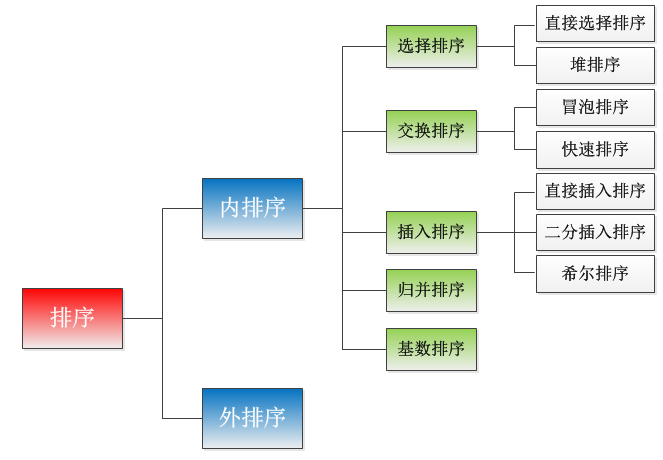
java排序从大的分类来看,可以分为内排序和外排序:其中,在排序过程中只使用了内存的排序称为内排序;内存和外存结合使用的排序成为外排序。
下面讲的都是内排序。
内排序在细分可以这样分:
1、选择排序:直接选择排序,堆排序
2、交换排序:冒泡排序,快速排序
3、插入排序:直接插入排序,二分插入排序,希尔排序
4、归并排序
5、基数排序
是不是觉得这样分类,文字的看着不形象,我也画了一张分类图:
下面是实现源码:
package sort;
/**
* Package: sort
*
* File: JavaSorts.java
*
* Copyright @ 2015 Corpration Name
*
*/
public class JavaSorts {
/**
* 希尔排序
* @param array
*/
public static void ShellSort(int[] array){
int d = array.length;
do {
d /= 2; //设置增量,通过设置增量来进行分组,分组后,每一组内采用直接插入排序
OneShell(array, d);//一个增量对应一趟希尔排序
} while (d > 1);
}
/**
* 一趟希尔排序
* @param array
* @param d
*/
public static void OneShell(int[] array,int d){
for (int i = 0; i
int temp = array[i+d]; //array[i+d]的拷贝,每一次插入操作所以插入的值
if (array[i] > array[i + d]) {
int j = i;
//此时分组为:j,j+d,j+2d,j+3d····,组内采用直接插入排序
while(j >= 0 && array[j] > temp){
array[j + d] = array[j]; //使用while循环寻找temp能够插入的位置,从右往左寻找,大于temp的往后移动
j -= d;
}
array[j + d] = temp; //插入数据
}
}
}
/**
* 快速排序
* @param array
* @param l
* @param r
*/
public static void QuickSort(int[] array,int l,int r){
if (l
int i = l,j = r,temp = array[l];
while(i
while(i temp){
j--; //从右边开始寻找比temp小的数
}
if(i
array[i++] = array[j]; //找到后,将这个数赋值到i位置上,然后i+1,因为下一轮寻找比temp大的数,从i+1位置开始
}
while(i
i++; //从左边寻找比temp大的数
}
if(i
array[j--] = array[i]; //找到后,将这个数赋值到j位置上,然后j-1,因为下一轮寻找比temp小的数从j-1位置开始
}
}
array[i] = temp; //此时比temp小的数都移动到左边,比temp大的数都移动到了右边,最后将temp赋值到中间位置
QuickSort(array, l, i - 1); //对temp左边的数进行递归
QuickSort(array, i + 1, r); //对temp右边的数进行递归
}
}
/**
* 堆排序
* @param array
*/
public static void HeapSort(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i
BuildMaxHeap(array, array.length - 1 - i);
Swap(array, 0, array.length - 1 - i);
}
}
/**
* 创建最大堆
* @param array
* @param lastOneIndex
*/
public static void BuildMaxHeap(int[] array,int lastOneIndex){
for (int i = (lastOneIndex - 1)/2; i >= 0; i--) {
int k = i;
while(2*k + 1 <= lastOneIndex){
int bigIndex = 2*k + 1; //bigIndex用于记录一个节点树中最大数的索引
if (bigIndex
if (array[bigIndex]
bigIndex++; //若满足这个条件,说明k节点下的右子节点大于左子结点,因而bigIndex加1
}
}
if (array[k]
Swap(array, bigIndex, k); //若k节点小于它其中一个子节点,则与这个子节点交换值
k = bigIndex; //交换完值后,此时k节点下面的bigIndex节点可能不满足堆的性质,所以赋值给k,重新进入下一轮while循环
}else {
break;//若k节点满足堆的性质,则直接跳出循环
}
}
}
}
/**
* 交换array中array[a]、array[b]
* @param array
* @param a
* @param b
*/
public static void Swap(int[] array,int a,int b){
if (a
int temp = array[a];
array[a] = array[b];
array[b] = temp;
}
}
/**
* 直接插入排序
* @param array
*/
public static void DirectInsertSort(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i
int temp = array[i + 1];
if (array[i] > array[i + 1]) {
int j = i;
while(j >= 0 && array[j] > temp){
