前些天,写了篇博客( 最后一年的时间,应该做些什么呢? )发誓要好好学一下《UNIX环境高级编译》(下面简称APUE),可一个小小的编译问题就悲剧了我好几天,比如APUE书上的第一个程序是这样的:
#include "apue.h" #include <dirent.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { DIR *dp; struct dirent *dirp; if(argc != 2) { err_quit("usage: ls directory_name"); } if((dp = opendir(argv[1])) == NULL) { err_sys("can`t open %s", argv[1]); } while((dirp = readdir(dp)) != NULL) { printf("%s/n", dirp->d_name); } closedir(dp); exit(0); }
直接这样用gcc编译会很悲剧的出现一大堆错误,错误这里就不罗列出来了。
其实细心的朋友会发现本程序第一行包含了一个apue.h的头文件,这个头文件在/usr/include可是没有的哦,也就是说这不是标准头文件,其实从它用双引号包含也可以看出来。那这个头文件在哪呢?
附录里。
找到了问题,解决就好办了,把附录里的apue.h和error.c敲进电脑里,我敲好了,懒得就直接复制吧。
/* Our own header, to be included before all standard system headers */ #ifndef _APUE_H #define _APUE_H #if defined(SOLARIS) #define _XOPEN_SOURCE 500 /* Single UNIX Specification, Version 2 for Solaris 9 */ #define CMSG_LEN(x) _CMSG_DATA_ALIGN(sizeof(struct cmsghdr)+(x)) #elif !defined(BSD) #define _XOPEN_SOURCE 600 /* Single UNIX Specification, Version 3 */ #endif #include <sys/types.h> /* some systems still require this */ #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/termios.h> /* for winsize */ #ifndef TIOCGWINSZ #include <sys/ioctl.h> #endif #include <stdio.h> /* for convenience */ #include <stdlib.h> /* for convenience */ #include <stddef.h> /* for offsetof */ #include <string.h> /* for convenience */ #include <unistd.h> /* for convenience */ #include <signal.h> /* for SIG_ERR */ #include <errno.h> #include <stdarg.h> #include <syslog.h> #include <error.h> #define MAXLINE 4096 /* max line length */ /****/ /* * Default file access permissions for new files. */ #define FILE_MODE (S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH) /* * Default permissions for new directories. */ #define DIR_MODE (FILE_MODE | S_IXUSR | S_IXGRP | S_IXOTH) typedef void Sigfunc(int); /* for signal handlers */ #if defined(SIG_IGN) && !defined(SIG_ERR) #define SIG_ERR ((Sigfunc *)-1) #endif #define min(a,b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) #define max(a,b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) /* * Prototypes for our own functions. */ char *path_alloc(int *); /* {Prog pathalloc} */ long open_max(void); /* {Prog openmax} */ void clr_fl(int, int); /* {Prog setfl} */ void set_fl(int, int); /* {Prog setfl} */ void pr_exit(int); /* {Prog prexit} */ void pr_mask(const char *); /* {Prog prmask} */ Sigfunc *signal_intr(int, Sigfunc *); /* {Prog signal_intr_function} */ int tty_cbreak(int); /* {Prog raw} */ int tty_raw(int); /* {Prog raw} */ int tty_reset(int); /* {Prog raw} */ void tty_atexit(void); /* {Prog raw} */ #ifdef ECHO /* only if <termios.h> has been included */ struct termios *tty_termios(void); /* {Prog raw} */ #endif void sleep_us(unsigned int); /* {Ex sleepus} */ ssize_t readn(int, void *, size_t); /* {Prog readn_writen} */ ssize_t writen(int, const void *, size_t); /* {Prog readn_writen} */ void daemonize(const char *); /* {Prog daemoninit} */ int s_pipe(int *); /* {Progs streams_spipe sock_spipe} */ int recv_fd(int, ssize_t (*func)(int, const void *, size_t));/* {Progs recvfd_streams recvfd_sockets} */ int send_fd(int, int); /* {Progs sendfd_streams sendfd_sockets} */ int send_err(int, int, const char *); /* {Prog senderr} */ int serv_listen(const char *); /* {Progs servlisten_streams servlisten_sockets} */ int serv_accept(int, uid_t *); /* {Progs servaccept_streams servaccept_sockets} */ int cli_conn(const char *); /* {Progs cliconn_streams cliconn_sockets} */ int buf_args(char *, int (*func)(int, char **)); /* {Prog bufargs} */ int ptym_open(char *, int); /* {Progs3 ptyopen_streams ptyopen_bsd ptyopen_linux} */ int ptys_open(char *); /* {Progs3 ptyopen_streams ptyopen_bsd ptyopen_linux} */ #ifdef TIOCGWINSZ pid_t pty_fork(int *, char *, int, const struct termios *, const struct winsize *); /* {Prog ptyfork} */ #endif int lock_reg(int, int, int, off_t, int, off_t); /* {Prog lockreg} */ #define read_lock(fd, offset, whence, len) / lock_reg((fd), F_SETLK, F_RDLCK, (offset), (whence), (len)) #define readw_lock(fd, offset, whence, len) / lock_reg((fd), F_SETLKW, F_RDLCK, (offset), (whence), (len)) #define