数塔
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 28544 Accepted Submission(s): 17166
Problem Description
在讲述DP算法的时候,一个经典的例子就是数塔问题,它是这样描述的:
有如下所示的数塔,要求从顶层走到底层,若每一步只能走到相邻的结点,则经过的结点的数字之和最大是多少?
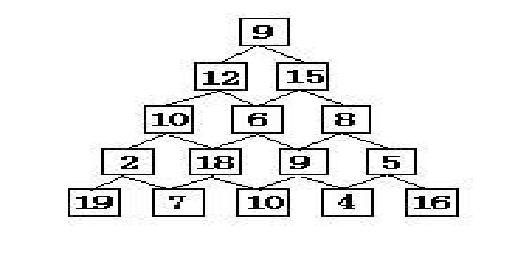
已经告诉你了,这是个DP的题目,你能AC吗?
有如下所示的数塔,要求从顶层走到底层,若每一步只能走到相邻的结点,则经过的结点的数字之和最大是多少?

已经告诉你了,这是个DP的题目,你能AC吗?
Input
输入数据首先包括一个整数C,表示测试实例的个数,每个测试实例的第一行是一个整数N(1 <= N <= 100),表示数塔的高度,接下来用N行数字表示数塔,其中第i行有个i个整数,且所有的整数均在区间[0,99]内。
Output
对于每个测试实例,输出可能得到的最大和,每个实例的输出占一行。
Sample Input
1 5 7 3 8 8 1 0 2 7 4 4 4 5 2 6 5
Sample Output
30
理解:我感觉DP首先找
最优子结构,这一点和贪心很像,当我们要解决一个大问题时,可以理解大问题是由小问题一步一步转化而来的。这时,DP的难处就在于找到这个
状态转移方程。
#include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <ctime> #include <cmath> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <list> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <set> using namespace std; const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; const double eps=1e-10; const double PI=acos(-1.0); #define maxn 500 int a[maxn][maxn]; int dp[maxn][maxn]; int main() { int t, n; scanf("%d", &t); while(t--) { memset(a, 0, sizeof a); memset(dp, 0, sizeof dp); scanf("%d", &n); for(int i = 1; i <= n ;i++) for(int j = 1; j <= i; j++) scanf("%d", &a[i][j]); int ans = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) for(int j = 1; j <= i; j++) { dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i-1][j-1]) + a[i][j];//状态转移方程 ans = max(ans, dp[i][j]); } printf("%d\n", ans); } return 0; }





















 653
653











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








