package com.atguigu.java; /* * 一、Java面向对象学习的三条主线:(第4-6章) * 1.Java类及类的成员:属性、方法、构造器;代码块、内部类 * * 2.面向对象的三大特征:封装性、继承性、多态性、(抽象性) * * 3.其它关键字:this、super、static、final、abstract、interface、package、import等 * * “大处着眼,小处着手” * * * 二、“人把大象装进冰箱” * * 1.面向过程:强调的是功能行为,以函数为最小单位,考虑怎么做。 * * ① 把冰箱门打开 * ② 抬起大象,塞进冰箱 * ② 把冰箱门关闭 * * 2.面向对象:强调具备了功能的对象,以类/对象为最小单位,考虑谁来做。 * * 人{ * 打开(冰箱){ * 冰箱.开开(); * } * * 抬起(大象){ * 大象.进入(冰箱); * } * * 关闭(冰箱){ * 冰箱.闭合(); * } * * } * * * 冰箱{ * 开开(){} * 闭合(){} * } * * 大象{ * 进入(冰箱){ * } * } * * 三、面向对象的两个要素: * 类:对一类事物的描述,是抽象的、概念上的定义 * 对象:是实际存在的该类事物的每个个体,因而也称为实例(instance) * >面向对象程序设计的重点是类的设计 * >设计类,就是设计类的成员。 * */ public class OOPTest { }
package com.atguigu.java; /* * 一、设计类,其实就是设计类的成员 * * 属性 = 成员变量 = field = 域、字段 * 方法 = 成员方法 = 函数 = method * * 创建类的对象 = 类的实例化 = 实例化类 * * 二、类和对象的使用(面向对象思想落地的实现): * 1.创建类,设计类的成员 * 2.创建类的对象 * 3.通过“对象.属性”或“对象.方法”调用对象的结构 * * 三、如果创建了一个类的多个对象,则每个对象都独立的拥有一套类的属性。(非static的) * 意味着:如果我们修改一个对象的属性a,则不影响另外一个对象属性a的值。 * * 四、对象的内存解析 */ //测试类 public class PersonTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //2. 创建Person类的对象 Person p1 = new Person(); //Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); //调用对象的结构:属性、方法 //调用属性:“对象.属性” p1.name = "Tom"; p1.isMale = true; System.out.println(p1.name); //调用方法:“对象.方法” p1.eat(); p1.sleep(); p1.talk("Chinese"); //******************************* Person p2 = new Person(); System.out.println(p2.name);//null System.out.println(p2.isMale); //******************************* //将p1变量保存的对象地址值赋给p3,导致p1和p3指向了堆空间中的同一个对象实体。 Person p3 = p1; System.out.println(p3.name);//Tom p3.age = 10; System.out.println(p1.age);//10 } } //1.创建类,设计类的成员 class Person{ //属性 String name; int age = 1; boolean isMale; //方法 public void eat(){ System.out.println("人可以吃饭"); } public void sleep(){ System.out.println("人可以睡觉"); } public void talk(String language){ System.out.println("人可以说话,使用的是:" + language); } }


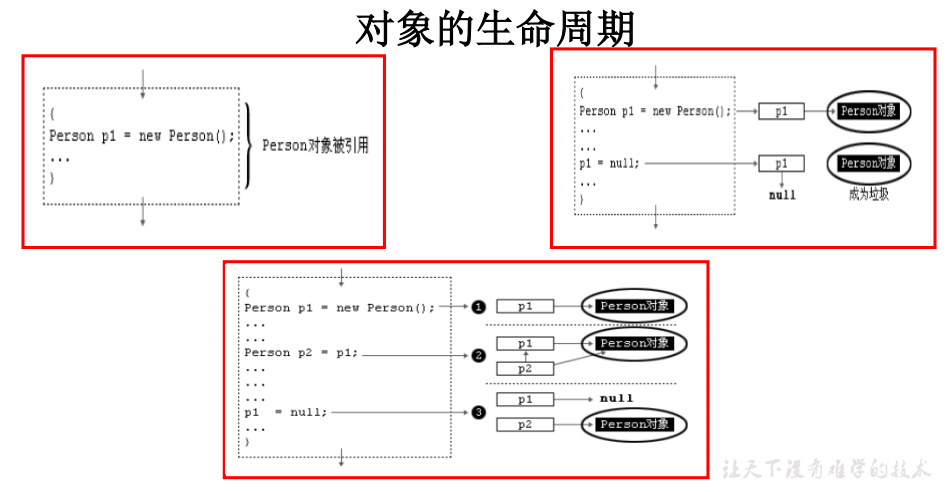
package com.atguigu.java; /* * 类中属性的使用 * * 属性(成员变量) vs 局部变量 * 1.相同点: * 1.1 定义变量的格式:数据类型 变量名 = 变量值 * 1.2 先声明,后使用 * 1.3 变量都有其对应的作用域 * * * 2.不同点: * 2.1 在类中声明的位置的不同 * 属性:直接定义在类的一对{}内 * 局部变量:声明在方法内、方法形参、代码块内、构造器形参、构造器内部的变量 * * 2.2 关于权限修饰符的不同 * 属性:可以在声明属性时,指明其权限,使用权限修饰符。 * 常用的权限修饰符:private、public、缺省、protected --->封装性 * 目前,大家声明属性时,都使用缺省就可以了。 * 局部变量:不可以使用权限修饰符。 * * 2.3 默认初始化值的情况: * 属性:类的属性,根据其类型,都有默认初始化值。 * 整型(byte、short、int、long):0 * 浮点型(float、double):0.0 * 字符型(char):0 (或'\u0000') * 布尔型(boolean):false * * 引用数据类型(类、数组、接口):null * * 局部变量:没有默认初始化值。 * 意味着,我们在调用局部变量之前,一定要显式赋值。 * 特别地:形参在调用时,我们赋值即可。 * * 2.4 在内存中加载的位置: * 属性:加载到堆空间中 (非static) * 局部变量:加载到栈空间 * */ public class UserTest { public static void main(String[] args) { User u1 = new User(); System.out.println(u1.name); System.out.println(u1.age); System.out.println(u1.isMale); u1.talk("韩语"); u1.eat(); } } class User{ //属性(或成员变量) String name; public int age; boolean isMale; public void talk(String language){//language:形参,也是局部变量 System.out.println("我们使用" + language + "进行交流"); } public void eat(){ String food = "烙饼";//局部变量 System.out.println("北方人喜欢吃:" + food); } }
package com.atguigu.java; /* * 类中方法的声明和使用 * * 方法:描述类应该具有的功能。 * 比如:Math类:sqrt()\random() \... * Scanner类:nextXxx() ... * Arrays类:sort() \ binarySearch() \ toString() \ equals() \ ... * * 1.举例: * public void eat(){} * public void sleep(int hour){} * public String getName(){} * public String getNation(String nation){} * * 2. 方法的声明:权限修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(形参列表){ * 方法体 * } * 注意:static、final、abstract 来修饰的方法,后面再讲。 * * 3. 说明: * 3.1 关于权限修饰符:默认方法的权限修饰符先都使用public * Java规定的4种权限修饰符:private、public、缺省、protected -->封装性再细说 * * 3.2 返回值类型: 有返回值 vs 没有返回值 * 3.2.1 如果方法有返回值,则必须在方法声明时,指定返回值的类型。同时,方法中,需要使用 * return关键字来返回指定类型的变量或常量:“return 数据”。 * 如果方法没有返回值,则方法声明时,使用void来表示。通常,没有返回值的方法中,就不需要 * 使用return.但是,如果使用的话,只能“return;”表示结束此方法的意思。 * * 3.2.2 我们定义方法该不该有返回值? * ① 题目要求 * ② 凭经验:具体问题具体分析 * * 3.3 方法名:属于标识符,遵循标识符的规则和规范,“见名知意” * * 3.4 形参列表: 方法可以声明0个,1个,或多个形参。 * 3.4.1 格式:数据类型1 形参1,数据类型2 形参2,... * * 3.4.2 我们定义方法时,该不该定义形参? * ① 题目要求 * ② 凭经验:具体问题具体分析 * * 3.5 方法体:方法功能的体现。 * * 4.return关键字的使用: * 1.使用范围:使用在方法体中 * 2.作用:① 结束方法 * ② 针对于有返回值类型的方法,使用"return 数据"方法返回所要的数据。 * 3.注意点:return关键字后面不可以声明执行语句。 * * 5. 方法的使用中,可以调用当前类的属性或方法 * 特殊的:方法A中又调用了方法A:递归方法。 * 方法中,不可以定义方法。 */ public class CustomerTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Customer cust1 = new Customer(); cust1.eat(); //测试形参是否需要设置的问题 // int[] arr = new int[]{3,4,5,2,5}; // cust1.sort(); cust1.sleep(8); } } //客户类 class Customer{ //属性 String name; int age; boolean isMale; //方法 public void eat(){ System.out.println("客户吃饭"); return; //return后不可以声明表达式 // System.out.println("hello"); } public void sleep(int hour){ System.out.println("休息了" + hour + "个小时"); eat(); // sleep(10); } public String getName(){ if(age > 18){ return name; }else{ return "Tom"; } } public String getNation(String nation){ String info = "我的国籍是:" + nation; return info; } //体会形参是否需要设置的问题 // public void sort(int[] arr){ // // } // public void sort(){ // int[] arr = new int[]{3,4,5,2,5,63,2,5}; // //。。。。 // } public void info(){ //错误的 // public void swim(){ // // } } }
