1.常用集合的分类
2.Collection接口中的常用方法
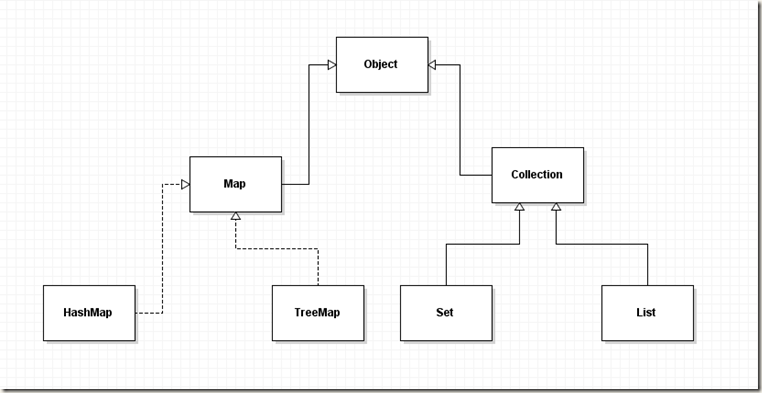
Collection是集合的根接口,用于保存一组元素,功能与数组类似,List 和 Set接口都继承了Collection接口,
其中List是可重复的,Set是不可重复的。
public classEmp {
String name;intage;intsalary;public Emp(String name, int age, intsalary) {super();this.name =name;this.age =age;this.salary =salary;
}//重写equals方法
public booleanequals(Object obj) {if(this ==obj){return true;
}if(obj == null){return false;
}if(getClass() !=obj.getClass()){return false;
}
Emp e=(Emp) obj;if(name !=e.name){return false;
}return true;
}//重写toString方法
publicString toString() {return this.name+","+this.age+","+this.salary;
}
}
public classCollectionTest {public static voidmain(String[] args) {
Collection c = new ArrayList<>();/*** boolean add(E e)
* 向当前集合中添加给定元素,若成功添加进集合则返回true;
* 集合中通常只放一种类型的实例*/c.add("one");
c.add("two");
c.add("three");
System.out.println(c);//[one, two, three]//查看当前集合中的元素个数
int num =c.size();
System.out.println(num);//3//是否包含某元素 equals比较相等则认为包含
boolean contain = c.contains("two");//true
System.out.println(contain);//清空集合
c.clear();
System.out.println("集合:"+c+"长度"+c.size());//集合:[]长度0//是否为空
boolean isEmpty =c.isEmpty();
System.out.println(isEmpty);//true//当Collection中的元素为对象时存的是对象的引用地址
Collection c2 = new ArrayList<>();
Emp e= new Emp("zhangsan", 12, 120);
c2.add(e);
System.out.println(c2);//[zhangsan,12,120]
e.age = 22;
System.out.println(c2);//[zhangsan,22,120]//删除元素 - 删除equals比较为true的第一个元素
c2.add(new Emp("lisi", 32, 111));
c2.add(new Emp("wangwu", 54, 231));
System.out.println(c2);//[zhangsan,22,120, lisi,32,111, wangwu,54,231]
Emp emp = new Emp("lisi", 61, 1200);
c2.remove(emp);
System.out.println(c2);//[zhangsan,22,120, wangwu,54,231]//批量添加
Collection colList = new ArrayList<>();
colList.add("one");
Collection colSet = new HashSet<>();
colSet.add("one");
colSet.add("tow");
colSet.add("Three");
colSet.add("one");
System.out.println(colSet);//[one, tow, Three]
/*** boolean addAll(Collection c);
* 将给定集合中的所有元素添加到当前集合中,操作完成后若当前集合的元素发生了变化就返回true;
**/
boolean bool1 = colList.addAll(colSet);//true
System.out.println(bool1);//true
System.out.println(colList);//[one, one, tow, Three]
boolean bool2 =colSet.addAll(colList);
System.out.println(bool2);//false
System.out.println(colSet);//[one, tow, Three]
/*** boolean containsAll(Collection c)
* 判断当前集合是否包含给定集合中的所有元素
* 全包含则返回true。包含依然是依靠元素的equals方法比较的结果。*/Collection col3 = new HashSet<>();
col3.addAll(colSet);boolean conts =colList.containsAll(col3);
System.out.println(conts);//true
/*** 集合提供了用于遍历集合元素的方法
* Iterator iterator()
* 该方法会获取一个用于遍历当前集合的迭代器
* Iterator本身也是一个借口,定义了用于遍历集合的相关方法,不同的集合实现类都提供了遍历自身的迭代器实现类
* 迭代器遍历集合遵循:问,取,删(删除不是必须操作)*/System.out.println("colList:"+colList);
Iterator itr =colList.iterator();while(itr.hasNext()){/*** E next()
* 从集合中取出下一个元素*/String str=itr.next();
System.out.println(str);if("one".equals(str)){//不能用colList.remove()方法 否则可能会抛出异常
itr.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(colList);
}
}
3.List常见方法
List接口继承了Collection接口,因此包含Collection的所有方法,还有一些独有的方法并且List是可重复集,同时也是有序集。
List还有两个常用的实现类:
ArrayList 内部由数组实现,查询快,增删元素效率相对较低
LinkedList 内部由链表实现,增删快,查询效率相对较低
public classListDemo {public static voidmain(String[] args) {//List接口定义了许多独有的方法(Set集合不具备的)
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("one");
list.add("two");
list.add("three");
list.add("four");//获取List集合中指定下标对应的元素
String str = list.get(1);
System.out.println(str);//two//传统for循环输出List
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
str=list.get(i);
System.out.println(str);
}//将给定元素设置到指定位置上,返回值为原位置上的元素。所以是替换元素操作
String replaceStr = list.set(1, "2");
System.out.println(replaceStr);//two
System.out.println(list);//[one, 2, three, four]//将给定元素插入到指定位置上,原位置及后续元素顺序向后移动
list.add(0, "zero");
System.out.println(list);//[zero, one, 2, three, four]//将给定位置上的元素删除,并将该元素返回
String removeStr = list.remove(list.size()-1);
System.out.println(removeStr);//four
System.out.println(list);//[zero, one, 2, three]//获取子集 对子集的操作会影响原集合
