BFS与DFS常考算法整理
- Preface
BFS(Breath-First Search,广度优先搜索)与DFS(Depth-First Search,深度优先搜索)是两种针对树与图数据结构的遍历或搜索算法,在树与图相关算法的考察中是非常常见的两种解题思路。
Definition of DFS and BFS
DFS的wikipedia定义:
Depth-first search (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. The algorithm starts at the root node (selecting some arbitrary node as the root node in the case of a graph) and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
BFS的wikipedia定义:
Breadth-first search (BFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. It starts at the tree root (or some arbitrary node of a graph, sometimes referred to as a ‘search key’[1]), and explores all of the neighbor nodes at the present depth prior to moving on to the nodes at the next depth level.
It uses the opposite strategy as depth-first search, which instead explores the highest-depth nodes first before being forced to backtrack and expand shallower nodes.
So obviously, as their name suggest, DFS focuses on ‘depth’ when searching or traversing while BFS focuses on ‘breath’.
By the way, because of DFS’s feature, it’s easy to relate it with ‘Backtracking’ algorithm as the wiki definition mentions. The relationship between DFS and backtracking is well explained by Reed Copsey on StackOverflow:
Backtracking is a more general purpose algorithm.
Depth-First search is a specific form of backtracking related to searching tree structures. From Wikipedia:
One starts at the root (selecting some node as the root in the graph case) and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
It uses backtracking as part of its means of working with a tree, but is limited to a tree structure.
Backtracking, though, can be used on any type of structure where portions of the domain can be eliminated - whether or not it is a logical tree. The Wiki example uses a chessboard and a specific problem - you can look at a specific move, and eliminate it, then backtrack to the next possible move, eliminate it, etc.
How to Implement DFS and BFS
DFS
In tree structure, DFS means we always start from a root node and try to reach the leaf node as direct as possible before we have to backtrack.