array[j + 1] = array[j];
j--;
}
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
/**
* 二分插入排序
* @param array
*/
public static void BinaryInsertSort(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i
int temp = array[i + 1]; //需要插入的数
if(array[i] > array[i + 1]){
int l = 0; //有序队列中左边标识
int r = i; //有序队列中右边标识
while(l
int mid = (l + r) / 2; //永远指向l->r中间的那个值,中间值与temp(需要插入的值)比较
if (array[mid] > temp) {
r--; //通过while循环,二分折半搜索temp应该插入的位置
}else {
l++;
}
}
//运行到这里,l==r,即是temp应该插入的位置是array[l](或者array[r])
for (int j = i + 1; j > l; j--) {
array[j] = array[j - 1]; //将l -> i的数都往后移动一位
}
array[l] = temp; //将temp插入到l位置
}
}
}
/**
* 直接选择排序
* @param array
*/
public static void DirectSelectSort(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i
int min = array[i];
for (int j = i + 1; j
if (array[j]
min = array[j];
array[j] = array[i];
array[i] = min;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 冒泡排序
* @param array
*/
public static void BubbleSort(int[] array){
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i
for (int j = 0; j
if (array[j] > array[j+1]) {
temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 归并排序
* @param array
*/
public static void MergeSort(int[] array){
int left = 0;
int right = array.length - 1;
MergeSortRecursive(array, left, right);
}
/**
* 归并排序的递归方法
* @param array
* @param left
* @param right
*/
public static void MergeSortRecursive(int[] array,int left,int right){
if (left >= right) {
return; //递归的停止判断,没有这个判断会报StackOverflowError
}
int mid = (left + right)/2;
MergeSortRecursive(array, left, mid);
MergeSortRecursive(array, mid+1, right);
Merge(array, left, mid, right);
}
/**
* 归并排序中合并方法
* @param array
* @param left
* @param mid
* @param right
*/
public static void Merge(int[] array,int left,int mid,int right){
int r_left = mid + 1; //需要合并数组中右边数组第一个数索引
int[] tempArray = new int[array.length];//一个临时数组,用于合并时暂时存储
int newIndex = left; //临时数组索引
int tempLeft = left; //合并完了以后,用于复制数组的索引
while(left <= mid && r_left <= right){ //将部分的数放入到临时数组中
if (array[left]
tempArray[newIndex++] = array[left++];
}else {
tempArray[newIndex++] = array[r_left++];
}
}
while (left <= mid) {
tempArray[newIndex++] = array[left++]; //将左边还剩余的数放入临时数组(若需要合并的左边还剩余数)
}
while(r_left <= right){
tempArray[newIndex++] = array[r_left++];//将右边还剩余的数放入临时数组(若需要和并的右边还剩余数)
}
while(tempLeft <= right){
array[tempLeft] = tempArray[tempLeft++]; //将临时数组复制到array
}
}
/**
* 基数排序
* @param array
*/
public static void RadixSort(int[] array){
int bits = FindMaxBit(array); //得到数组中最大的那个数的位数
for (int i = 0; i
OneBitSort(array, i+1); //一位基数的排序
}
}
/**
* 一位基数的排序
* @param array
* @param bit
*/
