文中代码地址:https://github.com/gaohanghbut/groovy-configuration
起因
Springboot支持yml和properties两种方式的配置,不知道有没有同学和我一样,对yml, properties, xml这类配置非常不喜欢,配置太多了之后,可读性急剧下降,维护配置非常困难,估计只有java这样的编程语言的框架使用大量的xml, properties等作为配置文件了
但是Java支持groovy脚本,我们可以利用groovy来取代yml和properties,使用application.groovy替代application.yml或application.propertie,使用application-xxx.groovy替代application-xxx.yml或application-xxx.properties,并且支持groovy语法,配置类似如下图,对于groovy类中类型为String或者GString的属性都会被认为是一个property,对于类型为Map的属性,会认为是property的集合,基于这个特性,我们可以将同一类型的配置用同一个Map表示,极大的增加了可读性,降低了维护成本:

如果只需要用一个Map表示所有的配置,则可以不定义类,只定义一个Map:

在工程的resources目录下,通过application.groovy或者application-xxx.groovy表示配置:

可支持profile,本文中的例子是一个简化的配置,实际中的配置要复杂得多,在实际应用中,可将application.groovy与application.properties或者application.yml共存。
应用的启动类则不变,还是原来的样子:

关于实现方式,我们先从springboot的扩展开始
SpringBoot的扩展
这里不从头讲述springboot的扩展,这不是文章的重点,我们直接进入到一个类PropertySourcesLoader,其中初始化相关代码:
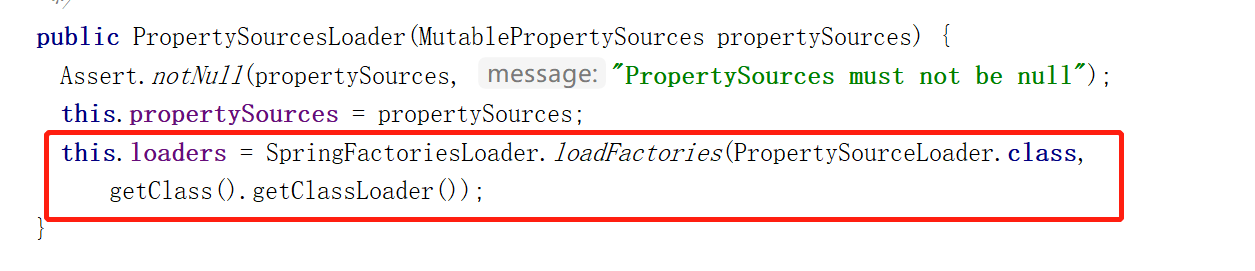
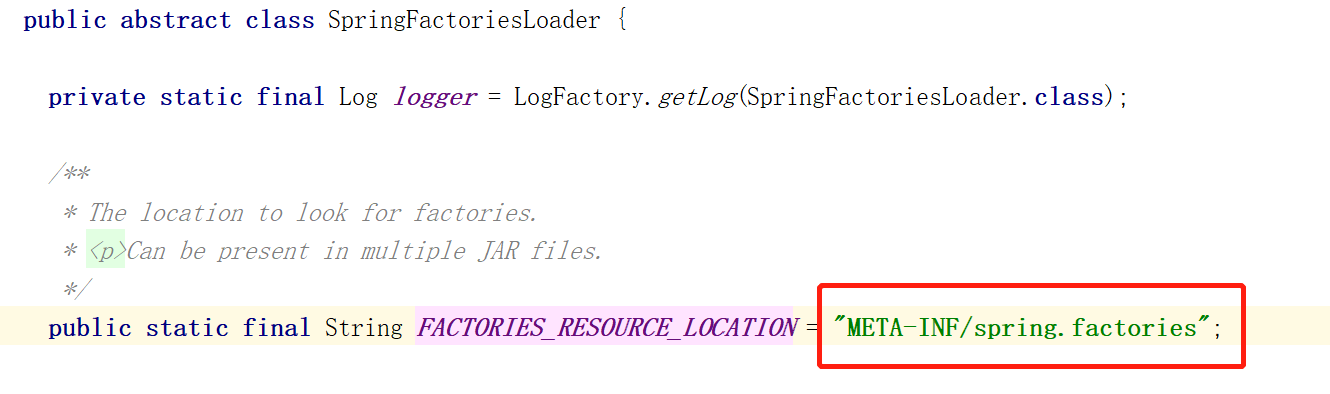
可以看到,这里通过SpringFactoriesLoader获取了PropertySourceLoader接口的实例,那么SpringFactoriesLoader是干嘛的?它就是用来加载spring的jar包中的spring.factories文件的,源码如下:

