简介:
dom4j是一个易于使用的开源库,用于使用Java集合框架在Java平台上处理XML,XPath和XSLT,并完全支持DOM,SAX和JAXP。
Document To XML字符串
document.asXML()方法用于将Document对象转换成xml字符串。
获取Document对象-解析XML:
可以通过 SAXReader 解析XML文件创建一个 document对象。SAX(Simple API for XML)
1.使用URL
public Document read(URL url) throws DocumentException {...}
public class Foo { public Document parse(URL url) throws DocumentException { SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); Document document = reader.read(url); return document; } }
2.使用InputStream
public Document read(InputStream in) throws DocumentException {...}
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, DocumentException { SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); InputStream in = new FileInputStream("c://test.xml"); Document document = reader.read(in); System.out.println(document.asXML()); }
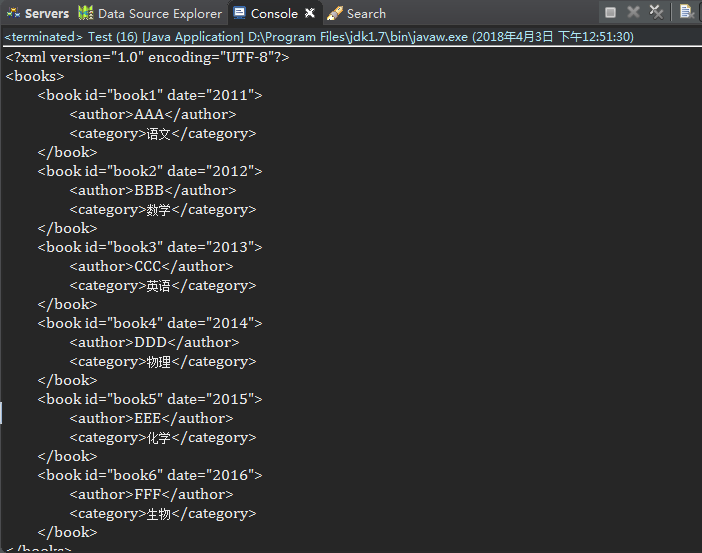
3.使用File
public Document read(File file) throws DocumentException {..}
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, DocumentException { SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); File file = new File("c://test.xml"); Document document = reader.read(file); System.out.println(document.asXML()); }
结果同上
4.使用InputSource(dom4j新实现的类,本质还是使用InputStream、File等)
public Document read(InputSource in) throws DocumentException {...}
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, DocumentException { SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); InputStream in = new FileInputStream("c://test.xml"); InputSource source = new InputSource(in); Document document = reader.read(source); System.out.println(document.asXML()); }
结果同上
5.使用Reader(本质还是使用InputStream、File等)
public Document read(Reader reader) throws DocumentException {...}
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, DocumentException { SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); Reader fileReader = new FileReader("c://test.xml"); // Reader streamReader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("c://test.xml")); Document document = reader.read(fileReader); System.out.println(document.asXML()); }
结果同上
获取Document对象-创建XML Document:
可以通过DocumentHelper创建(解析)一个Document对象,并为Document添加元素。
1.默认创建Document对象
public static Document createDocument() {...}
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, DocumentException { Document document = DocumentHelper.createDocument(); Element root = document.addElement("root"); Element p1 = root.addElement("person")
.addAttribute("age", "18")
.addText("张三"); Element p2 = root.addElement("person")
.addAttribute("age", "19")
.addText("李四"); Element p3 = root.addElement("person")
.addAttribute("age", "20")
.addText("王五"); System.out.println(document.asXML()); }
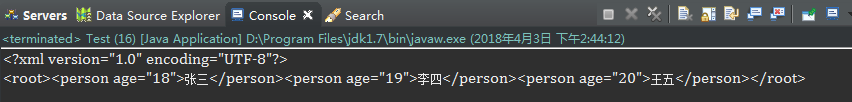
2.使用指定根元素创建Document对象
public static Document createDocument(Element rootElement) {...}
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, DocumentException { Element root = new DefaultElement("root"); Document document = DocumentHelper.createDocument(root); Element p1 = root.addElement("person")
.addAttribute("age", "18")
.addText("张三"); Element p2 = root.addElement("person")
.addAttribute("age", "19")
.addText("李四"); Element p3 = root.addElement("person")
.addAttribute("age", "20")
.addText("王五"); System.out.println(document.asXML()); }
结果同上
3.解析XML字符串获取Document对象
public static Document parseText(String text) throws DocumentException {...}