public static void OneBitSort(int[] array,int bit){
int[] tempArray = new int[array.length];
int index = 0;
int tempIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i
for (int j = 0; j
if (FindBitNum(array[j], bit) == i) {
tempArray[index++] = array[j];
}
}
}
while(tempIndex
array[tempIndex] = tempArray[tempIndex++]; //复制数组
}
}
/**
* 得到某个数某一位的数(例如:num=1234,n=2,FindBitNum(1234,2)=3)
* @param num
* @param n
* @return
*/
public static int FindBitNum(int num,int n){
int key1 = (int)Math.pow(10, n);
int key2 = (int)Math.pow(10, n-1);
num %= key1;
num /= key2;
return num;
}
/**
* 得到一个数组中最大数的位数
* @param array
* @return
*/
public static int FindMaxBit(int[] array){
if (array == null || array.length ==0) {
return 0;
}
int max = array[0];
for (int i = 1; i
if (array[i] > max) {
max = array[i];
}
}
int bit = 0;
while(max / 10 != 0 || max % 10 != 0){
max /= 10;
bit++;
}
return bit;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("冒泡排序:"+SortThreads.getBubbleSortTime());
System.out.println("直接选择排序:"+SortThreads.getDirSelectSortTime());
System.out.println("直接插入排序:"+SortThreads.getDirInsertSortTime());
System.out.println("二分插入排序:"+SortThreads.getBinaryInsertSortTime());
System.out.println("快速排序:"+SortThreads.getQuickSortTime());
System.out.println("希尔排序:"+SortThreads.getShellSortTime());
System.out.println("归并排序:"+SortThreads.getMergeSortTime());
System.out.println("基数排序:"+SortThreads.getRadixSortTime());
System.out.println("堆排序:"+SortThreads.getHeapSortTime());
}
}
对于这些排序算法,我对它们的排序速度比较感兴趣,所以自己也测试了一下,数组是通过随机数产生的,我测的时候每一个数是不大于4位数,即不大于10000。
ProduceRandomNum.java产生随机数的数组:
package sort;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* Package: sort
*
* File: SortRunnable.java
*
* Copyright @ 2015 Corpration Name
*
*/
public class ProduceRandomNum{
public synchronized static int[] RandomArray(int num,int n){
Random random = new Random();
int[] array = new int[num];
for (int i = 0; i
array[i] = random.nextInt((int)Math.pow(10, n));
}
return array;
}
}
SortThreads.java测试排序的时间的方法,封装都一个类中,这个类我一直想把它写成多线程的方式(即是将这些排序一起运行),但是后面没有找到一个好的方法,所以后面就用了这种最笨的方法,有好办法的大神一定要指出来。
package sort;
/**
* Package: sort
*
* File: SortThreads.java
*
* Copyright @ 2015 Corpration Name
*
*/
public class SortThreads {
private static final int arrayNum = 500000;
private static final int bit = 4;
public static long getBubbleSortTime(){
long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
JavaSorts.BubbleSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
return newTime - oldTime;
}
public static long getQuickSortTime(){
int[] array = ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit);
long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
