这几天碰到个问题:在weblogic中调用async webservice,如果客户端不等待结果(比如服务器端因为某些原因,web service需要执行很长时间),直接退出的话,weblogic server是否保存调用结果,结果保存多长时间? 如果这样的异常客户端很多,对服务器有什么负面影响,比如连接资源、内存开销等。
首先我们先阐述一下异步的概念 在weblogic webservice中,有两处异步的概念:
1:Synchronous request-response (the default behavior) means that every time a client application invokes a Web Service operation, it receives a SOAP response, even if the method that Choosing RPC-Oriented or Document-Oriented Web Services Programming WebLogic Web Services 4-3 implements the operation returns void. Asynchronous one-way means that the client never receives a SOAP response, even a fault or exception.
默认情况下,weblogic webservice是请求-应答模式的,即客户端会block当前线程,直到server端处理完该请求(即使该请求没有任何返回值,void)。当web service不返回结果,客户端只是提交请求,不需要知道执行结果的时候,可以采用异步单向模式。这种情况下,客户端线程为非阻塞的,它只负责提交请求,而不需要返回结果。定义这样的异步web service时,需要遵循如下的两个原则:
1.1:The back-end component that implements the operation must explicitly return void.
1.2:You cannot specify out or in-out parameters to the operation, you can only specify inparameters.
2:This section describes how to invoke an operation asynchronously. In this context, asynchronously means you invoke an operation and then optionally get the results of the invoke in a later step.
这种情况下虽然也是异步调用的,但这种调用方式客户端需要返回值。需要返回结果,但客户端又不乐意阻塞在服务器端请求处理上(可能服务器端处理该请求需要很长时间)。客户端希望继续执行它的其他业务逻辑,需要执行结果的时候,我在过来取这个结果。这样可以提高客户端的响应速度。
这篇文章,我们主要看看2这种情况。
2.1: web service开发
开发web service不存在任何区别,但在build client jar的时候,需要在调用clientgen的时候加上generateAsyncMethods = true, 这样clientgen生成的JAX-RPC stub中会多出两个方法,如下:
FutureResult startMethod (params, AsyncInfo asyncInfo);
result endMethod (FutureResult futureResult);
其中:Method对应于web service中的方法名,如sayHello---->startSayHello(params, AsyncInfo asyncInfo)。这两个方法就是我们客户端代码中异步调用的时候需要的。
2.2:客户端代码
客户端代码有两种写法,一种是客户端线程主动调用FutuerResult.isCompleted()来检查web service请求是否执行完成,另一种方式是通过Listenter来处理服务器端的返回结果。
//client thread checking
1 publicvoidrunUnblock(){2 initializeEnv();3 try{4 System.out.println(port.getClass().getName());5 FutureResult result=port.startSayHello(3,"test",null);6 //you other business logic here7 if(result.isCompleted())8 {9 String ret=port.endSayHello(result);10 System.out.println("result from remote HelloWorld web service:");11 System.out.println(ret);12 }13 }catch(Exception e){14 e.printStackTrace();15 }16 }17 18 publicvoidinitializeEnv(){19 try{20 helloService=newHelloWorld_Impl();21 port=helloService.getHelloWorldPort();22 }catch(Exception e){23 e.printStackTrace();24 }25 }
//listener
1 AsyncInfo asyncInfo=newAsyncInfo();2 asyncInfo.setResultListener(newResultListener(){3 publicvoidonCompletion( InvokeCompletedEvent event ){4 SimpleTestSoap source=(SimpleTestSoap)event.getSource();5 try{6 String result=source.endEchoString ( event.getFutureResult() );7 }catch( RemoteException e ){8 e.printStackTrace ( System.out );9 }10 }11 });12 echoPort.startEchoString("94501", asyncInfo );
现在回头看看开篇的问题,客户端线程退出时,如果服务器端还没有处理完,请求结果会怎么办?是否会保存下来?如果这样的客户端很多,服务器内存开销岂不是很大?
要解释这个问题,我们先来看看这种调用方式的流程。对于服务器而言,异步、同步调用是一样的,它只负责接收、处理请求,web service的处理,在服务器端是由weblogic.webservice. server.servlet. WebServiceServlet .serverSideInvoke(WebService webservice, Binding binding, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)。同步、异步的处理完全是在客户端完成的,下面就看看客户端的调用流程。
FutureResult result =port.startSayHello(3,"test",null);
//it's a JAX-RPC stub, and it extends StubImpl.java
====>
weblogic.webservice.core.rpc.StubImpl._startAsyncInvoke( String method, Map args, AsyncInfo wsAsyncContext )
//in this method, Operation is retrieved from Port
====>
weblogic.webservice.core.DefaultOperation.asyncInvoke( Map outParams, Object[] args, AsyncInfo wsContext, PrintStream logStream )
//a ClientDispatcher is created here and then we dispatch our requst with this dispatcher
====>
weblogic.webservice.core.ClientDispatcher.asyncDispatch(final Object[] args, final AsyncInfo async)
//in this method, FutureResultImpl is created and it will be returned to client. It's responsible to send message and
//receive response from server in another. For receiving response, it's will be discussed later.
