写法不一样而功能完全相同的两条 SQL 的在性能方面的差异。
示例一
需求:取出某个 group(假设 id 为 100)下的用户编号(id),用户昵称(nick_name)、用户性别
( sexuality ) 、 用 户 签 名 ( sign ) 和 用 户 生 日 ( birthday ) , 并 按 照 加 入 组 的 时 间
(user_group.gmt_create)来进行倒序排列,取出前 20 个。
解决方案一、
SELECT id,nick_name
FROM user,user_group
WHERE user_group.group_id = 1
and user_group.user_id = user.id
limit 100,20;
解决方案二、
SELECT user.id,user.nick_name
FROM (
SELECT user_id
FROM user_group
WHERE user_group.group_id = 1
ORDER BY gmt_create desc
limit 100,20) t,user
WHERE t.user_id = user.id;
我们先来看看执行计划:
sky@localhost : example 10:32:13> explain
-> SELECT id,nick_name
-> FROM user,user_group
-> WHERE user_group.group_id = 1
-> and user_group.user_id = user.id
-> ORDER BY user_group.gmt_create desc
-> limit 100,20\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: user_group
type: ref
possible_keys: user_group_uid_gid_ind,user_group_gid_ind
key: user_group_gid_ind
key_len: 4
ref: const
rows: 31156
Extra: Using where; Using filesort
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: user
type: eq_ref
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 4
ref: example.user_group.user_id
rows: 1
Extra:
sky@localhost : example 10:32:20> explain
-> SELECT user.id,user.nick_name
-> FROM (
-> SELECT user_id
-> FROM user_group
-> WHERE user_group.group_id = 1
-> ORDER BY gmt_create desc
-> limit 100,20) t,user
-> WHERE t.user_id = user.id\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: PRIMARY
table:
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 20
Extra:
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: PRIMARY
table: user
type: eq_ref
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 4
ref: t.user_id
rows: 1
Extra:
*************************** 3. row ***************************
id: 2
select_type: DERIVED
table: user_group
type: ref
possible_keys: user_group_gid_ind
key: user_group_gid_ind
key_len: 4
ref: const
rows: 31156
Extra: Using filesort
执行计划对比分析:
解决方案一中的执行计划显示 MySQL 在对两个参与 Join 的表都利用到了索引,user_group 表利用了
user_group_gid_ind 索 引 ( key: user_group_gid_ind ) , user 表 利 用 到 了 主 键 索 引 ( key:
PRIMARY),在参与 Join 前 MySQL 通过 Where 过滤后的结果集与 user 表进行 Join,最后通过排序取出
Join 后结果的“limit 100,20”条结果返回。
解决方案二的 SQL 语句利用到了子查询,所以执行计划会稍微复杂一些,首先可以看到两个表都和
解决方案 1 一样都利用到了索引(所使用的索引也完全一样),执行计划显示该子查询以 user_group 为
驱动,也就是先通过 user_group 进行过滤并马上进行这一论的结果集排序,也就取得了 SQL 中的
“limit 100,20”条结果,然后与 user 表进行 Join,得到相应的数据。这里可能有人会怀疑在自查询中
从 user_group 表所取得与 user 表参与 Join 的记录条数并不是 20 条,而是整个 group_id=1 的所有结果。
那么清大家看看该执行计划中的第一行,该行内容就充分说明了在外层查询中的所有的 20 条记录全部被
返回。
通过比较两个解决方案的执行计划,我们可以看到第一中解决方案中需要和 user 表参与 Join 的记录
数 MySQL 通过统计数据估算出来是 31156,也就是通过 user_group 表返回的所有满足 group_id=1 的记录
数(系统中的实际数据是 20000)。而第二种解决方案的执行计划中,user 表参与 Join 的数据就只有 20
条,两者相差很大,通过本节最初的分析,我们认为第二中解决方案应该明显优于第一种解决方案。
下面我们通过对比两个解决觉方案的 SQL 实际执行的 profile 详细信息,来验证我们上面的判断。由
于 SQL 语句执行所消耗的最大两部分资源就是 IO 和 CPU,所以这里为了节约篇幅,仅列出 BLOCK IO 和 CPU
两项 profile 信息(Query Profiler 的详细介绍将在后面章节中独立介绍):
先打开 profiling 功能,然后分别执行两个解决方案的 SQL 语句:
sky@localhost : example 10:46:43> set profiling = 1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
sky@localhost : example 10:46:50> SELECT id,nick_name
-> FROM user,user_group
-> WHERE user_group.group_id = 1
-> and user_group.user_id = user.id
-> ORDER BY user_group.gmt_create desc
-> limit 100,20;
+--------+-----------+
| id | nick_name |
+--------+-----------+
| 990101 | 990101 |
| 990102 | 990102 |
| 990103 | 990103 |
| 990104 | 990104 |
| 990105 | 990105 |
| 990106 | 990106 |
| 990107 | 990107 |
| 990108 | 990108 |
| 990109 | 990109 |
| 990110 | 990110 |
| 990111 | 990111 |
| 990112 | 990112 |
| 990113 | 990113 |
| 990114 | 990114 |
| 990115 | 990115 |
| 990116 | 990116 |
| 990117 | 990117 |
| 990118 | 990118 |
| 990119 | 990119 |
| 990120 | 990120 |
+--------+-----------+
20 rows in set (1.02 sec)
sky@localhost : example 10:46:58> SELECT user.id,user.nick_name
-> FROM (
-> SELECT user_id
-> FROM user_group
-> WHERE user_group.group_id = 1
-> ORDER BY gmt_create desc
-> limit 100,20) t,user
-> WHERE t.user_id = user.id;
+--------+-----------+
| id | nick_name |
+--------+-----------+
| 990101 | 990101 |
| 990102 | 990102 |
| 990103 | 990103 |
| 990104 | 990104 |
| 990105 | 990105 |
| 990106 | 990106 |
| 990107 | 990107 |
| 990108 | 990108 |
| 990109 | 990109 |
| 990110 | 990110 |
| 990111 | 990111 |
| 990112 | 990112 |
| 990113 | 990113 |
| 990114 | 990114 |
| 990115 | 990115 |
| 990116 | 990116 |
| 990117 | 990117 |
| 990118 | 990118 |
| 990119 | 990119 |
| 990120 | 990120 |
+--------+-----------+
20 rows in set (0.96 sec)
查看系统中的 profile 信息,刚刚执行的两个 SQL 语句的执行 profile 信息已经记录下来了:
sky@localhost : example 10:47:07> show profiles\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Query_ID: 1
Duration: 1.02367600
Query: SELECT id,nick_name
FROM user,user_group
WHERE user_group.group_id = 1
and user_group.user_id = user.id
ORDER BY user_group.gmt_create desc
limit 100,20
*************************** 2. row ***************************
Query_ID: 2
Duration: 0.96327800
Query: SELECT user.id,user.nick_name
FROM (
SELECT user_id
FROM user_group
WHERE user_group.group_id = 1
ORDER BY gmt_create desc
limit 100,20) t,user
WHERE t.user_id = user.id
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
sky@localhost : example 10:47:34> SHOW profile CPU,BLOCK IO io FOR query 1;
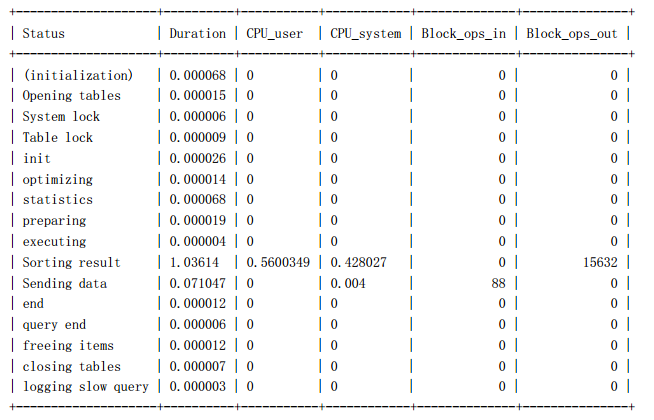
16 rows in set (0.00 sec)
sky@localhost : example 10:47:40> SHOW profile CPU,BLOCK IO io FOR query 2;
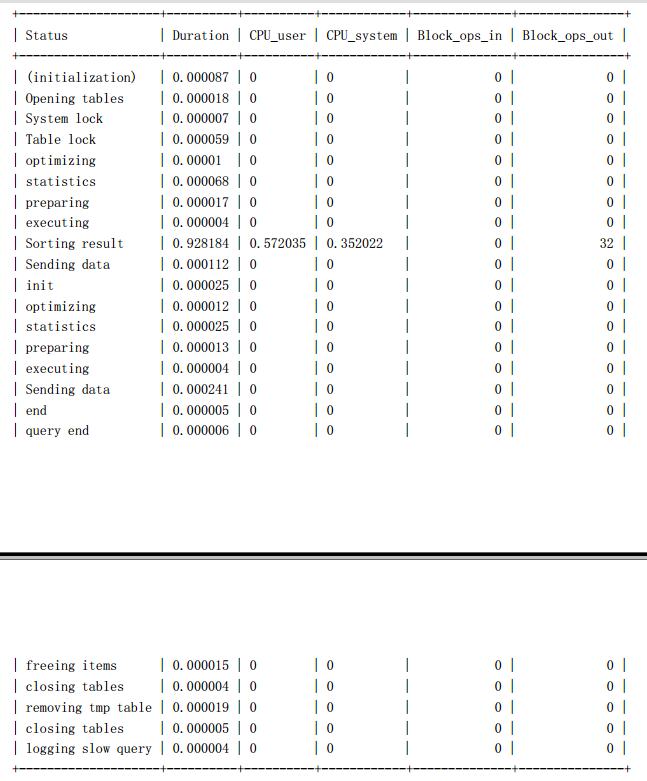
我们先看看两条 SQL 执行中的 IO 消耗,两者区别就在于“Sorting result”,我们回
顾一下前面执行计划的对比,两个解决方案的排序过滤数据的时机不一样,排序后需要取
得的数据量一个是 20000,一个是 20,正好和这里的 profile 信息吻合,第一种解决方案的
“Sorting result”的 IO 值是第二种解决方案的将近 500 倍。
然后再来看看 CPU 消耗,所有消耗中,消耗最大的也是“Sorting result”这一项,第
一个消耗多出的缘由和上面 IO 消耗差异是一样的。
结论:
通过上面两条功能完全相同的 SQL 语句的执行计划分析,以及通过实际执行后的
profile 数据的验证,都证明了第二种解决方案优于第一种解决方案。





















 392
392











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








