Web服务器也称为超文本传输协议服务器,使用http与其客户端进行通信,基于java的web服务器会使用两个重要的类,
java.net.Socket类和java.net.ServerSocket类,并基于发送http消息进行通信。
这个简单的Web服务器会有以下三个类:
*HttpServer
*Request
*Response
应用程序的入口在HttpServer类中,main()方法创建一个HttpServer实例,然后调用其await()方法,顾名思义,await()方法会在指定端口上等待HTTP请求,对其进行处理,然后发送响应信息回客户端,在接收到关闭命令前,它会保持等待状态。
该应用程序仅发送位于指定目录的静态资源的请求,如html文件和图像,它也可以将传入到的http请求字节流显示到控制台,但是,它并不发送任何头信息到浏览器,如日期或者cookies等。
下面为这几个类的源码
Request:
package cn.com.server;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class Request {
private InputStream input;
private String uri;
public Request(InputStream input){
this.input=input;
}
public void parse(){
//Read a set of characters from the socket
StringBuffer request=new StringBuffer(2048);
int i;
byte[] buffer=new byte[2048];
try {
i=input.read(buffer);
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
i=-1;
}
for (int j=0;j
request.append((char)buffer[j]);
}
System.out.print(request.toString());
uri=parseUri(request.toString());
}
public String parseUri(String requestString){
int index1,index2;
index1=requestString.indexOf(" ");
if(index1!=-1){
index2=requestString.indexOf(" ",index1+1);
if(index2>index1){
return requestString.substring(index1+1,index2);
}
}
return null;
}
public String getUri(){
return this.uri;
}
}
Request类表示一个HTTP请求,可以传递InputStream对象来创建Request对象,可以调用InputStream对象中的read()方法来读取HTTP请求的原始数据。
上述源码中的parse()方法用于解析Http请求的原始数据,parse()方法会调用私有方法parseUrI()来解析HTTP请求的URI,除此之外,并没有做太多的工作,parseUri()方法将URI存储在变量uri中,调用公共方法getUri()会返回请求的uri。
Response:
package cn.com.server;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* HTTP Response = Status-Line
* *(( general-header | response-header | entity-header ) CRLF)
* CRLF
* [message-body]
* Status-Line=Http-Version SP Status-Code SP Reason-Phrase CRLF
*
*/
public class Response {
private static final int BUFFER_SIZE=1024;
Request request;
OutputStream output;
public Response(OutputStream output){
this.output=output;
}
public void setRequest(Request request){
this.request=request;
}
public void sendStaticResource()throws IOException{
byte[] bytes=new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
FileInputStream fis=null;
try {
File file=new File(HttpServer.WEB_ROOT,request.getUri());
if(file.exists()){
fis=new FileInputStream(file);
int ch=fis.read(bytes,0,BUFFER_SIZE);
while(ch!=-1){
output.write(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE);
ch=fis.read(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE);
}
} else{
//file not found
String errorMessage="HTTP/1.1 404 File Not Found\r\n"+
"Content-Type:text/html\r\n"+
"Content-Length:23\r\n"+
"\r\n"+
"
File Not Found
";output.write(errorMessage.getBytes());
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
finally{
if(fis!=null){
fis.close();
}
}
}
}
Response对象在HttpServer类的await()方法中通过传入套接字中获取的OutputStream来创建。
Response类有两个公共方法:setRequest()和sendStaticResource(),setRequest()方法会接收一个Request对象为参数,sendStaticResource()方法用于发送一个静态资源到浏览器,如Html文件。
HttpServer:
package cn.com.server;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class HttpServer {
/**
* WEB_ROOT is the directory where our html and other files reside.
* For this package,WEB_ROOT is the "webroot" directory under the
* working directory.
* the working directory is the location in the file system
* from where the java command was invoke.
*/
public static final String WEB_ROOT=System.getProperty("user.dir")+File.separator+"webroot";
private static final String SHUTDOWN_COMMAND="/SHUTDOWN";
private Boolean shutdown=false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
HttpServer server=new HttpServer();
server.await();
}
public void await(){
ServerSocket serverSocket=null;
int port=8080;
try {
serverSocket=new ServerSocket(port,1,InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"));
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(0);
}
while(!shutdown){
Socket socket=null;
InputStream input=null;
OutputStream output=null;
try {
socket=serverSocket.accept();
input=socket.getInputStream();
output=socket.getOutputStream();
//create Request object and parse
Request request=new Request(input);
request.parse();
//create Response object
Response response=new Response(output);
response.setRequest(request);
response.sendStaticResource();
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
continue;
}
}
}
}
这个类表示一个Web服务器,这个Web服务器可以处理对指定目录的静态资源的请求,该目录包括由公有静态变量final WEB_ROOT指明的目录及其所有子目录。
现在在webroot中创建一个html页面,命名为index.html,源码如下:
Insert title hereHello World!
现在启动该WEB服务器,并请求index.html静态页面。
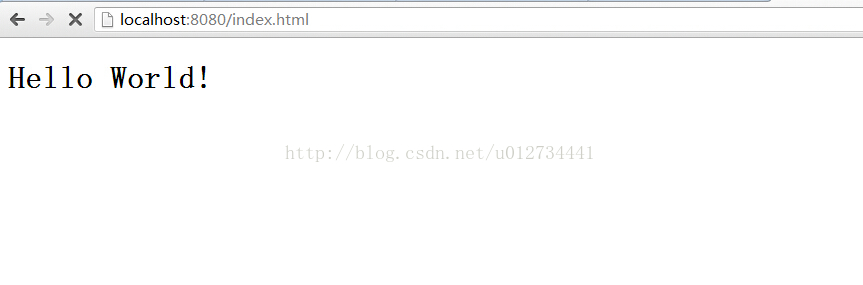
所对应的控制台的输出:
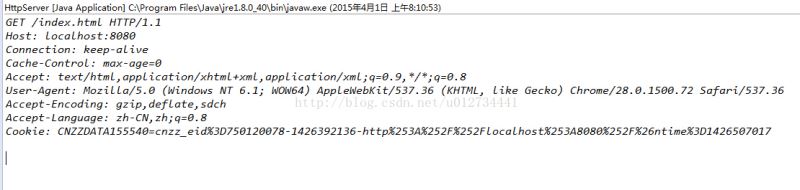
如此,一个简单的http服务器便完成了。
总结
以上就是本文关于java实现一个简单的Web服务器实例解析的全部内容,希望对大家有所帮助。感兴趣的朋友可以继续参阅本站其他相关专题,如有不足之处,欢迎留言指出。感谢朋友们对本站的支持!





















 906
906











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








