在内核2.4中堆栈是这么定义的:
union task_union {
struct task_struct task;
unsigned long stack[INIT_TASK_SIZE/sizeof(long)];
};
而INIT_TASK_SIZE只能是8K。
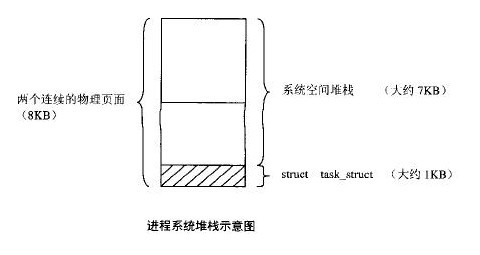
内核为每个进程分配一个task_struct结构时,实际上分配两个连续的物理页面(8192字节),如图所示。底部用作task_struct结构(大小约为1K字节),结构的上面用作内核堆栈(大小约为7K字节)。访问进程自身的task_struct结构,使用宏操作current, 在2.4中定义如下:
#define current get_current()
static inline struct task_struct * get_current(void)
{
struct task_struct *current;
__asm__("andl %%esp,%0; ":"=r" (current) : "" (~8191UL));
return current;
}
~8191UL表示最低13位为0, 其余位全为1。 %esp指向内核堆栈中,当屏蔽掉%esp的最低13后,就得到这个”两个连续的物理页面”的开头,而这个开头正好是task_struct的开始,从而得到了指向task_struct的指针。
在内核2.6中堆栈这么定义:
union thread_union {
struct thread_info thread_info;
unsigned long stack[THREAD_SIZE/sizeof(long)];
};
根据内核的配置,THREAD_SIZE既可以是4K字节(1个页面)也可以是8K字节(2个页面)。thread_info是52个字节长。
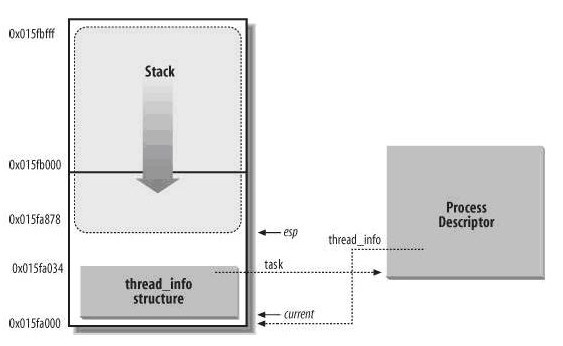
下图是当设为8KB时候的内核堆栈:Thread_info在这个内存区的开始处,内核堆栈从末端向下增长。进程描述符不是在这个内存区中,而分别通过task与thread_info指针使thread_info与进程描述符互联。所以获得当前进程描述符的current定义如下:
#define current get_current()
static inline struct task_struct * get_current(void)
{
return current_thread_info()->task;
}
static inline struct thread_info *current_thread_info(void)
{
struct thread_info *ti;
__asm__("andl %%esp,%0; ":"=r" (ti) : "" (~(THREAD_SIZE - 1)));
return ti;
}
根据THREAD_SIZE大小,分别屏蔽掉内核栈的12-bit LSB(4K)或13-bit LSB(8K),从而获得内核栈的起始位置。
struct thread_info {
struct task_struct *task; /* main task structure */
struct exec_domain *exec_domain; /* execution domain */
unsigned long flags; /* low level flags */
unsigned long status; /* thread-synchronous flags */
... ..
}
fork系统调用中调用dup_task_struct,其执行:
1, 执行alloc_task_struct宏,为新进程获取进程描述符,并将描述符放在局部变量tsk中。
2, 执行alloc_thread_info宏以获取一块空闲的内存区,用以存放新进程的thread_info结构和内核栈,并将这块内存区字段的地址放在局部变量ti中(8K 或 4K, 可配置)。
3, 将current进程描述符的内容复制到tsk所指向的task_struct结构中,然后把tsk->thread_info置为ti。
4, 把current进程的thread_info描述符的内容复制到ti中,然后把ti->task置为tsk。
5, 返回新进程的描述符指针tsk。
static struct task_struct *dup_task_struct(struct task_struct *orig)
{
struct task_struct *tsk;
struct thread_info *ti;
prepare_to_copy(orig);
tsk = alloc_task_struct();
if (!tsk)
return NULL;
ti = alloc_thread_info(tsk);
if (!ti) {
free_task_struct(tsk);
return NULL;
}
*tsk = *orig;
tsk->thread_info = ti;
setup_thread_stack(tsk, orig);
…..
}
# define alloc_task_struct() kmem_cache_alloc(task_struct_cachep, GFP_KERNEL)
#define alloc_thread_info(tsk) \
((struct thread_info *) __get_free_pages(GFP_KERNEL,THREAD_ORDER))
#endif
内核栈空间大小非常有限,故在内核中写程序时,注意尽量不要定义大的局部变量,尽量不要使用递归(导致函数调用栈过大而导致栈溢出),当需要空间时,使用kmalloc在堆中申请。





















 407
407











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








