完成时间:17:10
package 四则运算试题;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class jisuanti {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int a1,a2;
int b;
int num=0;
int i=0;
//Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String f[]=new String[4];
f[0]="+";
f[1]="-";
f[2]="*";
f[3]="/";
int a[]=new int[100];
//System.out.println("请选择100以内或1000以内");
//m=sc.nextInt()+1;
//System.out.println("请输入要产生的题数");
//n=sc.nextInt();
PrintStream out = System.out;
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("Test.txt");
System.setOut(ps);
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
a1=(int)(Math.random()*100);
a2=(int)(Math.random()*100);
b=(int)(Math.random()*4);
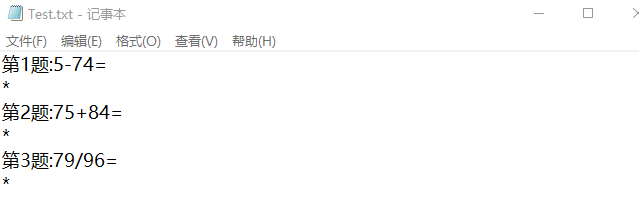
System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"题:"+a1+f[b]+a2+"=");
System.out.println("*");
switch(b) {
case 0:a[i]=(a1+a2);break;
case 1:a[i]=(a1-a2);break;
case 2:a[i]=(a1*a2);break;
case 3:a[i]=(a1/a2);break;
}
}
ps.close();
System.setOut(out);
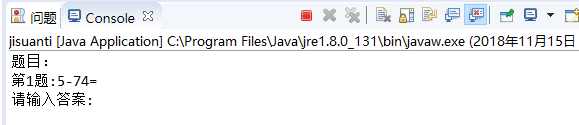
System.out.println("题目:");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Test.txt"));
String line = "";
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int answer[]=new int[100];
int m=0;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
if(line.charAt(0)=='*') {
System.out.print("请输入答案:");
// System.out.println(a[m]);
int n;
n=sc.nextInt();
answer[m]=n;
if(answer[m]==a[m])num++;
m++;
}
else {
System.out.println(line);
}
}
sc.close();
br.close();
System.out.println("共答对"+num+"题");
}
}
问题:问题卡在对比结果。





















 458
458











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








