获得表示烧伤疤痕的二进制输出图。
数据集 (Datasets)
This dataset consists of a visible and near infrared satellite imagery from LANDSAT8 of the Amazon Rainforest. The dataset was acquired for 2017 and 2018 from over 4 states, namely Tocantins, Maranhao, Mato Grosso, Para covering over four terrestrial Brazilian biomes namely Cerrado, Amazonia, Caatinga, Pantanal. It consists of 299 samples VISNIR image pairs of size 1024x1024 with ground truth, which are binary images, in which 1 represent burn scars in the forest and 0 are areas that were not affected by the fire. As can be seen the ground truth is noisy and also partially labelled, sometimes mislabelled as can be verified from the figure. The dataset was curated by National Institute for Space Research (INPE) as part of the Quiemadas Project.
该数据集由来自亚马逊雨林的LANDSAT8的可见和近红外卫星图像组成。 该数据集是在2017年和2018年从4个州(即Tocantins,Maranhao,Mato Grosso,Para)采集的,覆盖了巴西的四个陆地生物群落,即塞拉多,亚马逊,卡廷加,潘塔纳尔。 它由299个具有地面真实性的VISNIR图像对样本组成,大小为1024x1024,它们是二进制图像,其中1代表森林中的烧伤痕迹,0代表不受火灾影响的区域。 可以看出,地面真相是嘈杂的,也有部分标记,有时可以贴错标签,这可以从图中得到验证。 该数据集由美国国家空间研究所(INPE)整理,是Quiemadas项目的一部分。
结果 (Results)
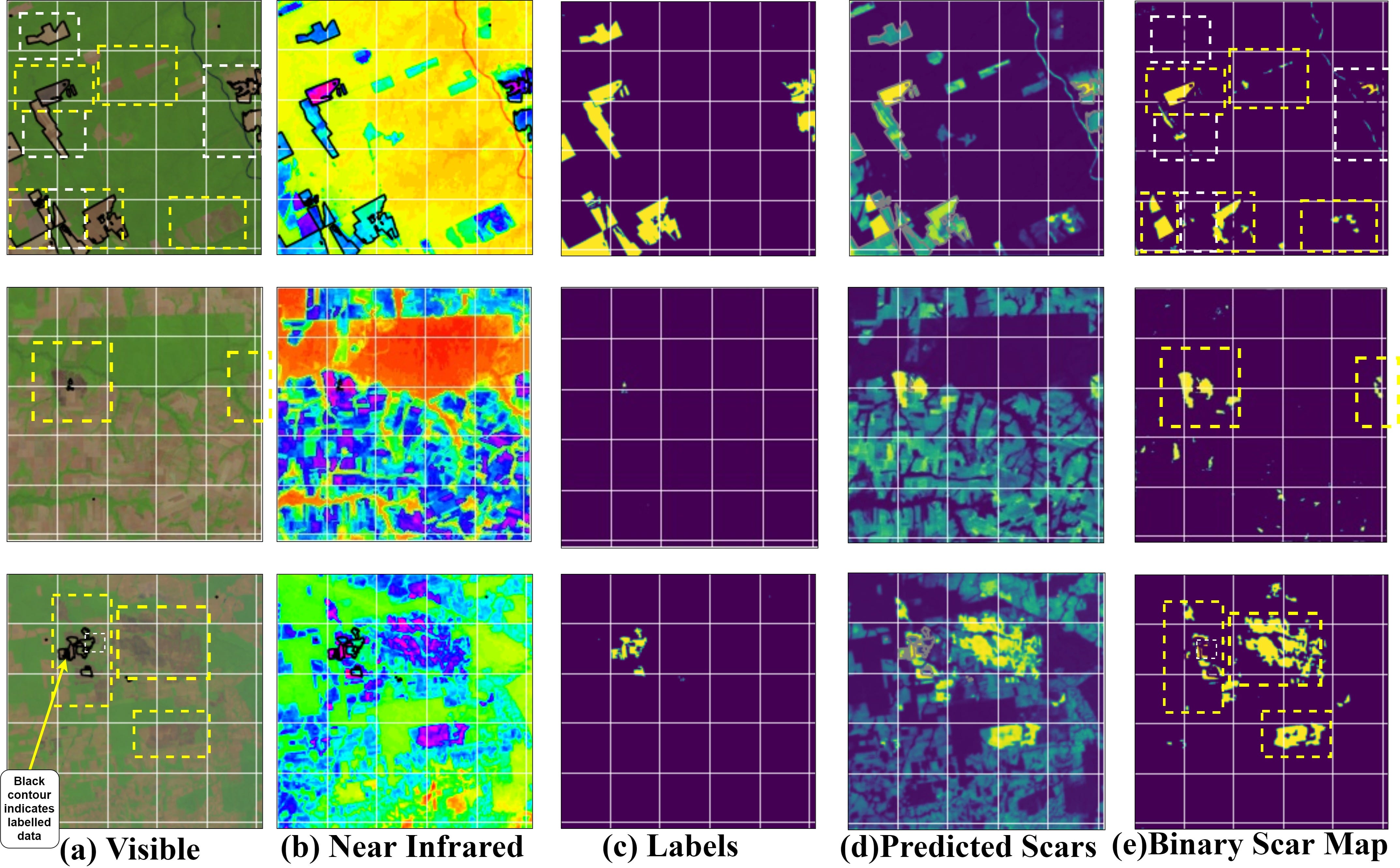
The model obtained a training accuracy of 69.51% & a validation accuracy of 63.33%. The results validate the efficacy of the utilising U-net based segmentation in burn scar identification.