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, DocumentException { Document document = DocumentHelper.parseText("<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?><root><person age='18'>张三</person><person age='19'>李四</person><person age='20'>王五</person></root>"); System.out.println(document.asXML()); }
结果同上
获取元素
Element root = document.getRootElement();//获取根元素
Iterator it = root.elementIterator();//获取根元素的直接子元素的迭代,也可以对其他Element对象进行迭代查询其子元素
Iterator it = root.attributeIterator();//获取根元素的属性的迭代,也可对其他Element对象进行迭代查询其属性
public void bar(Document document) throws DocumentException { Element root = document.getRootElement(); // 迭代根元素的子元素 for ( Iterator i = root.elementIterator(); i.hasNext(); ) { Element element = (Element) i.next(); // do something } // 迭代根元素下name为“foo”的子元素 for ( Iterator i = root.elementIterator( "foo" ); i.hasNext(); ) { Element foo = (Element) i.next(); // do something } // 迭代根元素的属性 for ( Iterator i = root.attributeIterator(); i.hasNext(); ) { Attribute attribute = (Attribute) i.next(); // do something } }
例如,模拟SpringIOC 依赖注入机制(通过反射实现),有如下spring_core.xml配置,
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans> <bean id="testBean" class="com.just.Test"/> </beans>
可以根据spring_core.xml配置来获取bean id为 “testBean” 的 class,即类的全路径,获取类的全路径后,就可以随心所欲的进行反射调用了~
for (Iterator i = root.elementIterator("bean"); i.hasNext();){ foo = (Element) i.next(); //针对每一个bean实例获取id和name属性 Attribute id = foo.attribute("id"); Attribute clazz = foo.attribute("class"); //利用反射,通过class名称获取class对象 Class bean = Class.forName(clazz.getText()); // other 省略无关的反射操作 }
快速循环(Fast Looping)
如果需要遍历一个大型的XML文档树,那么为了提高性能,可以使用快速循环(Fast Looping)方法,避免为每个循环创建一个Iterator对象。
public class Test { // 循环获取根元素的所有子(孙)元素 public static void treeWalk(Element element) { for (int i = 0, size = element.nodeCount(); i < size; i++) { Node node = element.node(i); //因格式化的xml的换行符等也属于节点,所以需判断是否是Element if (node instanceof Element) { treeWalk((Element) node); System.out.println(node.getName()); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws DocumentException { String xmlStr = "<books>" + "<book><title>AAA</title><author>aaa</author></book>" + "<book><title>BBB</title><author>bbb</author></book>" + "<book><title>CCC</title><author>ccc</author></book>" + "</books>"; // 解析字符串获取document对象 Document document = DocumentHelper.parseText(xmlStr); treeWalk(document.getRootElement()); } }

将Document写出
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, DocumentException { String xmlStr = "<books>" + "<book><title>AAA</title><author>aaa</author></book>" + "<book><title>BBB</title><author>bbb</author></book>" + "<book><title>CCC</title><author>ccc</author></book>" + "</books>"; // 解析字符串获取document对象 Document document = DocumentHelper.parseText(xmlStr); //设置输出样式(整洁) OutputFormat format = OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint(); // 将document写出到output.xml中,并指定输出样式 XMLWriter writer = new XMLWriter(new FileOutputStream("output.xml"),format); writer.write(document); // 使用pretty(整洁)样式输出到控制台 writer = new XMLWriter(System.out, format); writer.write(document); System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------"); // 使用紧凑样式输出到控制台 format = OutputFormat.createCompactFormat(); writer = new XMLWriter(System.out, format); writer.write(document); } }
output.xml文件中的内容

控制台输出:
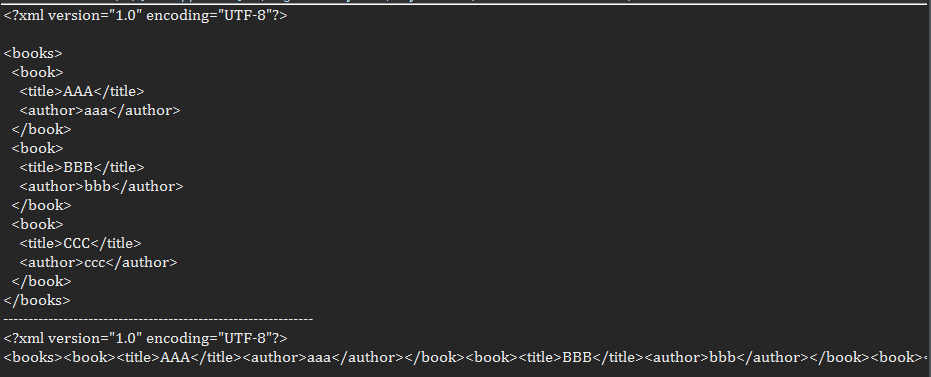
结合xPath解析Xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <books> <book id = "book1" date = "2011"> <author>AAA</author> <category>语文</category> </book> <book id = "book2" date = "2012"> <author>BBB</author> <category>数学</category> </book> <book id = "book3" date = "2013"> <author>CCC</author> <category>英语</category> </book> <book id = "book4" date = "2014"> <author>DDD</author> <category>物理</category> </book> </books>