Order in which the nodes are visited
In graph, DFS means we start from a random assigned node in the graph, and explores as far as possible along the branch before we have to backtrack.
So the key points for DFS are:
- How to explore as far as possible?
- How to backtrack?
How to explore as far as possible
Normally, for tree node, it would have left child or right child, so we would continuously go on exploring current node’s child node until we encounter a null node, then we go back to last node. Repeat above procedures until all nodes have been visited.
for graph node, we do the similar exploration: explore as further as possible according to the representation of graph (adjacency list, adjacency matrix or incidence matrix) until we find no more node that hasn’t been visited and connected with current node, then we go back to last node. Repeat above procedures until all nodes have been visited.
How to backtrack/go back?
‘Go back’ generally can be realized using data structure ——stack—— or by recursion. And if we use stack, it means we would need to push each node we visited in the process of exploring each branch, and pop when we can’t explore further starting from current node.
BFS
In tree structure, BFS means we always start from a root node and try to all the other nodes in the same breath before we further try exploring nodes at next depth level. (The same explanation for graph)
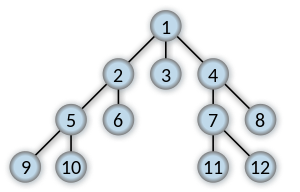
Order in which the nodes are visited
So the key points for BFS are:
- How to explore all nodes of same depth level?
How to explore all nodes of same depth level?
We can use a queue to do this: Starting from root node of a tree (Or a random node in a graph), we add visit all nodes connected with the starting node and add them to the queue. Then, we poll node from queue one by one and repeat above procedures until all nodes have been visited.
Typical Leetcode Prbolems
DFS
Path Sum II
Given a binary tree and a sum, find all root-to-leaf paths where each path’s sum equals the given sum.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given the below binary tree and sum = 22,
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ / \
7 2 5 1Return:
[
[5,4,11,2],
[5,8,4,5]
]- My Answer
package medium2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author Tom Qian
* @email tomqianmaple@outlook.com
* @github https://github.com/bluemapleman
* @date 2018年6月7日
*/
public class PathSumII
{
// DFS: make use of recursion to backtrack
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
List<List<Integer>> ans=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if(root==null)
return ans;
int goal=sum-root.val;
if(goal==0) {
if(root.left==null && root.right==null) {
List<Integer> tempList=new ArrayList<>();
tempList.add(root.val);
ans.add(tempList);
return ans;
}
}
List<List<Integer>> temp;
if((temp=pathSum(root.left, goal)).size()!=0) {
for(List<Integer> list:temp) {
list.add(0, root.val);
ans.add(list);
}
}
if((temp=pathSum(root.right, goal)).size()!=0) {
for(List<Integer> list:temp) {
list.add(0,root.val);
ans.add(list);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
Given a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example:
Given the sorted linked list: [-10,-3,0,5,9],
One possible answer is: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the following height balanced BST:
0
/ \
-3 9
/ /
-10 5- My Answer
package medium2;
/**
* @author Tom Qian
* @email tomqianmaple@outlook.com
* @github https://github.com/bluemapleman
* @date 2018年6月11日
*/
public class ConvertSortedListtoBinarySearchTree
{
// DFS: make use of recursion to backtrack
// find the middle node of sorted linked list, and take it as the root node of the BST.
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
if(head==null)
return null;
ListNode slow=head,fast=head,followSlow=head;
boolean moveFlag=false;
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null) {
if(moveFlag)
followSlow=followSlow.next;
moveFlag=true;
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
}
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(slow.val);
if(moveFlag) {
followSlow.next=null;
root.left=sortedListToBST(head);
root.right=sortedListToBST(slow.next);
}
return root;
}
}Course Schedule
There are a total of n courses you have to take, labeled from 0 to n-1.
Some courses may have prerequisites, for example to take course 0 you have to first take course 1, which is expressed as a pair: [0,1]
Given the total number of courses and a list of prerequisite pairs, is it possible for you to finish all courses?
Example 1:
Input: 2, [[1,0]]
Output: true
Explanation: There are a total of 2 courses to take.
To take course 1 you should have finished course 0. So it is possible.Example 2:
Input: 2, [[1,0],[0,1]]
Output: false
Explanation: There are a total of 2 courses to take.
To take course 1 you should have finished course 0, and to take course 0 you should
also have finished course 1. So it is impossible.Note:
1.The input prerequisites is a graph represented by a list of edges, not adjacency matrices. Read more about how a graph is represented.
2.You may assume that there are no duplicate edges in the input prerequisites.
- My Answer
// DFS
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map=new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<numCourses;i++)
map.put(i, new ArrayList<>());
for(int i=0;i<prerequisites.length;i++) {
map.get(prerequisites[i][0]).add(prerequisites[i][1]);
}
// start DFS: detect if there is any circle in course graph, i.e. whether DFS starting from certain start point i would lead to the start point again.
for(int i=0;i<numCourses;i++) {
// Use a set to avoid infinite loop: when met same node twice, ignore it.
Set<Integer> set=new HashSet<>();
// Use a stack to backtrack
ArrayDeque<Integer> stack=new ArrayDeque<>();
List<Integer> preCourseList=map.get(i);
for(Integer preCourse:preCourseList)
stack.push(preCourse);
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
int preCourse=stack.pop();
if(set.contains(preCourse))
continue;
else
set.add(preCourse);
if(preCourse==i)
return false;
else {
preCourseList=map.get(preCourse);
for(Integer tempPreCourse:preCourseList) {
stack.push(tempPreCourse);
}
}
}
}
return true;
}BFS
Course Schedule
- My Answer
// BFS
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map=new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<numCourses;i++)
map.put(i, new ArrayList<>());
for(int i=0;i<prerequisites.length;i++) {
map.get(prerequisites[i][0]).add(prerequisites[i][1]);
}
// start DFS: detect if there is any circle in course graph, i.e. whether BFS starting from certain start point i would lead to the start point again.
for(int i=0;i<numCourses;i++) {
// Use a set to avoid infinite loop: when met same node twice, ignore it.
Set<Integer> set=new HashSet<>();
// Use a queue to remember nodes of same depth level
ArrayDeque<Integer> queue=new ArrayDeque<>();
List<Integer> preCourseList=map.get(i);
for(Integer preCourse:preCourseList)
queue.add(preCourse);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int preCourse=queue.poll();
if(set.contains(preCourse))
continue;
else
set.add(preCourse);
if(preCourse==i)
return false;
else {
preCourseList=map.get(preCourse);
for(Integer tempPreCourse:preCourseList) {
queue.add(tempPreCourse);
}
}
}
}
return true;
}Binary Tree Right Side View
Given a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
Output: [1, 3, 4]
Explanation:
1 <---
/ \
2 3 <---
\ \
5 4 <---- My Answer
package medium2;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author Tom Qian
* @email tomqianmaple@outlook.com
* @github https://github.com/bluemapleman
* @date 2018年6月12日
*/
public class BinaryTreeRightSideView
{
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans=new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null)
return ans;
ans.add(root.val);
ArrayDeque<TreeNode> queue1=new ArrayDeque<>(),queue2=new ArrayDeque<>();;
queue1.add(root);
while(!queue1.isEmpty() || !queue2.isEmpty()){
TreeNode rightestNode=null;
if(!queue1.isEmpty()) {
while(!queue1.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode fatherNode=queue1.poll();
if(fatherNode.right!=null) {
queue2.add(fatherNode.right);
if(rightestNode==null)
rightestNode=fatherNode.right;
}
if(fatherNode.left!=null) {
queue2.add(fatherNode.left);
if(rightestNode==null)
rightestNode=fatherNode.left;
}
}
}else{
while(!queue2.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode fatherNode=queue2.poll();
if(fatherNode.right!=null) {
queue1.add(fatherNode.right);
if(rightestNode==null)
rightestNode=fatherNode.right;
}
if(fatherNode.left!=null) {
queue1.add(fatherNode.left);
if(rightestNode==null)
rightestNode=fatherNode.left;
}
}
}
if(rightestNode!=null)
ans.add(rightestNode.val);
}
return ans;
}
}.





















 290
290

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