咱们再来看看PropertySourceLoader有哪些实现:
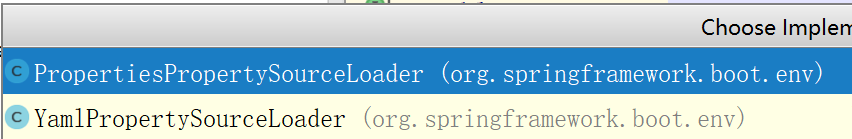
可以看到,springboot提供了properties和yml两种实现,咱们再看看PropertySourcesLoader中加载配置的代码:
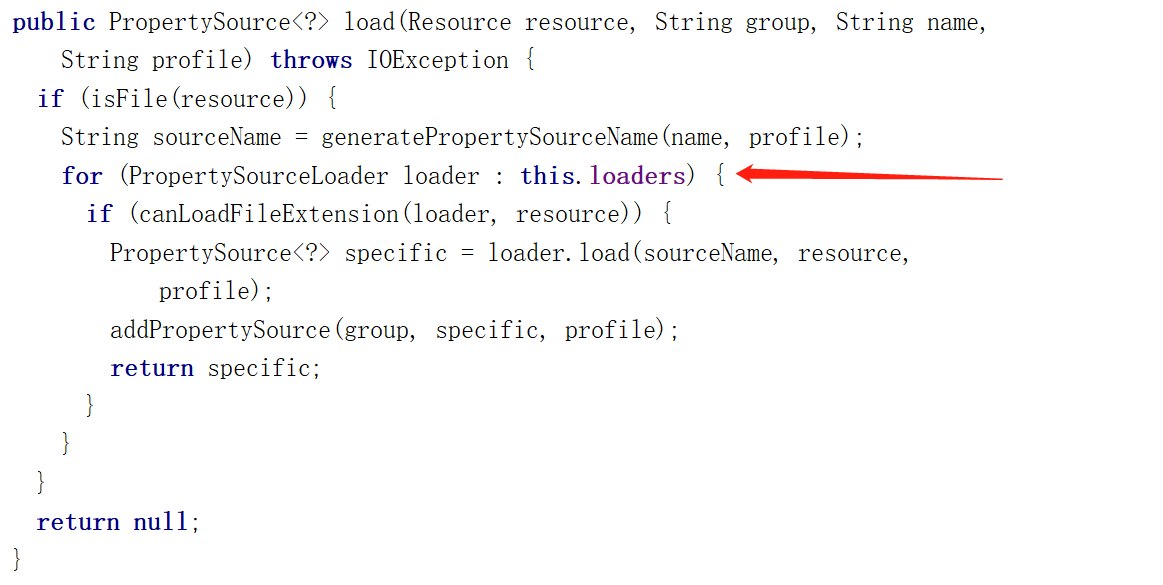
通过这个方法我们可以看到,springboot分别用了不同的PropertySourceLoader加载不同格式的配置
实现对groovy配置的支持
咱们先看看PropertySourceLoader接口的定义:

它只有两个方法:
- getFileExtensions:用于获取支持的配置文件的后缀
- load:用于加载配置,得到PropertySource
讲到这里,大家应该就明白了,想要支持groovy,分两步即可:
- 实现一个PropertySourceLoader,用于加载groovy文件并得到PropertySource
- 创建META-INF/spring.factories并将实现的PropertySourceLoader配置在此文件中
咱们来看代码,先是对PropertySourceLoader的实现:
import com.google.common.collect.Sets;
import groovy.lang.GString;
import org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertiesPropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.scripting.groovy.GroovyScriptFactory;
import org.springframework.scripting.support.ResourceScriptSource;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* springboot 支持groovy配置
*
* @author gaohang
*/
public class GroovyPropertySourceLoader implements PropertySourceLoader {
private static final String[] STRINGS = {"groovy"};
private final Set<String> loaded = Sets.newHashSet();
@Override
public String[] getFileExtensions() {
return STRINGS;
}
@Override
public PropertySource<?> load(final String name, final Resource resource, final String profile) throws IOException {
return createStringValueResolver((ClassPathResource) resource);
}
private PropertySource createStringValueResolver(final ClassPathResource resource) throws IOException {
if (loaded.contains(resource.getPath())) {
return null;
}
final Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
final Object scriptedObject = getGroovyConfigObject(resource);
if (scriptedObject instanceof Map) {
putToProperties(properties, (Map<?, ?>) scriptedObject);
} else {
final List<Field> fields = Reflections.getFields(scriptedObject.getClass());
for (Field field : fields) {
final Object value = Reflections.getField(field.getName(), scriptedObject);
if (value instanceof Map) {
putToProperties(properties, (Map<?, ?>) value);
} else if (value instanceof String || value instanceof GString) {
properties.put(field.getName(), String.valueOf(value));
}
}
}
return new PropertiesPropertySource("groovy:" + resource.getPath(), properties);
} finally {
loaded.add(resource.getPath());
}
}
private void putToProperties(final Properties properties, final Map<?, ?> values) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(values)) {
return;
}
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> en : values.entrySet()) {
properties.put(String.valueOf(en.getKey()), String.valueOf(en.getValue()));
}
}
private Object getGroovyConfigObject(final ClassPathResource scriptSourceLocator) throws IOException {
final GroovyScriptFactory groovyScriptFactory = new GroovyScriptFactory(scriptSourceLocator.getPath());
groovyScriptFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClass().getClassLoader());
final ResourceScriptSource resourceScriptSource = new ResourceScriptSource(scriptSourceLocator);
return groovyScriptFactory.getScriptedObject(resourceScriptSource);
}
}
有了这个GroovyPropertySourceLoader后,我们再创建spring.factories:

其中的内容:
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=cn.yxffcode.springboot.configuration.groovy.GroovyPropertySourceLoader
最后,GroovyPropertySourceLoader中使用到的Reflections类:
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author gaohang on 15/12/4.
*/
final class Reflections {
private Reflections() {
}
private static Field findField(Class<?> clazz, String name) {
return findField(clazz, name, null);
}
public static Field findField(Class<?> clazz, String name, Class<?> type) {
Class<?> searchType = clazz;
while (!Object.class.equals(searchType) && searchType != null) {
Field[] fields = searchType.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if ((name == null || name.equals(field.getName())) && (type == null || type
.equals(field.getType()))) {
return field;
}
}
searchType = searchType.getSuperclass();
}
return null;
}
public static List<Field> getFields(Class<?> clazz) {
final List<Field> fields = Lists.newArrayList();
Class<?> type = clazz;
while (type != Object.class) {
final Field[] declaredFields = type.getDeclaredFields();
fields.addAll(Arrays.asList(declaredFields));
type = type.getSuperclass();
}
return fields;
}
public static Object getField(String fieldName, Object target) {
Field field = findField(target.getClass(), fieldName);
if (!field.isAccessible()) {
field.setAccessible(true);
}
try {
return field.get(target);
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected reflection exception - " + ex.getClass()
.getName() + ": " + ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
}



 本文介绍了如何利用Groovy脚本来替代SpringBoot中的YML和Properties配置文件,提高配置的可读性和维护性。作者创建了一个名为GroovyPropertySourceLoader的类,实现了PropertySourceLoader接口,加载Groovy配置文件并将其转换为PropertySource。同时,通过编辑spring.factories文件,将GroovyPropertySourceLoader注册为SpringBoot的配置加载器。这种方式允许开发者使用更直观的Groovy语法进行配置管理。
本文介绍了如何利用Groovy脚本来替代SpringBoot中的YML和Properties配置文件,提高配置的可读性和维护性。作者创建了一个名为GroovyPropertySourceLoader的类,实现了PropertySourceLoader接口,加载Groovy配置文件并将其转换为PropertySource。同时,通过编辑spring.factories文件,将GroovyPropertySourceLoader注册为SpringBoot的配置加载器。这种方式允许开发者使用更直观的Groovy语法进行配置管理。
















 1571
1571

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