package com.atguigu.exer; /* * 3.1 编写程序,声明一个method方法,在方法中打印一个10*8 的*型矩形,在main方法中调用该方法。 * 3.2 修改上一个程序,在method方法中,除打印一个10*8的*型矩形外,再计算该矩形的面积, * 并将其作为方法返回值。在main方法中调用该方法,接收返回的面积值并打印。 * * 3.3 修改上一个程序,在method方法提供m和n两个参数,方法中打印一个m*n的*型矩形, * 并计算该矩形的面积, 将其作为方法返回值。在main方法中调用该方法,接收返回的面积值并打印。 */ public class Exer3Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Exer3Test test = new Exer3Test(); //3.1测试 // test.method(); //3.2测试 //方式一: // int area = test.method(); // System.out.println("面积为:" + area); //方式二: // System.out.println(test.method()); //3.3测试 int area = test.method(12, 10); System.out.println("面积为:" + area); } //3.1 // public void method(){ // for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++){ // for(int j = 0;j < 8;j++){ // System.out.print("* "); // } // System.out.println(); // } // } //3.2 // public int method(){ // for(int i = 0;i < 10;i++){ // for(int j = 0;j < 8;j++){ // System.out.print("* "); // } // System.out.println(); // } // // return 10 * 8; // } //3.3 public int method(int m,int n){ for(int i = 0;i < m;i++){ for(int j = 0;j < n;j++){ System.out.print("* "); } System.out.println(); } return m * n; } }
package com.atguigu.exer; /* * 4. 对象数组题目: 定义类Student,包含三个属性:学号number(int),年级state(int),成绩score(int)。 创建20个学生对象,学号为1到20,年级和成绩都由随机数确定。 问题一:打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。 问题二:使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息 提示: 1) 生成随机数:Math.random(),返回值类型double; 2) 四舍五入取整:Math.round(double d),返回值类型long。 * * * * */ public class StudentTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // Student s1 = new Student(); // Student s1 = new Student(); // Student s1 = new Student(); // Student s1 = new Student(); // Student s1 = new Student(); // Student s1 = new Student(); //声明Student类型的数组 Student[] stus = new Student[20]; //String[] arr = new String[10]; for(int i = 0;i < stus.length;i++){ //给数组元素赋值 stus[i] = new Student(); //给Student对象的属性赋值 stus[i].number = (i + 1); //年级:[1,6] stus[i].state = (int)(Math.random() * (6 - 1 + 1) + 1); //成绩:[0,100] stus[i].score = (int)(Math.random() * (100 - 0 + 1)); } //遍历学生数组 for(int i = 0;i <stus.length;i++){ // System.out.println(stus[i].number + "," + stus[i].state // + "," + stus[i].score); System.out.println(stus[i].info()); } System.out.println("********************"); //问题一:打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。 for(int i = 0;i <stus.length;i++){ if(stus[i].state == 3){ System.out.println(stus[i].info()); } } System.out.println("********************"); //问题二:使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息 for(int i = 0;i < stus.length - 1;i++){ for(int j = 0;j < stus.length - 1 - i;j++){ if(stus[j].score > stus[j + 1].score){ //如果需要换序,交换的是数组的元素:Student对象!!! Student temp = stus[j]; stus[j] = stus[j + 1]; stus[j + 1] = temp; } } } //遍历学生数组 for(int i = 0;i <stus.length;i++){ System.out.println(stus[i].info()); } } } class Student{ int number;//学号 int state;//年级 int score;//成绩 //显示学生信息的方法 public String info(){ return "学号:" + number + ",年级:" + state + ",成绩:" + score; } }
