Intent
- Define a one-to-many dependency between objects so that when one object changes state, all its dependents are notified and updated automatically.
- Encapsulate the core (or common or engine) components in a Subject abstraction, and the variable (or optional or user interface) components in an Observer hierarchy.
- The “View” part of Model-View-Controller.
Problem
A large monolithic design does not scale well as new graphing or monitoring requirements are levied.
Discussion
Define an object that is the “keeper” of the data model and/or business logic (the Subject). Delegate all “view” functionality to decoupled and distinct Observer objects. Observers register themselves with the Subject as they are created. Whenever the Subject changes, it broadcasts to all registered Observers that it has changed, and each Observer queries the Subject for that subset of the Subject’s state that it is responsible for monitoring.
This allows the number and “type” of “view” objects to be configured dynamically, instead of being statically specified at compile-time.
The protocol described above specifies a “pull” interaction model. Instead of the Subject “pushing” what has changed to all Observers, each Observer is responsible for “pulling” its particular “window of interest” from the Subject. The “push” model compromises reuse, while the “pull” model is less efficient.
Issues that are discussed, but left to the discretion of the designer, include: implementing event compression (only sending a single change broadcast after a series of consecutive changes has occurred), having a single Observer monitoring multiple Subjects, and ensuring that a Subject notify its Observers when it is about to go away.
The Observer pattern captures the lion’s share of the Model-View-Controller architecture that has been a part of the Smalltalk community for years.
Structure
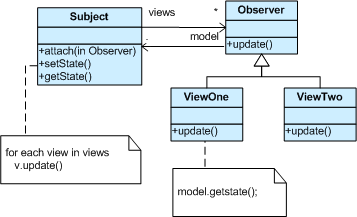
Subject represents the core (or independent or common or engine) abstraction. Observer represents the variable (or dependent or optional or user interface) abstraction. The Subject prompts the Observer objects to do their thing. Each Observer can call back to the Subject as needed.
Example
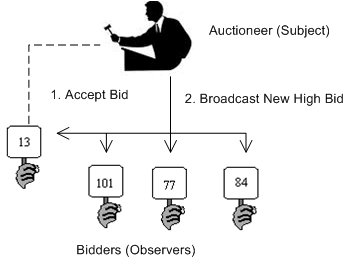
The Observer defines a one-to-many relationship so that when one object changes state, the others are notified and updated automatically. Some auctions demonstrate this pattern. Each bidder possesses a numbered paddle that is used to indicate a bid. The auctioneer starts the bidding, and “observes” when a paddle is raised to accept the bid. The acceptance of the bid changes the bid price which is broadcast to all of the bidders in the form of a new bid.
Check list
- Differentiate between the core (or independent) functionality and the optional (or dependent) functionality.
- Model the independent functionality with a “subject” abstraction.
- Model the dependent functionality with an “observer” hierarchy.
- The Subject is coupled only to the Observer base class.
- The client configures the number and type of Observers.
- Observers register themselves with the Subject.
- The Subject broadcasts events to all registered Observers.
- The Subject may “push” information at the Observers, or, the Observers may “pull” the information they need from the Subject.
Rules of thumb
- Chain of Responsibility, Command, Mediator, and Observer, address how you can decouple senders and receivers, but with different trade-offs. Chain of Responsibility passes a sender request along a chain of potential receivers. Command normally specifies a sender-receiver connection with a subclass. Mediator has senders and receivers reference each other indirectly. Observer defines a very decoupled interface that allows for multiple receivers to be configured at run-time.
- Mediator and Observer are competing patterns. The difference between them is that Observer distributes communication by introducing “observer” and “subject” objects, whereas a Mediator object encapsulates the communication between other objects. We’ve found it easier to make reusable Observers and Subjects than to make reusable Mediators.
- On the other hand, Mediator can leverage Observer for dynamically registering colleagues and communicating with them.
Observer in Delphi
A common side-effect of partitioning a system into a collection of co-operating classes, is the need to maintain consistency between related objects. You don’t want to achieve consistency by making the classes tightly coupled, because that reduces their reusability
Delphi’s events (which are actually method pointers) let you deal with this problem in a structured manner. Events let you decouple classes that need to co-operate. For example: The TButton.OnClick event is dispatched ‘to whom it may concern’, the button does not store a (typed) reference to the class handling the event. In fact the event might not even be handled at all. In terms of the observer pattern the object dispatching an event is called subject, the object handling the event is called observer.
