A group of two or more people wants to meet and minimize the total travel distance. You are given a 2D grid of values 0 or 1, where each 1 marks the home of someone in the group. The distance is calculated usingManhattan Distance, where distance(p1, p2) = |p2.x - p1.x| + |p2.y - p1.y|.
For example, given three people living at (0,0), (0,4), and(2,2):
1 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 1 | | | | | 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 | | | | | 0 - 0 - 1 - 0 - 0
The point (0,2) is an ideal meeting point, as the total travel distance of 2+2+2=6 is minimal. So return 6.
分析:http://massivealgorithms.blogspot.com/2015/10/leetcode-best-meeting-point-segmentfault.html
|p2.x - p1.x| + |p2.y - p1.y|)= sum(|p2.x - p1.x|)+sum(|p2.y - p1.y|). 也就是说, 可以分别计算x和y的合, 然后加起来.
Suppose we have a set S of real numbers that ∑s∈S|s−x|is minimal if x is equal to themedian.
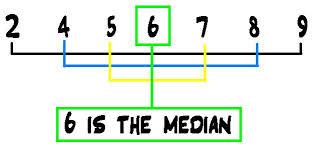
6是median,那么 (6-2)+(6-4) + (6-5) + (7-6) + (8-6) + (9-6) = 4 + 2+ 1+ 1+ 2+ 3 = 13 = (9-2) + (8-4) + (7-5)
public class Solution { public int minTotalDistance(int[][] grid) { List<Integer> xPoints = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> yPoints = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) { if (grid[i][j] == 1) { xPoints.add(i); yPoints.add(j); } } } return getMP(xPoints) + getMP(yPoints); } private int getMP(List<Integer> points) { Collections.sort(points); int i = 0, j = points.size() - 1; int res = 0; while (i < j) { res += points.get(j--) - points.get(i++); } return res; } }





















 1675
1675

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