List subList = list.subList(1, 3);
System.out.println(subList);//[one, 2]
subList.clear();
System.out.println(subList);//[]
System.out.println(list);//[zero, three]
}
}
4.数组与集合之间的转换
public classCelloctionAndArray {public static voidmain(String[] args) {//集合转换为数组
Collection c = new ArrayList<>();
c.add("a");
c.add("b");
c.add("c");
String [] array= c.toArray(new String[c.size()]);//c.size()改为0时可以运行,当放不下时重新建立数组
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));//[a, b, c]//数组转为集合 只能转为List集合,因为Set集合不可重复,会丢失元素
String [] arr = {"1","2","3","4"};
List list =Arrays.asList(arr);//有数组转换的List 当修改元素时原数组也会变化
list.set(0, "one");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));//[one, 2, 3, 4]//对于由数组转换的集合而言,不能增删元素//list.add("5");//java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException//只能新建List才能进行操作
List list1 = new ArrayList<>(list);
list1.add("5");
System.out.println(list1);
}
}
5.集合的排序
依靠的是集合的工具类Collections提供的静态方法sort,针对的List的排序
使用sort进行排序的前提是List里的元素实现了Comparable接口并重写方法。
同时sort方法可以传入第二个参数,实现Comparator接口的比较器进行比较规则的自定义。
public classCollectionSortDemo {public static voidmain(String[] args) {//自然排序
List strList = new ArrayList<>();
strList.add("a");
strList.add("c");
strList.add("b");
Collections.sort(strList);
System.out.println(strList);//[a, b, c]//按照重写的方法排序
List
pList = new ArrayList<>();
pList.add(new P(1,9));
pList.add(new P(2,5));
pList.add(new P(3,1));
Collections.sort(pList);
System.out.println(pList);//[(1,9), (2,5), (3,1)]//当元素的比较方法不能满足我们时可以向sort方法传入一个比较器定义比较的形式
Collections.sort(pList, newPcomparator());
System.out.println(pList);//构造器的定义使用匿名内部类 建议使用
Collections.sort(pList,new Comparator
() {public intcompare(P o1, P o2) {return (o1.a/o1.b)-(o2.a/o2.b);
}
});
System.out.println(pList);//集合反转
Collections.reverse(pList);
System.out.println(pList);
}
}//定义比较器
class Pcomparator implements Comparator
{public intcompare(P o1, P o2) {return (o1.a*o1.b-o2.a*o2.b);
}
}class P implements Comparable
{protected inta;protected intb;public P(int a, intb) {super();this.a =a;this.b =b;
}public intgetA() {returna;
}public void setA(inta) {this.a =a;
}public intgetB() {returnb;
}public void setB(intb) {this.b =b;
}
@OverridepublicString toString() {return "("+a+","+b+")";
}//重写比较方法
/*** 比较方法的返回值不关注具体取值,关注取值范围,
* 若返回值>0:当前对象大于参数对象o
* 若返回值<0:当前对象小于参数对象o
* 若返回值=0:两个对象相等*/
public intcompareTo(P o) {return (this.a+this.b)-(o.a+o.b);
}
}
6.Map的常见方法
Map提供的是key到value的映射,key值不允许重复,每个key对应一个value
public classMapDemo {public static voidmain(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();/*** V put(K k,V v)
* 将给定的Key,value存入Map中
* 由于Map要求key不允许重复,所以使用Map中已有的key存人value时,
* 会将该key原来对应的value值替换并返回。*/map.put("zhangsan", 22);
map.put("lisi", 34);
map.put("wangwu", 54);
System.out.println(map);
Integer age= map.put("wangwu", 45);
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(map);/*** V get(K V)
* 根据给定的key获取对应的value
* 若给定的key在map中不存在,返回值为null。*/age= map.get("zhangsan");
System.out.println(age);/*** boolean containsKey(K k)
* 查看当前Map是否包含给定的key
* 判断的依据是看key的equals比较结果*/
boolean bool = map.containsKey("zhangsan");
System.out.println(bool);/*** boolean containsValue(V v)
* 判断当前Map是否包含给定的value*/bool= map.containsValue(34);
System.out.println(bool);/*** V remove(K k)
* 根据给定的key删除Map中这组key-value对并将对应的value返回。*/age= map.remove("lisi");
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(map);/*** 遍历所有的key
* Set keySet()
* 该方法会将当前Map中所有的key存入一个Set集合的实现类中,然后将其返回
* 遍历该集合就相当于拿到Map中每一个key了*/Set keySet =map.keySet();//循环输出
keySet.forEach((str)->System.out.println(str));/*** 在Map中,每一组键对是靠一个Entry的实例存储的。
* Set entrySet()
* 该方法将当前Map中每一组键对(若干Entry实例)存入一个set集合
* 然后将其返回*/Set> kvSet =map.entrySet();
kvSet.forEach((e)->System.out.println(e.getKey()+":"+e.getValue()));/*** 遍历所有的value
* Collection values()
* 将当前Map中所有的value存入一个集合后返回。
* 返回的集合并非是一个Set,因为value是可以重复的*/Collection values =map.values();//循环输出
values.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