write_lock(fd, offset, whence, len) / lock_reg((fd), F_SETLK, F_WRLCK, (offset), (whence), (len)) #define writew_lock(fd, offset, whence, len) / lock_reg((fd), F_SETLKW, F_WRLCK, (offset), (whence), (len)) #define un_lock(fd, offset, whence, len) / lock_reg((fd), F_SETLK, F_UNLCK, (offset), (whence), (len)) pid_t lock_test(int, int, off_t, int, off_t); /* {Prog locktest} */ #define is_read_lockable(fd, offset, whence, len) / (lock_test((fd), F_RDLCK, (offset), (whence), (len)) == 0) #define is_write_lockable(fd, offset, whence, len) / (lock_test((fd), F_WRLCK, (offset), (whence), (len)) == 0) void err_dump(const char *, ...); /* {App misc_source} */ void err_msg(const char *, ...); void err_quit(const char *, ...); void err_exit(int, const char *, ...); void err_ret(const char *, ...); void err_sys(const char *, ...); void log_msg(const char *, ...); /* {App misc_source} */ void log_open(const char *, int, int); void log_quit(const char *, ...); void log_ret(const char *, ...); void log_sys(const char *, ...); void TELL_WAIT(void); /* parent/child from {Sec race_conditions} */ void TELL_PARENT(pid_t); void TELL_CHILD(pid_t); void WAIT_PARENT(void); void WAIT_CHILD(void); #endif /* _APUE_H */
#include "apue.h" #include <errno.h> /* for definition of errno */ #include <stdarg.h> /* ISO C variable aruments */ static void err_doit(int, int, const char *, va_list); /* * Nonfatal error related to a system call. * Print a message and return. */ void err_ret(const char *fmt, ...) { va_list ap; va_start(ap, fmt); err_doit(1, errno, fmt, ap); va_end(ap); } /* * Fatal error related to a system call. * Print a message and terminate. */ void err_sys(const char *fmt, ...) { va_list ap; va_start(ap, fmt); err_doit(1, errno, fmt, ap); va_end(ap); exit(1); } /* * Fatal error unrelated to a system call. * Error code passed as explict parameter. * Print a message and terminate. */ void err_exit(int error, const char *fmt, ...) { va_list ap; va_start(ap, fmt); err_doit(1, error, fmt, ap); va_end(ap); exit(1); } /* * Fatal error related to a system call. * Print a message, dump core, and terminate. */ void err_dump(const char *fmt, ...) { va_list ap; va_start(ap, fmt); err_doit(1, errno, fmt, ap); va_end(ap); abort(); /* dump core and terminate */ exit(1); /* shouldn't get here */ } /* * Nonfatal error unrelated to a system call. * Print a message and return. */ void err_msg(const char *fmt, ...) { va_list ap; va_start(ap, fmt); err_doit(0, 0, fmt, ap); va_end(ap); } /* * Fatal error unrelated to a system call. * Print a message and terminate. */ void err_quit(const char *fmt, ...) { va_list ap; va_start(ap, fmt); err_doit(0, 0, fmt, ap); va_end(ap); exit(1); } /* * Print a message and return to caller. * Caller specifies "errnoflag". */ static void err_doit(int errnoflag, int error, const char *fmt, va_list ap) { char buf[MAXLINE]; vsnprintf(buf, MAXLINE, fmt, ap); if (errnoflag) snprintf(buf+strlen(buf), MAXLINE-strlen(buf), ": %s", strerror(error)); strcat(buf, " "); fflush(stdout); /* in case stdout and stderr are the same */ fputs(buf, stderr); fflush(NULL); /* flushes all stdio output streams */ }
这样涉及到两个文件的同时编译问题,如果你更懒,那么还有办法解决。
给个批处理用用吧。
#!/bin/sh #gg #以下是修改的gg脚本,添加了一个函数,indent每一个.c和.h的功能 #wraper the gcc #set -x #用indent所有的c文件和头文件(因为我向ssh中拷代码的时候缩进总是出问题,所以需要indent) go2indent() { for tt in $* do char=`echo $tt|cut -d. -f2` if [ $char = "c" -o $char = "h" ]; then char="" #此处indent格式自己修改。 indent -ts2 -bli0 $tt rm $tt~ >/dev/null 2>&1 fi done } #不需要indent的话,直接注释下面这条语句 go2indent $* exec_obj=`echo $1|cut -d. -f1` if gcc error.c $* -Wall -o $exec_obj; then echo "gcc Done! Create executable file /"$exec_obj/"." else echo "gcc failed!" exit 1 fi #end
把批处理命名为gg,是不是迫不及待的想试试了?
不过,还有等一下,应该此时你还没有执行权限,敲命令sudo chmod 755 gg提升权限。然后别忘了用ls -l看一下,如果是该文件权限是-rwxr-xr-x,即本用户和超级用户读写执行,本组用户读执行,其他用户执行。
以后只要把这3个文件拷贝到你编写的APUE例程文件夹中,以./gg 文件名,来进行编译就可以了

这样操作就可以了。
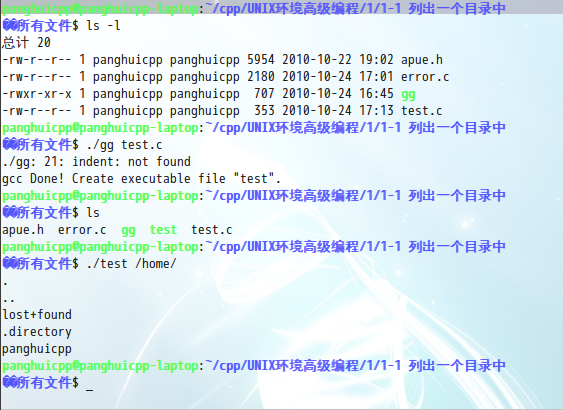
好了,可以好好的,认真的,仔细的,开始看伟大的著作APUE喽。
但愿可以学好。






















 583
583

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