package com.atguigu.exer; /* * 4. 对象数组题目: 定义类Student,包含三个属性:学号number(int),年级state(int),成绩score(int)。 创建20个学生对象,学号为1到20,年级和成绩都由随机数确定。 问题一:打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。 问题二:使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息 提示: 1) 生成随机数:Math.random(),返回值类型double; 2) 四舍五入取整:Math.round(double d),返回值类型long。 * * * 此代码是对StudentTest.java的改进:将操作数组的功能封装到方法中。 * */ public class StudentTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) { //声明Student类型的数组 Student1[] stus = new Student1[20]; for(int i = 0;i < stus.length;i++){ //给数组元素赋值 stus[i] = new Student1(); //给Student对象的属性赋值 stus[i].number = (i + 1); //年级:[1,6] stus[i].state = (int)(Math.random() * (6 - 1 + 1) + 1); //成绩:[0,100] stus[i].score = (int)(Math.random() * (100 - 0 + 1)); } StudentTest1 test = new StudentTest1(); //遍历学生数组 test.print(stus); System.out.println("********************"); //问题一:打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。 test.searchState(stus, 3); System.out.println("********************"); //问题二:使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息 test.sort(stus); //遍历学生数组 test.print(stus); } /** * * @Description 遍历Student1[]数组的操作 * @author shkstart * @date 2019年1月15日下午5:10:19 * @param stus */ public void print(Student1[] stus){ for(int i = 0;i <stus.length;i++){ System.out.println(stus[i].info()); } } /** * * @Description 查找Stduent数组中指定年级的学生信息 * @author shkstart * @date 2019年1月15日下午5:08:08 * @param stus 要查找的数组 * @param state 要找的年级 */ public void searchState(Student1[] stus,int state){ for(int i = 0;i <stus.length;i++){ if(stus[i].state == state){ System.out.println(stus[i].info()); } } } /** * * @Description 给Student1数组排序 * @author shkstart * @date 2019年1月15日下午5:09:46 * @param stus */ public void sort(Student1[] stus){ for(int i = 0;i < stus.length - 1;i++){ for(int j = 0;j < stus.length - 1 - i;j++){ if(stus[j].score > stus[j + 1].score){ //如果需要换序,交换的是数组的元素:Student对象!!! Student1 temp = stus[j]; stus[j] = stus[j + 1]; stus[j + 1] = temp; } } } } } class Student1{ int number;//学号 int state;//年级 int score;//成绩 //显示学生信息的方法 public String info(){ return "学号:" + number + ",年级:" + state + ",成绩:" + score; } }




















 99
99











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








