用户须要关心的事件是有限的。其它都由网络库负责。
TcpConnection中封装了InputBuffer和OutputBuffer,用来表示应用层的缓冲区。在发送数据时,假设不能一次将Buffer中的数据发送完成,它还会继续关注Channel中的可写事件,当sockfd可写时,会再次发送。
前面提到TcpConnection的生存期模糊,主要是由于我们不能在TcpServer中直接erase掉TcpConnection对象。由于此时有可能Channel中的handleEvent还在运行,假设析构TcpConnection对象。那么他的成员channel_也会被析构,会导致core dump。也就是说我们须要TcpConnection 对象生存期要长于handleEvent() 函数,直到运行完connectDestroyed() 后才会析构。
断开连接:
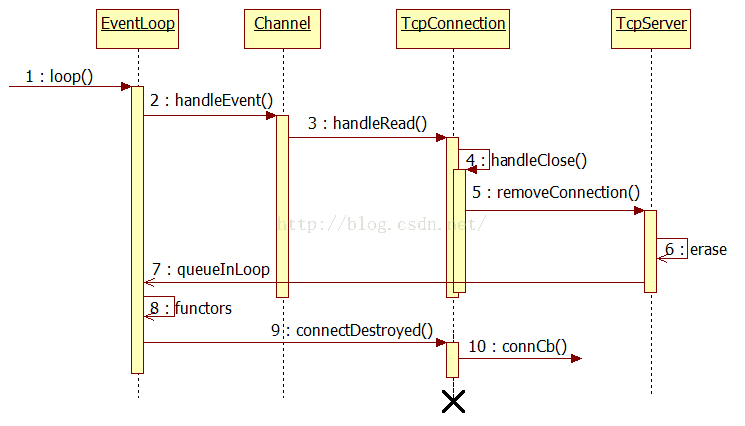
TcpConnection的断开是採用被动方式,即对方先关闭连接。本地read(2)返回0后。调用顺序例如以下:
handleClose()->TcpServer::removeConnection->TcpConnection::connectDestroyed()。
详细我们查看以下的连接关闭时序图:
当连接到来,创建一个TcpConnection对象。立马用shared_ptr来管理,引用计数为1,在Channel中维护一个weak_ptr(tie_),将这个shared_ptr对象赋值给_tie。引用计数仍然为1。当连接关闭时,在handleEvent中,将tie_提升,得到一个shard_ptr对象,引用计数就变成了2。当shared_ptr的计数不为0时,TcpConnection不会被销毁。
TcpConnection.h
class TcpConnection : boost::noncopyable,
public boost::enable_shared_from_this<TcpConnection>
{
public:
/// Constructs a TcpConnection with a connected sockfd
///
/// User should not create this object.
TcpConnection(EventLoop* loop,
const string& name,
int sockfd,
const InetAddress& localAddr,
const InetAddress& peerAddr);
~TcpConnection();
EventLoop* getLoop() const { return loop_; }
const string& name() const { return name_; }
const InetAddress& localAddress() { return localAddr_; }
const InetAddress& peerAddress() { return peerAddr_; }
bool connected() const { return state_ == kConnected; }
void setConnectionCallback(const ConnectionCallback& cb)
{ connectionCallback_ = cb; }
void setMessageCallback(const MessageCallback& cb)
{ messageCallback_ = cb; }
/// Internal use only.
void setCloseCallback(const CloseCallback& cb)
{ closeCallback_ = cb; }
// called when TcpServer accepts a new connection
void connectEstablished(); // should be called only once
// called when TcpServer has removed me from its map
void connectDestroyed(); // should be called only once
private:
enum StateE { kDisconnected, kConnecting, kConnected, kDisconnecting };
void handleRead(Timestamp receiveTime);
void handleClose();
void handleError();
void setState(StateE s) { state_ = s; }
EventLoop* loop_; // 所属EventLoop
string name_; // 连接名
StateE state_; // FIXME: use atomic variable
// we don't expose those classes to client.
boost::scoped_ptr<Socket> socket_;
boost::scoped_ptr<Channel> channel_;
InetAddress localAddr_;
InetAddress peerAddr_;
ConnectionCallback connectionCallback_;
MessageCallback messageCallback_;
CloseCallback closeCallback_;
};
typedef boost::shared_ptr<TcpConnection> TcpConnectionPtr;
}TcpConnection::TcpConnection(EventLoop* loop,
const string& nameArg,
int sockfd,
const InetAddress& localAddr,
const InetAddress& peerAddr)
: loop_(CHECK_NOTNULL(loop)),
name_(nameArg),
state_(kConnecting),
socket_(new Socket(sockfd)),
channel_(new Channel(loop, sockfd)),
localAddr_(localAddr),
peerAddr_(peerAddr)/*,
highWaterMark_(64*1024*1024)*/
{
// 通道可读事件到来的时候。回调TcpConnection::handleRead。_1是事件发生时间
channel_->setReadCallback(
boost::bind(&TcpConnection::handleRead, this, _1));
// 连接关闭,回调TcpConnection::handleClose
channel_->setCloseCallback(
boost::bind(&TcpConnection::handleClose, this));
// 错误发生,回调TcpConnection::handleError
channel_->setErrorCallback(
boost::bind(&TcpConnection::handleError, this));
LOG_DEBUG << "TcpConnection::ctor[" << name_ << "] at " << this
<< " fd=" << sockfd;
socket_->setKeepAlive(true);
}
TcpConnection::~TcpConnection()
{
LOG_DEBUG << "TcpConnection::dtor[" << name_ << "] at " << this
<< " fd=" << channel_->fd();
}
void TcpConnection::connectEstablished()
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
assert(state_ == kConnecting);
setState(kConnected);
LOG_TRACE << "[3] usecount=" << shared_from_this().use_count();
channel_->tie(shared_from_this());
channel_->enableReading(); // TcpConnection所相应的通道增加到Poller关注
connectionCallback_(shared_from_this());
LOG_TRACE << "[4] usecount=" << shared_from_this().use_count();
}
void TcpConnection::connectDestroyed()
{
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
if (state_ == kConnected)
{
setState(kDisconnected);
channel_->disableAll();
connectionCallback_(shared_from_this());
}
channel_->remove();
}
void TcpConnection::handleRead(Timestamp receiveTime)
{
/*
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
int savedErrno = 0;
ssize_t n = inputBuffer_.readFd(channel_->fd(), &savedErrno);
if (n > 0)
{
messageCallback_(shared_from_this(), &inputBuffer_, receiveTime);
}
else if (n == 0)
{
handleClose();
}
else
{
errno = savedErrno;
LOG_SYSERR << "TcpConnection::handleRead";
handleError();
}
*/
loop_->assertInLoopThread();
int savedErrno = 0;
char buf[65536];
ssize_t n = ::read(channel_->fd(), buf, sizeof buf);
if (n > 0)
{
messageCallback_(shared_from_this(), buf, n);
}
else if (n == 0)
{
handleClose();
}
else
{
errno = savedErrno;
LOG_SYSERR << "TcpConnection::handleRead";
handleError();
}
void Channel::handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime)
{
boost::shared_ptr<void> guard;
if (tied_)
{
guard = tie_.lock();
if (guard)
{
LOG_TRACE << "[6] usecount=" << guard.use_count();
handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime);
LOG_TRACE << "[12] usecount=" << guard.use_count();
}
}
else
{
handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime);
}
}參考:
《linux多线程服务端编程》
《muduo使用手冊》






















 7836
7836

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