xPath的操作的几种主要形式
- /AAA/DDD/BBB: 表示一层一层的,AAA下面 DDD下面的BBB
- //BBB: 表示和这个名称相同,表示只要名称是BBB,都得到
- /*: 所有元素
- BBB[1]: 表示第一个BBB元素; BBB[last()]:表示最后一个BBB元素
- //BBB[@id]: 表示只要BBB元素上面有id属性,都得到
- //BBB[@id='b1'] 表示元素名称是BBB,在BBB上面有id属性,并且id的属性值是b1
默认的情况下,dom4j不支持xpath,如果想要在dom4j里面是有xpath,第一步需要,引入支持xpath的jar包--jaxen.jar
在dom4j里面提供了两个方法,用来支持xpath
- selectNodes("xpath表达式"),获取多个节点
- selectSingleNode("xpath表达式"),获取一个节点
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws DocumentException { SAXReader reader = new SAXReader(); Document document = reader.read(new File("c://test.xml")); xPathOne(document); xPathTwo(document); xPathThree(document); xPathFour(document); xPathFive(document); xPathSix(document); } // 按层查找所有author元素的内容 private static void xPathOne(Document document) { List<Node> list = document.selectNodes("/books/book/author"); System.out.println("按层查找所有author元素的内容:"); for (Node node : list) { System.out.print(node.getText() + " "); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------"); } // 按名称查找所有category元素的内容 private static void xPathTwo(Document document) { List<Node> list = document.selectNodes("//category"); System.out.println("按名称查找所有category元素的内容:"); for (Node node : list) { System.out.print(node.getText() + " "); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------"); } // 获取book下的所有元素的内容 private static void xPathThree(Document document) { List<Node> list = document.selectNodes("//books//book/*"); System.out.println("获取book下的所有元素的内容"); for (Node node : list) { System.out.print(node.getText() + " "); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------"); } // 获取第一、最后一个book元素下的author中的内容 private static void xPathFour(Document document) { Node node1 = document.selectSingleNode("/books/book[1]//author"); Node node2 = document.selectSingleNode("/books/book[last()]//author"); System.out.println("获取第一、最后一个book元素下的author中的内容:"); System.out.println(node1.getText()); System.out.println(node2.getText()); System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------"); } // 获取包含Id属性的元素的字符串内容(包含换行符、制表符等) private static void xPathFive(Document document) { List<Node> list = document.selectNodes("//book[@id]"); System.out.println("获取包含Id属性的元素的字符串内容:"); for (Node node : list) { System.out.print(node.getStringValue()); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------"); } // 分别获取id为book1、book2的元素节点 private static void xPathSix(Document document) { Node node1 = document.selectSingleNode("//book[@id='book1']"); Node node2 = document.selectSingleNode("//book[@id='book2']"); System.out.println("分别获取id为book1、book2的元素节点:"); System.out.println(node1.getStringValue()); System.out.println(node2.getStringValue()); System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------"); } }
运行结果
按层查找所有author元素的内容:
AAA BBB CCC DDD
--------------------------------------------------------------
按名称查找所有category元素的内容:
语文 数学 英语 物理
--------------------------------------------------------------
获取book下的所有元素的内容
AAA 语文 BBB 数学 CCC 英语 DDD 物理
--------------------------------------------------------------
获取第一、最后一个book元素下的author中的内容:
AAA
DDD
--------------------------------------------------------------
获取包含Id属性的元素的字符串内容:
AAA
语文
BBB
数学
CCC
英语
DDD
物理
--------------------------------------------------------------
分别获取id为book1、book2的元素节点:
AAA
语文
BBB
数学
--------------------------------------------------------------