该模型的训练精度为69.51%,验证精度为63.33%。 结果证实了利用基于U-net的分割在烧伤疤痕识别中的功效。
As can be seen, the network correctly identifies unlabeled fragmented burn scars (denoted as yellow-dash boxes) and deselects wrongly labelled areas (denoted as white-dash boxes) in the output binary map (correctly labelled outputs are highlighted as yellow and deselected labels as white).
可以看出,网络可以正确识别未标记的碎片烧伤疤痕(表示为黄色虚线框),并在输出二进制映射中取消选择错误标记的区域(表示为白色虚线框)(正确标记的输出会突出显示为黄色,并取消选择标签如白色)。
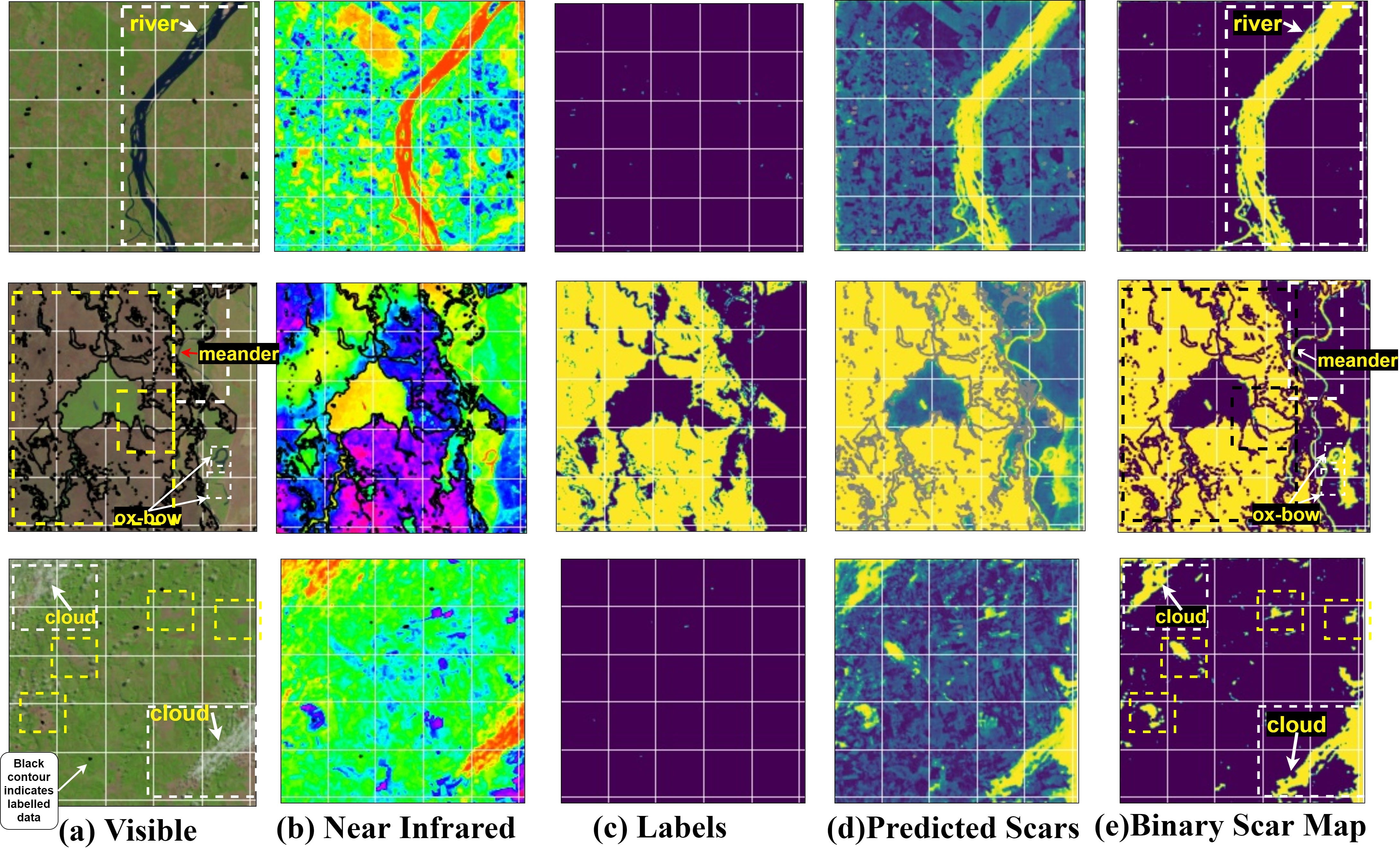
Our network, however, fails to distinguish river and cloud patterns from burn scars as can be seen below. Defects emerge when our network segments (a) river (b) meanders and ox-bow lake and © clouds as burn scar patterns. It is interesting how in sample 2 and 3 in the figure, the network accurately segments the small fragmented burn scars but absolutely fails to reject these. This can be attributed primarily to (i) lack of any labelled examples and (ii) negligible samples containing the above geographical features in the datasets.
但是,我们的网络无法从灼伤痕迹中区分出河流和云层的形态,如下所示。 当我们的网络分段(a)河流(b)蜿蜒曲折,牛弓湖和©云彩作为烧伤疤痕时,就会出现缺陷。 有趣的是,在图中的样本2和3中,网络如何精确地分割小的碎片烧伤疤痕,但绝对不能拒绝这些。 这主要归因于(i)缺少任何带标签的示例,以及(ii)数据集中包含上述地理特征的样本可忽略不计。
