本文和大家一起做一个带箭头的圆角矩形菜单,大概长下面这个样子:
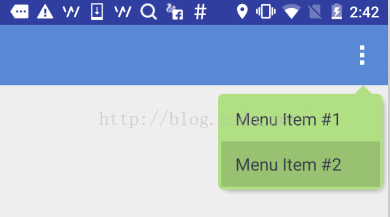
要求顶上的箭头要对准菜单锚点,菜单项按压反色,菜单背景色和按压色可配置。
最简单的做法就是让UX给个三角形的图片往上一贴,但是转念一想这样是不是太low了点,而且不同分辨率也不太好适配,干脆自定义一个ViewGroup吧!
自定义ViewGroup其实很简单,基本都是按一定的套路来的。
一、定义一个attrs.xml
就是声明一下你的这个自定义View有哪些可配置的属性,将来使用的时候可以自由配置。这里声明了7个属性,分别是:箭头宽度、箭头高度、箭头水平偏移、圆角半径、菜单背景色、阴影色、阴影厚度。
二、写一个继承ViewGroup的类,在构造函数中初始化这些属性
这里需要用到一个obtainStyledAttributes()方法,获取一个TypedArray对象,然后就可以根据类型获取相应的属性值了。需要注意的是该对象用完以后需要显式调用recycle()方法释放掉。public class ArrowRectangleView extends ViewGroup {
... ...
public ArrowRectangleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
TypedArray a = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,
R.styleable.ArrowRectangleView, defStyleAttr, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < a.getIndexCount(); i++) {
int attr = a.getIndex(i);
switch (attr) {
case R.styleable.ArrowRectangleView_arrow_width:
mArrowWidth = a.getDimensionPixelSize(attr, mArrowWidth);
break;
case R.styleable.ArrowRectangleView_arrow_height:
mArrowHeight = a.getDimensionPixelSize(attr, mArrowHeight);
break;
case R.styleable.ArrowRectangleView_radius:
mRadius = a.getDimensionPixelSize(attr, mRadius);
break;
case R.styleable.ArrowRectangleView_background_color:
mBackgroundColor = a.getColor(attr, mBackgroundColor);
break;
case R.styleable.ArrowRectangleView_arrow_offset:
mArrowOffset = a.getDimensionPixelSize(attr, mArrowOffset);
break;
case R.styleable.ArrowRectangleView_shadow_color:
mShadowColor = a.getColor(attr, mShadowColor);
break;
case R.styleable.ArrowRectangleView_shadow_thickness:
mShadowThickness = a.getDimensionPixelSize(attr, mShadowThickness);
break;
}
}
a.recycle();
}
三、重写onMeasure()方法
onMeasure()方法,顾名思义,就是用来测量你这个ViewGroup的宽高尺寸的。
我们先考虑一下高度:
•首先要为箭头跟圆角预留高度,maxHeight要加上这两项
•然后就是测量所有可见的child,ViewGroup已经提供了现成的measureChild()方法
•接下来就把获得的child的高度累加到maxHeight上,当然还要考虑上下的margin配置
•除此以外,还需要考虑到上下的padding,以及阴影的高度
•最后通过setMeasuredDimension()设置生效
在考虑一下宽度:
•首先也是通过measureChild()方法测量所有可见的child
•然后就是比较这些child的宽度以及左右的margin配置,选最大值
•接下来还有加上左右的padding,以及阴影宽度
•最后通过setMeasuredDimension()设置生效@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int count = getChildCount();
int maxWidth = 0;
// reserve space for the arrow and round corners
int maxHeight = mArrowHeight + mRadius;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = maxHeight + child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
}
}
maxWidth = maxWidth + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight() + mShadowThickness;
maxHeight = maxHeight + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom() + mShadowThickness;
setMeasuredDimension(maxWidth, maxHeight);
}
看起来是不是很简单?当然还有两个小问题:
1. 高度为圆角预留尺寸的时候,为什么只留了一个半径,而不是上下两个半径?
其实这是从显示效果上来考虑的,如果上下各留一个半径,会造成菜单的边框很厚不好看,后面实现onLayout()的时候你会发现,我们布局菜单项的时候会往上移半个半径,这样边框看起来就好看多了。
