文 | 微谈教育
文章原创,版权归作者所有,欢迎点赞评论。
东莞理工学院,有两个校区,一个位于东莞莞城,称为莞城校区,另外一个校区位于东莞市松山湖区,临近华为小镇。

东莞理工学院松山湖校区,基本上集中了整个学校的教学资源,是东莞市内一个不错的高水平大学。
2020年的高考志愿填报之后,东莞理工学院也公布出来2020年招生的基本情况。
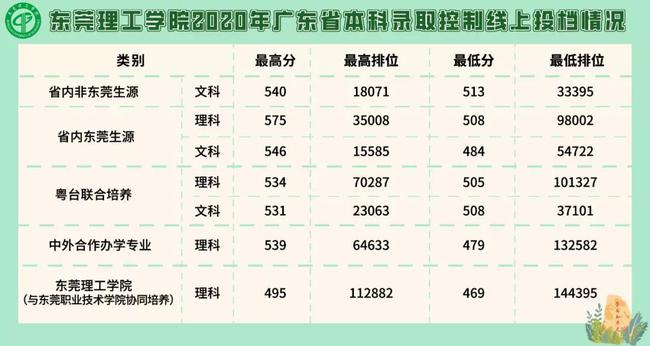
在学校所给出的投档情况上来看,省内非东莞理科生源,一次性满档,所录取的学生,都是高分优投线以上。

东莞生源比非东莞生源所录取的分数要低得多,这是学校给东莞生源的优惠。莞工为地方性大学,自然会给本地的高考生们以降分录取。
像深圳大学一样,对于深圳的生源,同样是给予降分录取。
这里的“降分录取”,是学校给予东莞生源一定的名额,报考的人数,数量少,因此比省内的非东莞生源分数线低。

东莞理工学院,从录取的分数线来看,是一所刚过一本线的理工科大学。在这所大学当中,也有几个王牌专业,整个学校最优秀的资源,集中在这几个专业当中。
一、软件工程专业
一所理工科的大学,必不可少,一定会有计算机的专业。莞工的软件工程专业,是学校录取分数最高的专业之一,一般会超过高分优投线三十分左右。
在软件工程专业的基础之上,再设立软件工程卓越班,从报考软件工程专业的学生当中,排名录取两个班的学生,进入软件工程卓越班。

在每一年的期末考试中,会对软卓的同学们进行考核,不合格的同学,将会被淘汰下来,回到软件工程班。
软件工程卓越班,是整个学校录取最高分的班级之一,是名副其实的一本专业。
二、计算机类专业
计算机类专业,在2018年之前,命名为计算机科学与技术专业,到2019年,学校对专业进行改革,把名字改为“计算机类专业”。

软件工程专业,是从计算机类专业分支出去,只不过软件工程专业学生所学的专业知识,分得更细。
大体上,两个专业的专业方向,还是会有异曲同工之处,所涉及到的专业知识,大体上是相同的。
三、机械专业
机械专业,同样也是东莞理工学院的王牌专业之一。在2020年,机械专业被设立为东莞理工学院的硕士专业学位授权点。
其中机械专业的导师,马宏伟教授,是东莞理工学院的校长,曾经参与建设港珠澳大桥的设计工作。

这三个专业,是这所大学比较出名的专业。当然,过了高考这一关,还有大学。虽说高考是千军万马过独木桥,大学四年又何尝不是。
只不过,大学四年比较自由,学校、老师、家长限制得比较少,就靠学生们的自律。未来,还是要把握在自己的手上的。
作者:微谈教育,欢迎关注。文章图片来源于网络,如果侵权,请联系删除。







 本文介绍了东莞理工学院的莞城和松山湖校区,重点解析了该校的三个王牌专业:软件工程、计算机类(包括计算机科学与技术)和机械专业。软件工程卓越班对学生要求严格,不合格者将淘汰回普通班级。机械专业因其优秀师资,如校长马宏伟教授,以及硕士专业学位授权点的设立,显示出其学术实力。文章指出,虽然高考竞争激烈,但大学期间的自我管理也至关重要,未来掌握在自己手中。
本文介绍了东莞理工学院的莞城和松山湖校区,重点解析了该校的三个王牌专业:软件工程、计算机类(包括计算机科学与技术)和机械专业。软件工程卓越班对学生要求严格,不合格者将淘汰回普通班级。机械专业因其优秀师资,如校长马宏伟教授,以及硕士专业学位授权点的设立,显示出其学术实力。文章指出,虽然高考竞争激烈,但大学期间的自我管理也至关重要,未来掌握在自己手中。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








