本文将围绕冒泡排序、桶排序、计数排序、堆排序、插入排序、并归排序、快速排序和选择排序,按照描述、时间复杂度(最坏情况)、动态图展示和代码实现来讲解。本文默认排序为从小到大。
本文相关代码已上传至github,欢迎关注https://github.com/zhuzhenke/common-algorithms
公用方法
SortUtils
public class SortUtils {
public static void check(int[] sortingData) {
if (sortingData == null || sortingData.length == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("sortingData can not be empty!");
}
}
public static void swap(int[] swapArray, int i, int j) {
check(swapArray);
if (i < 0 || i > swapArray.length - 1) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("illegal index i:" + i);
}
if (j < 0 || j > swapArray.length - 1) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("illegal index j:" + j);
}
int temp = swapArray[i];
swapArray[i] = swapArray[j];
swapArray[j] = temp;
}
public static int getMaxValue(int[] sortingData) {
check(sortingData);
int max = sortingData[0];
for (int value : sortingData) {
if (value < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("value could not be negative:" + value);
}
if (value > max) {
max = value;
}
}
return max;
}
}
冒泡排序
描述
比较前后两个数的大小,如果前者大于后者,则交换两个数的位置
最大的数字在进行一轮比较和交换后,会出现在数组的最后一个位置
每一轮之后,可减少最大数字的比较。重复上述操作直到没有需要比较的元素为止
时间复杂度
O(n^2)
动态图展示

代码实现
github代码
public int[] sort(int[] sortingData) {
SortUtils.check(sortingData);
for (int j = sortingData.length - 1; j > 0; j--) {
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
if (sortingData[i] > sortingData[i + 1]) {
SortUtils.swap(sortingData, i, i + 1);
}
}
}
return sortingData;
}
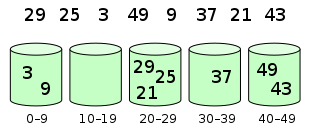
桶排序
描述
挑选数组中最大的数字,设置默认分配的桶数,得到每个桶容纳的数字范围。如最大是10,桶是4个,则每个桶最大容纳3个数字。第0个桶放0、1、2、3,第1个桶方4、5、6,第2桶方7,8,9,以此类推
对每个桶内进行冒泡排序或选择排序
遍历所有桶,依次取出每个桶中的元素,得到的就是一个排好序的数组
时间复杂度
O(n^2)
动态图展示

代码实现
github代码
@Override
public int[] sort(int[] sortingData) {
SortUtils.check(sortingData);
int bucketSize = (int) Math.round(Math.sqrt(sortingData.length)) + 1;
int[][] buckets = new int[bucketSize][];
int max = SortUtils.getMaxValue(sortingData);
double avgContain = Math.ceil((double) max / (double) bucketSize);
for (int value : sortingData) {
int bucketIndex = (int) Math.ceil(value / avgContain) - 1;
if (bucketIndex < 0) {
bucketIndex = 0;