JavaSorts.QuickSort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
return newTime - oldTime;
}
public static long getDirSelectSortTime(){
long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
JavaSorts.DirectSelectSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
return newTime - oldTime;
}
public static long getDirInsertSortTime(){
long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
JavaSorts.DirectInsertSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
return newTime - oldTime;
}
public static long getBinaryInsertSortTime(){
long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
JavaSorts.BinaryInsertSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
return newTime - oldTime;
}
public static long getShellSortTime(){
long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
JavaSorts.ShellSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
return newTime - oldTime;
}
public static long getMergeSortTime(){
long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
JavaSorts.MergeSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
return newTime - oldTime;
}
public static long getRadixSortTime(){
long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
JavaSorts.RadixSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
return newTime - oldTime;
}
public static long getHeapSortTime(){
long oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
JavaSorts.HeapSort(ProduceRandomNum.RandomArray(arrayNum, bit));
long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
return newTime - oldTime;
}
}
通过测试,我的测试数据(后面数据量大了,有的排序时间太长,我就用*代替了):

通过测试数据来看,不同排序适用于不同的场景,快速排序也不一定是最快的,在数据量比较小的时候,希尔排序反而更快,只是在不断增加数据量的时候,快速排序比较快也很明显。同时,排序也不能只看排序的速度,还需要看它的空间复杂度,即对内存空间利用的要求。例如,快排、归并、堆排序这三者,通过随机数产生数组,它们的时间复杂度可以说是基本一样的,但是当n比较大的时候,你会发现归并排序会比其他两个慢。
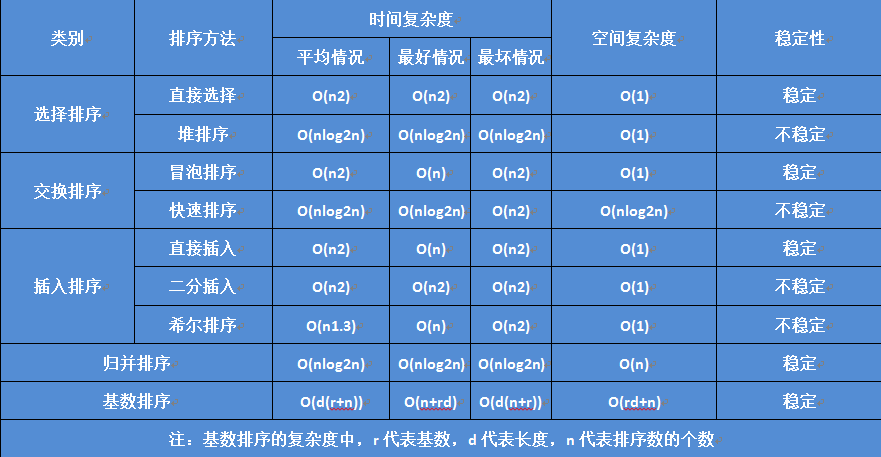
各种排序的时间复杂度、空间复杂度和稳定性,同样图形比较形象:
最后总结一下:
稳定性:
1、稳定:冒泡排序、插入排序、归并排序和基数排序
2、 不稳定:选择排序、快速排序、希尔排序、堆排序
平均时间复杂度
1、O(n^2):直接插入排序,简单选择排序,冒泡排序。
2、在数据量特别大的时候,冒泡排序基本是最慢的。
3、在数据规模较小时(9W内),直接插入排序,简单选择排序差不多。当数据较大时,冒泡排序算法的时间代价最高。性能为O(n^2)的算法基本
上是相邻元素进行比较,基本上都是稳定的。
1、O(nlogn):快速排序,归并排序,希尔排序,堆排序。
2、其中,快排是最好的, 其次是归并和希尔,但数据量特别大的时候,归并排序很容易出现内存溢出的错误,如普通机器n>1000万时。
空间复杂度
1、O(1):冒泡排序、直接插入排序、二分插入排序、希尔排序、直接选择排序、堆排序
2、 O(n):归并排序
3、 O(nlog2n):快速排序
4、O(rd+n):基数排序
排序算法的选择
1、数据规模较小
(1)待排序列基本序的情况下,可以选择直接插入排序;
(2)对稳定性不作要求宜用简单选择排序,对稳定性有要求宜用插入或冒泡
2、数据规模不是很大
(1)完全可以用内存空间,序列杂乱无序,对稳定性没有要求,快速排序,此时要付出log(N)的额外空间。
(2)序列本身可能有序,对稳定性有要求,空间允许下,宜用归并排序
3、数据规模很大
(1)对稳定性有求,则可考虑归并排序。
(2)对稳定性没要求,可以用快速排序。
4、数组初始基本有序的时候,宜用直接插入排序,否则,可以用希尔排序。





















 966
966











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