结论与未来工作 (Conclusion and Future Work)
We utilised a partially/mis-labelled dataset representing burn patterns in Amazon rainforest to propose U-net based segmentation network to correctly identify burn scars & reject incorrect labels, demonstrating the effectiveness of AI in fragmented burn scar identification. We presented shortcomings & consider resolving these as future work.
我们利用表示亚马逊雨林烧伤模式的部分/错误标签数据集来提出基于U-net的分割网络,以正确识别烧伤疤痕并拒绝不正确的标签,证明了AI在碎片化烧伤疤痕识别中的有效性。 我们提出了缺点,并考虑将其作为未来的工作来解决。
Multimodal Noisy Segmentation based fragmented burn scars identification in Amazon Rainforest
基于多模式噪声分割的亚马逊热带雨林碎片化烧伤疤痕识别
(Accepted) Satyam Mohla, Sidharth Mohla, Anupam Guha, Biplab Banerjee; IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, & Cybernetics (IEEE SMC 2020)
(接受) 萨蒂扬·莫拉 ( Satyam Mohla) ,西达斯· 莫拉 (Sidharth Mohla),阿努帕姆·古哈(Anupam Guha),比帕拉·班纳吉(Biplab Banerjee); IEEE系统,人与控制论国际会议(IEEE SMC 2020)
(Presented) Satyam Mohla, Sidharth Mohla, Anupam Guha; Harvard CRCS AI for Social Good Workshop 2020
(赠送) 萨蒂扬·莫拉 ( Satyam Mohla) ,西达斯· 莫拉 (Sidharth Mohla),阿努帕姆(Anupam Guha) 哈佛CRCS人工智能社会公益研讨会2020
亚马逊 ai 解雇






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