2. Child的布局参数为什么可以强转成MarginLayoutParams?
这里其实需要重写另一个方法generateLayoutParams(),返回你想要布局参数类型。一般就是用MarginLayoutParams,当然你也可以用其他类型或者自定义类型。@Override
public ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
四、重写onLayout()方法
onLayout()方法,顾名思义,就是用来布局这个ViewGroup里的所有子View的。
实际上每个View都有一个layout()方法,我们需要做的只是把合适的left/top/right/bottom坐标传入这个方法就可以了。
这里就可以看到,我们布局菜单项的时候往上提了半个半径,因此topOffset只加了半个半径,另外右侧的坐标也只减了半个半径。@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int count = getChildCount();
int topOffset = t + mArrowHeight + mRadius/2;
int top = 0;
int bottom = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
top = topOffset + i * child.getMeasuredHeight();
bottom = top + child.getMeasuredHeight();
child.layout(l, top, r - mRadius/2 - mShadowThickness, bottom);
}
}
五、重写dispatchDraw()方法
这里因为我们是写了一个ViewGroup容器,本身是不需要绘制的,因此我们就需要重写它的dispatchDraw()方法。如果你重写的是一个具体的View,那也可以重写它的onDraw()方法。
绘制过程分为三步:
1. 绘制圆角矩形
这一步比较简单,直接调用Canvas的drawRoundRect()就完成了。
2. 绘制三角箭头
这个需要根据配置的属性,设定一个路径,然后调用Canvas的drawPath()完成绘制。
3. 绘制菜单阴影
这个说白了就是换一个颜色再画一个圆角矩形,位置略有偏移,当然还要有模糊效果。
要获得模糊效果,需要通过Paint的setMaskFilter()进行配置,并且需要关闭该图层的硬件加速,这一点在API里有明确说明。
除此以外,还需要设置源图像和目标图像的重叠模式,阴影显然要叠到菜单背后,根据下图可知,我们需要选择DST_OVER模式。
其他细节看代码就清楚了:@Override
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
// disable h/w acceleration for blur mask filter
setLayerType(View.LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE, null);
Paint paint = new Paint();
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
paint.setColor(mBackgroundColor);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
// set Xfermode for source and shadow overlap
paint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode.DST_OVER));
// draw round corner rectangle
paint.setColor(mBackgroundColor);
canvas.drawRoundRect(new RectF(0, mArrowHeight, getMeasuredWidth() - mShadowThickness, getMeasuredHeight() - mShadowThickness), mRadius, mRadius, paint);
// draw arrow
Path path = new Path();
int startPoint = getMeasuredWidth() - mArrowOffset;
path.moveTo(startPoint, mArrowHeight);
path.lineTo(startPoint + mArrowWidth, mArrowHeight);
path.lineTo(startPoint + mArrowWidth / 2, 0);
path.close();
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
// draw shadow
if (mShadowThickness > 0) {
paint.setMaskFilter(new BlurMaskFilter(mShadowThickness, BlurMaskFilter.Blur.OUTER));
paint.setColor(mShadowColor);
canvas.drawRoundRect(new RectF(mShadowThickness, mArrowHeight + mShadowThickness, getMeasuredWidth() - mShadowThickness, getMeasuredHeight() - mShadowThickness), mRadius, mRadius, paint);
}
super.dispatchDraw(canvas);
}
六、在layout XML中引用该自定义ViewGroup
到此为止,自定义ViewGroup的实现已经完成了,那我们就在项目里用一用吧!使用自定义ViewGroup和使用系统ViewGroup组件有两个小区别:
一、是要指定完整的包名,否则运行的时候会报找不到该组件。
二、是配置自定义属性的时候要需要另外指定一个名字空间,避免跟默认的android名字空间混淆。比如这里就指定了一个新的app名字空间来引用自定义属性。<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="@android:color/transparent"
android:paddingLeft="3dp"
android:paddingRight="3dp"
android:splitMotionEvents="false"
app:arrow_offset="31dp"
app:arrow_width="16dp"
app:arrow_height="8dp"
app:radius="5dp"
app:background_color="#ffb1df83"
app:shadow_color="#66000000"
app:shadow_thickness="5dp">
android:id="@+id/cmx_toolbar_menu_turn_off"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="42dp">
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="#FF393F4A"
android:paddingLeft="16dp"
android:paddingRight="32dp"
android:clickable="false"
android:text="Menu Item #1"/>
android:id="@+id/cmx_toolbar_menu_feedback"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="42dp">
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="#FF393F4A"
android:paddingLeft="16dp"
android:paddingRight="32dp"
android:clickable="false"
android:text="Menu Item #2"/>
七、在代码里引用该layout XML
这个就跟引用正常的layout XML没有什么区别了,这里主要是在创建弹出菜单的时候指定了刚刚那个layout XML,具体看下示例代码就清楚了。
至此,一个完整的自定义ViewGroup的流程就算走了一遍了,后面有时间可能还会写一些复杂一些的自定义组件,但是万变不离其宗,基本的原理跟步骤都是相同的。本文就是抛砖引玉,希望能给需要自定义ViewGroup的朋友一些帮助。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持PHP中文网
更多Android自定义ViewGroup实现带箭头的圆角矩形菜单相关文章请关注PHP中文网!
声明:本文原创发布php中文网,转载请注明出处,感谢您的尊重!如有疑问,请联系admin@php.cn处理





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