}
int[] bucketIndexs = buckets[bucketIndex];
if (bucketIndexs == null || bucketIndexs.length == 0) {
bucketIndexs = new int[1];
bucketIndexs[0] = value;
buckets[bucketIndex] = bucketIndexs;
} else {
int[] newBucketIndexs = new int[bucketIndexs.length + 1];
System.arraycopy(bucketIndexs, 0, newBucketIndexs, 0, bucketIndexs.length);
newBucketIndexs[bucketIndexs.length] = value;
buckets[bucketIndex] = newBucketIndexs;
}
}
Sort sort = new InsertionSort();
for (int a = 0; a < buckets.length; a++) {
int[] bucket = buckets[a];
if (bucket == null || bucket.length == 0) {
continue;
}
bucket = sort.sort(bucket);
buckets[a] = bucket;
}
int[] result = new int[sortingData.length];
int resultIndex = 0;
for (int[] bucket : buckets) {
if (bucket == null || bucket.length == 0) {
continue;
}
for (int bucketValue : bucket) {
result[resultIndex++] = bucketValue;
}
}
return result;
}
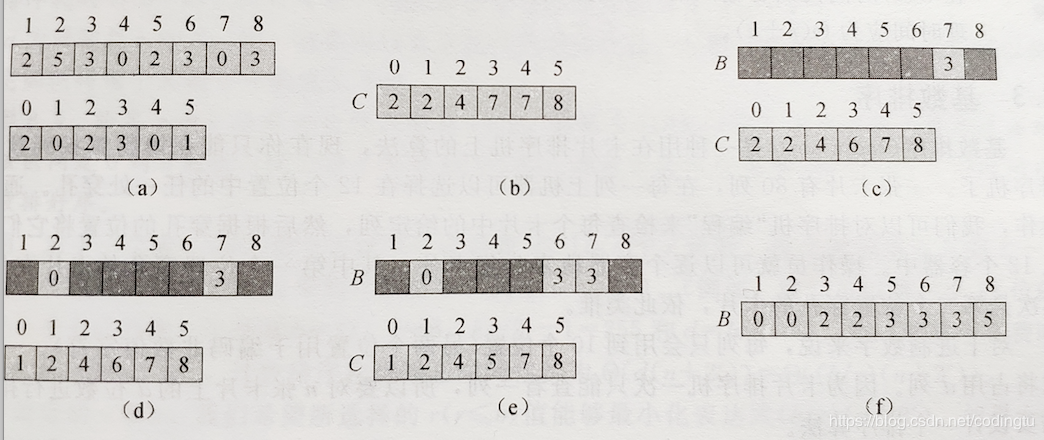
计数排序
描述
获取数组中最大的值(这个值需要在可控范围,最好是在10000以内)
创建一个长度为最大值加1的计数数组,
遍历待排序数组,将元素的值落入到计数数组的下标元素,将下标元素的值加1
遍历下标数组,将后一个元素的值标为当前元素值加前一个元素的值(用于排序后的数组下标)。
创建一个长度跟待排序数组大小相同的结果数组
遍历待排序数组,取出待排序元素,对应计数数组的下标元素,并放在计数元素值的前一个位置,并将计数元素值减1
时间复杂度
O(n)
动态图展示
代码实现
github代码
private int[] sort2(int[] sortingData) {
int maxValue = SortUtils.getMaxValue(sortingData);
//get max,check all numbers must be bigger or equal 0
int[] count = new int[maxValue + 1];
//count every number
for (int value : sortingData) {
count[value] = count[value] + 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < count.length; i++) {
count[i] = count[i] + count[i - 1];
}
//output
int[] result = new int[sortingData.length];
for (int value : sortingData) {
result[count[value] - 1] = value;
count[value] = count[value] - 1;
}
return result;
}
堆排序
描述
为了方便理解,将数组元素映射成二叉树,array[0]对一个根节点,array[1]为根的左节点,array[2]为根的右节点,一次类推
从最后一个元素开始遍历到第一个,让其与父节点比较大小,如果子节点大,则交换位置。(另外一种方式是从中间元素开始比较,得到当前元素和子元素的最大值,这样则遍历深度为logn,这种方式属于推荐方式)
遍历一轮结束后,则最大值已经位于index为0的位置,这时交换index为0和最后一位的位置,则最大值确定。下一轮比较从最大值的前一个index下标元素开始遍历,依次进行遍历
最后全部遍历完成,则得到一个拍好序的数组
时间复杂度
O(nlogn)
动态图展示

代码实现
github代码
public int[] sort(int[] sortingData) {
int highIndex = sortingData.length - 1;
while (highIndex > 0) {