So Delphi’s events take care of decoupling classes, but what if you want to handle an event in more than one place?
An observer pattern describes how to establish one-to-many notifications. A subject may have any number of observers. All observers are notified whenever the subject undergoes a change in state (such as a button being clicked). In response each observer may query the subject to synchronise its state with the subject’s state.
This kind of interaction is also known as publish-subscribe, the subject is the publisher of notifications. It sends out these notifications without having to know who it’s observers are. Any number of observers can subscribe to receive notifications.
Implementation
The implementation of the observer pattern is taking advantage of Delphi’s events to deal with decoupling classes. The one-to-many aspect is implemented by registering and un-registering dedicated observers. The one-to-many mechanism is actually implemented by iterating over the list of observers.
Let’s assume you’ve got a class TSubject which defines useful behaviour. The following code demonstrates the implementation of the observer pattern.
1: type
2: TSubject = class (TObject)
3: private
4: FObservers: TList;
5: public
6: procedure RegisterObserver(Observer: TSubjectObserver);
7: procedure UnregisterObserver(Observer: TSubjectObserver);
8: end;
9:
10: TSubjectObserver = class (TComponent)
11: private
12: FEnabled: Boolean;
13: published
14: property Enabled: Boolean read FEnabled write FEnabled; default True;
15: end;
In this interface: A registration mechanism has been added to the class TSubject, consisting of: FObservers: TList; which stores all registered observers. RegisterObserver, which registers an observer by adding it to FObservers. UnregisterObserver, which unregisters an observer by removing it from FObservers.
A new class Observer pattern has been created: TSubjectObserver. This class is a TComponent descendant. It has an Enabled property which allows you to switch the observer on and off rather than having to register/unregister it each time. How this property actually cooperates in the one-to-many event dispatch mechanism will be explained shortly.
The actual implementation of this pattern is:
1: procedure TSubject.RegisterObserver(Observer: TSubjectObserver);
2: begin
3: if FObservers.IndexOf(Observer) = -1 then
4: FObservers.Add(Observer);
5: end;
6:
7: procedure TSubject.UnregisterObserver(Observer: TSubjectObserver);
8: begin
9: FObservers.Remove(Observer);
10: end;
11:
As you see in the implementation: this deals only with the registration part of the observer pattern. Now you may ask: ‘where is my one-to-many notification’? Well, it’s not possible to implement this as part of the pattern. The actual one-to-many notifications you have to implement yourself. Assume that TSubject has a method Change which notifies all it’s registered observers of a change. The observers would have an OnChange event property which is actually dispatched. You could implement this like:
1: type
2: TSubject = class (TObject)
3: private
4: FObservers: TList;
5: protected
6: procedure Change; //Call this method to dispatch change
7: public
8: procedure RegisterObserver(Observer: TSubjectObserver);
9: procedure UnregisterObserver(Observer: TSubjectObserver);
10: end;
11:
12: TSubjectObserver = class (TComponent)
13: private
14: FEnabled: Boolean;
15: FOnChange: TNotifyEvent;
16: protected
17: procedure Change;
18: published
19: property Enabled: Boolean read FEnabled write FEnabled;
20: property OnChange: TNotifyEvent read FOnChange write FOnChange;
21: end;
22:
23: implementation
24:
25: procedure TSubject.Change;
26: var
27: Obs: TSubjectObserver;
28: I: Integer;
29: begin
30: for I := 0 to FObservers.Count - 1 do
31: begin
32: Obs := FObservers[I];
33: if Obs.Enabled then Obs.Change;
34: end;
35: end;
36:
37: procedure TSubject.RegisterObserver(Observer: TSubjectObserver);
38: begin
39: if FObservers.IndexOf(Observer) = -1 then
40: FObservers.Add(Observer);
41: end;
42:
43: procedure TSubject.UnregisterObserver(Observer: TSubjectObserver);
44: begin
45: FObservers.Remove(Observer);
46: end;
47:
48: procedure TSubjectObserver.Change;
49: begin
50: if Assigned(FOnChange) then FOnChange(Self);
51: end;
In this example notice: the method TSubject.Change which iterates the registered observers, calling each observer’s Change method. This is the actual one-to-many notification. the observer’s Enabled property which is checked to determine whether the observer should be notified; the event OnChange in the class TSubjectObserver which can be wired using the object inspector.




















 456
456











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