====>
weblogic.webservice.core.ClientDispatcher.send(Object[] args)
//MessageContext is set(for example, BindInfo is set) here and the request will be handle by a handler chain.
====>
weblogic.webservice.core.handler.ClientHandler.handleRequest(MessageContext ctx)
//it check bind info and the delegate the request to binding
====>
weblogic.webservice.binding.http11.Http11ClientBinding.send(MessageContext ctx)
//it retrieve endpoint from bindinfo and then open a HttpURLConnection with the URL created basing on endpoint.
//Reqeust is sent to server with this HttpURLConnection.
1 connection=(HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection();2 
 3 outputStream=connection.getOutputStream();4 request.writeTo( outputStream );
3 outputStream=connection.getOutputStream();4 request.writeTo( outputStream );
请求发送完了,交给服务器去执行,下面我们再来看看客户端是如何处理response的。weblogic.webservice. core.ClientDispatcher.asyncDispatch()中,请求发送结束后,weblogic将启用一个新线程来接受服务器的response,如下:
1 getThreadPool().addTask(newRunnable() {2 publicvoidrun() {3 callReceive(messageContext);4 }5 });
注意:这个线程是在客户端启动的。该接收线程启动后,FutureResultImpl实例会返回给客户端,客户端由此可以继续他的业务逻辑,而不必block在等待response上。response由接收线程负责处理,收到response,处理后的结果会被植入FutureResultImpl,客户端执行它的其他逻辑,需要处理处理该结果时,只需要检查请求是否处理结束,如果结束,处理请求结果,如果请求依然没有结束,则由客户端决定继续等待,还是放弃(主线程退出),如下:
1 //you other business logic here2 if(result.isCompleted())3 {4 String ret=port.endSayHello(result);5 System.out.println(ret);6 }
客户端接受流程:
weblogic.webservice.core.ClientDispatcher.asyncDispatch(final Object[] args, final AsyncInfo async)
====>
weblogic.webservice.core.ClientDispatcher.callReceive(WLMessageContext ctx)
//call receive() here, and if response was received, set it to FutureResultImpl that owned by the client and if Listener is configured, trigger the listner.
1 if(listener!=null) {2 InvokeCompletedEvent event=newInvokeCompletedEvent(3 async.getCaller());4 5 event.setFutureResult(futureResult);6 listener.onCompletion(event);7 }
====>
weblogic.webservice.core.ClientDispatcher.receive(WLMessageContext ctx)
//resoponse is handled by a handler chain
====>
weblogic.webservice.core.handler.ClientHandler.handleResponse(MessageContext ctx)
====>
weblogic.webservice.binding.http11.Http11ClientBinding.receive( MessageContext context )
//read response from the input stream of connect that we send request with, and the thread will be blocked in
//waiting data from server.
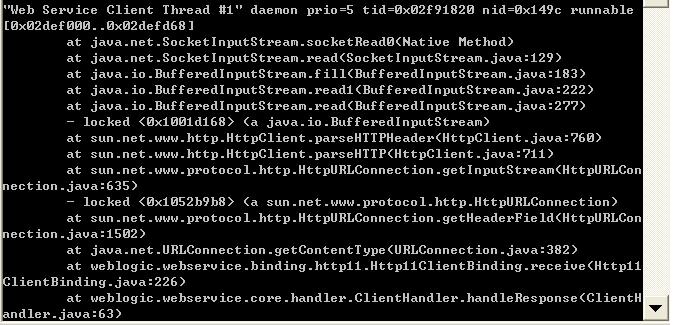
好了,基本流程都列出来了。下面据此回答开篇的问题:
1:如果客户端不等待结果(比如服务器端因为某些原因,web service需要执行很长时间),直接退出的话,weblogic server是否保存调用结果,结果保存多长时间?
不会。如果客户端退出前,请求已处理,保存在FutureResultImpl将会因为客户端的退出而销毁。如果没有处理结束,服务器端回写response的时候,虽然指向客户端的连接已经因为客户端退出而close了,但服务器端从该connection中拿到的output stream还在,服务器仍然会将response写入到该output stream中(这是写入的数据是没有接收者的),response写完后,weblogic会关闭output stream, 并close socket。
2:如果这样的异常客户端很多,对服务器有什么负面影响,比如连接资源、内存开销等。
不会。如果客户端退出前,请求已处理,则连接已经释放。如果连接保持的时间略大于web service请求在服务器段的处理时间。请求处理结束后,服务器会在回写完response后,主动断开连接(可以看到客户端至server端的连接为TIME_WAIT)。如果客户端退出时,请求依然在服务器端上处理,客户端的退出会导致连接的CLOSE。两种情形都不会因为异常客户端而导致连接浪费。至于内存开销,服务器不会保存执行结果,请求处理结束后,直接回写客户端,所以也不会造成内存资源leak。
对于那些web service执行时间较长,客户端又希望其他业务并行的应用,这种异步调用是个不错的选择。
posted on 2008-11-24 22:38 走走停停又三年 阅读(2626) 评论(1) 编辑 收藏 所属分类: Weblogic





















 3066
3066











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