for (int i = 1; i <= highIndex; i++) {
sortBiggestToIndex0(sortingData, i);
}
SortUtils.swap(sortingData, 0, highIndex);
highIndex--;
}
return sortingData;
}
public static void sortBiggestToIndex0(int[] sortingData, int sortIndex) {
while (sortIndex > 0 && sortingData[sortIndex] > sortingData[(sortIndex - 1) / 2]) {
SortUtils.swap(sortingData, sortIndex, (sortIndex - 1) / 2);
sortIndex = (sortIndex - 1) / 2;
}
}
插入排序
描述
插入排序类似于扑克摸牌排序
第一次只有一种牌,牌是有序的。当摸到第二张牌时,则插入到已有的排好序的牌中,此时前两张牌有序
依次进行同样的操作,摸到第n张牌时,前n-1张牌已经有序,进行插入到合适位置即可
时间复杂度
O(n^2)
动态图展示
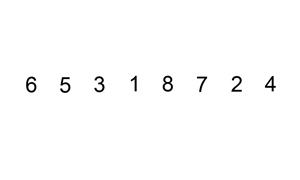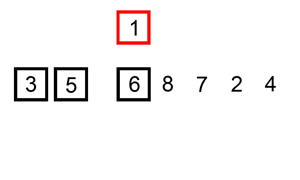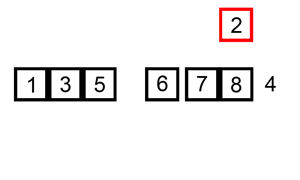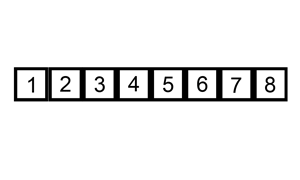
代码实现
github代码
public int[] sort(int[] sortingData) {
SortUtils.check(sortingData);
for (int i = 1; i < sortingData.length; i++) {
int currentValue = sortingData[i];
int j = i;
while (j - 1 >= 0 && currentValue < sortingData[j - 1]) {
sortingData[j] = sortingData[j - 1];
j--;
}
sortingData[j] = currentValue;
}
return sortingData;
}
并归排序
描述
并归排序利用递归思想,递归思想的核心在于找到一个模式,分解为子模式,子模式又可以分解子模式,则对于最小子模式,可以直接求解。
首先会将待排序数组分为两份,两份分别排好序后进行合并
两份中的每一份,又可以查分为更小的一份,直到每份只有一个元素,则此份为已排好序的子数组。对两个子数组进行合并的排序
时间复杂度
O(nlogn)
动态图展示
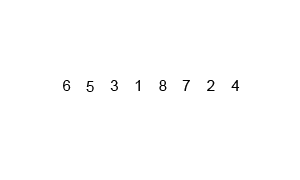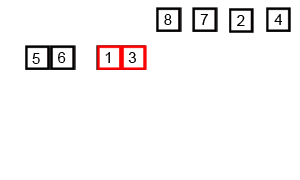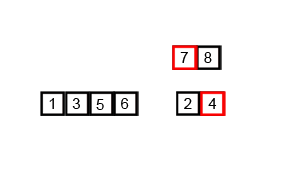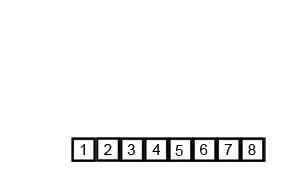
代码实现
github代码
@Override
public int[] sort(int[] sortingData) {
SortUtils.check(sortingData);
splitDate(sortingData, 0, sortingData.length - 1);
return sortingData;
}
private void splitDate(int[] sortingData, int start, int end) {
if (end - start < 1) {
return;
}
int middle = (start + end) / 2;
splitDate(sortingData, start, middle);
splitDate(sortingData, middle + 1, end);
mergeData(sortingData, start, middle, end);
}
private void mergeData(int[] sortingData, int start, int middle, int end) {
int[] left = Arrays.copyOfRange(sortingData, start, middle + 1);
int[] right = Arrays.copyOfRange(sortingData, middle + 1, end + 1);
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (int k = start; k <= end; k++) {
if (i < left.length && j < right.length) {