其他参考:https://blog.csdn.net/louislip/article/details/52896182
| expression | description |
| nodename | 当前节点的所有子节点 |
| / | 根节点选取 |
| // | 匹配文档中节点,不考虑位置 |
| . | 当前节点 |
| .. | 当前节点的父节点 |
| @ | 选取属性 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans> <bean id="testBean" class="com.just.Test"/> </beans>
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader(); File file = new File("out.xml"); Document document = saxReader.read(file); Element rootElement = document.getRootElement(); List<Object> list = document.selectNodes("//bean"); for (Object n : list) { if(n instanceof Element){ Element e = (Element) n; System.out.println(e.getName()); List<Object> aList = e.selectNodes("@class"); for(Object a :aList) if(a instanceof Attribute){ Attribute attribute = (Attribute) a; System.out.println(attribute.getText()); } } }
输出
bean
com.just.Test
XSLT的简单使用
XSLT:在计算机科学中,XSLT是 扩展样式表转换语言 的外语缩写,这是一种对XML(标准通用标记语言的子集)文档进行转化的语言,XSLT中的T代表英语中的“转换”(Transformation)。它是XSL(eXtensible Stylesheet Language)规范的一部分。简单来说就是实用XSLT技术将xml存储的数据根据.xsl样式表转换显示出来(比如HTML文件)。
使用Sun的JAXP API可以直接将XSLT应用于xml文档中。 这使您可以针对任何XSLT引擎(如Xalan或SAXON)进行工作。 以下是使用JAXP创建变换器并将其应用于文档的示例。
样式表(test.xsl)如下,XML文件使用上面的XML文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <xsl:stylesheet version="1.0 " xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"> <xsl:template match="/books"> <html> <head> <title>First XSLT example</title> </head> <body> <table border="1"> <tr> <td bgcolor="#9acd32">标题</td> <td bgcolor="#9acd32">类别</td> </tr> <xsl:for-each select="book"> <tr> <td><xsl:value-of select="author" /></td> <td><xsl:value-of select="category" /></td> </tr> </xsl:for-each> </table> </body> </html> </xsl:template> </xsl:stylesheet>
测试代码:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Document document = new SAXReader().read(new File("c://test.xml")); //读取XML文档 Document transformedDoc = xsltTest(document,"c://test.xsl");//根据XML文档和样式表路径返回转换后的文档 //将转换后的文档写出到test.html文件中 OutputFormat format = OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint(); XMLWriter writer = new XMLWriter(new FileOutputStream("c://test.html"),format); writer.write(transformedDoc); } /** * /使用xml文档及样式表路径获取转换后的文档 * * @param document * 需要被转换的xml文档 * @param stylesheet * 样式表所在路径 * @return * @throws TransformerException */ private static Document xsltTest(Document document, String stylesheet) throws TransformerException { Document document2 = null; // 使用JAXP(Java API for XML Processing)加载转换器 TransformerFactory factory = TransformerFactory.newInstance(); Transformer transformer = factory.newTransformer(new StreamSource(new File(stylesheet))); // 将给定文档样式化 DocumentSource source = new DocumentSource(document); DocumentResult result = new DocumentResult(); transformer.transform(source, result); // 返回转化后的文档 Document transformedDoc = result.getDocument(); return transformedDoc; } }
结果展示:
test.html内容
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <html> <head> <title>First XSLT example</title> </head> <body> <table border="1"> <tr> <td bgcolor="#9acd32">标题</td> <td bgcolor="#9acd32">类别</td> </tr> <tr> <td>AAA</td> <td>语文</td> </tr> <tr> <td>BBB</td> <td>数学</td> </tr> <tr> <td>CCC</td> <td>英语</td> </tr> <tr> <td>DDD</td> <td>物理</td> </tr> </table> </body> </html>
页面显示:

THE END
主要参考自dom4j官方指南,部分内容参考自其他文章,其内容已添加链接。
欢迎转载,转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/maxudong/p/8710291.html





















 1016
1016











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