if (left[i] <= right[j]) {
sortingData[k] = left[i];
i++;
} else {
sortingData[k] = right[j];
j++;
}
} else {
if (i >= left.length) {
sortingData[k] = right[j];
j++;
} else if (j >= right.length) {
sortingData[k] = left[i];
i++;
}
}
}
}
快速排序
描述
选择待排序数组的中元元素,一般选择第一个或最后一个元素,将数组拆分为两部分,左边部分元素小于等于中元元素,右边部分元素大于中元元素
继续将子数组按中元元素进行拆分,直到全部排好序位置
时间复杂度
O(n^2)
动态图展示
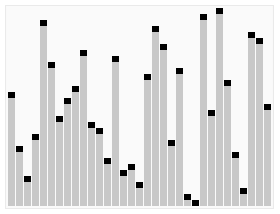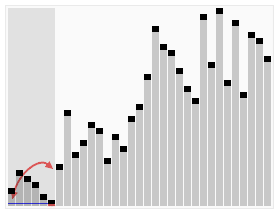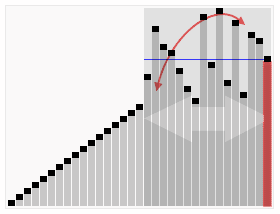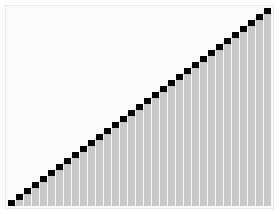
代码实现
github代码
@Override
public int[] sort(int[] sortingData) {
SortUtils.check(sortingData);
quickSort(sortingData, 0, sortingData.length - 1);
return sortingData;
}
private void quickSort(int[] sortingData, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) {
return;
}
int middle = getQuickSortMiddle(sortingData, start, end);
quickSort(sortingData, start, middle - 1);
quickSort(sortingData, middle + 1, end);
}
/**
* one side
*/
public int getQuickSortMiddle(int[] sortingData, int start, int end) {
int i = start;
int pivot = end;
for (int j = start; j < end; j++) {
if (sortingData[j] < sortingData[pivot]) {
SortUtils.swap(sortingData, i, j);
i++;
}
}
SortUtils.swap(sortingData, i, pivot);
return i;
}
选择排序
描述
从第一个元素开始遍历,记录最小值和对应元素下标,遍历一轮则可以得到最小值,将这个值与下标为0的元素交换,则完成第一轮最小值输出
从第2个进行同样的遍历操作,遍历取剩余元素的最小值,将这个值与下标为1的元素交换
从第index个开始进行遍历操作,遍历取剩余元素的最小值,将这个值与下标为index的元素交换
遍历直到最后一个元素位置,得到一个排好序的数组
时间复杂度
O(n^2)
动态图展示
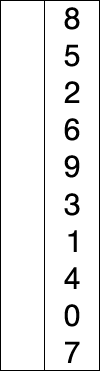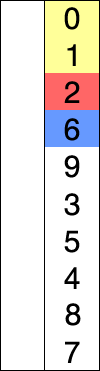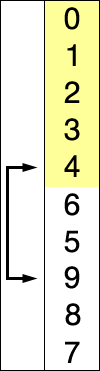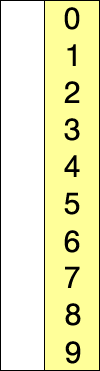
代码实现
github代码
public int[] sort(int[] sortingData) {
SortUtils.check(sortingData);
for (int index = 0; index < sortingData.length; index++) {
int smallestIndex = index;
int smallestValue = sortingData[index];
for (int j = index; j < sortingData.length; j++) {
if (sortingData[j] < smallestValue) {
smallestValue = sortingData[j];
smallestIndex = j;
}
}
sortingData[smallestIndex] = sortingData[index];
sortingData[index] = smallestValue;
}
return sortingData;
}





















 8222
8222

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








