1、STL算法--find_if()
(1)、代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
using namespace std;
template<typename Type>
class IsDiv{
public:
IsDiv(const Type &divisor){
this->divisor = divisor;
}
bool operator()(Type &t){
return t%divisor == 0;
}
protected:
private:
Type divisor;
};
int main(void){
vector<int> v2;
for(int i = 10; i < 33; i++){
v2.push_back(i);
}
int a = 4;
IsDiv<int> myDiv(a);
//find_if(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myDiv);
vector<int>::iterator it;
it =find_if(v2.begin(), v2.end(), IsDiv<int>(a) );
if(it == v2.end()){
cout<<"容器中没有值是4的元素"<<endl;
}else{
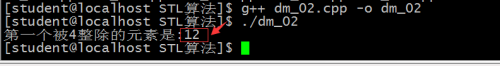
cout<<"第一个被4整除的元素是:"<<*it<<endl;
}
return 0;
}(2)、运行结果:
2、STL算法--plus的使用
(1)、代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
using namespace std;
//plus 预定义好的函数对象,能实现不同数据 + 算法;
//实现了数据类型和算法的分离======》通过函数对象技术实现的;
//
//思考,怎么知道plus<type>是2个参数------>多看看源码;
void main21(){
plus<int> intAdd;
int x = 10;
int y = 20;
int z = intAdd(x, y);
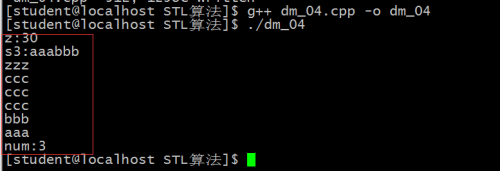
cout<<"z:"<<z<<endl;
plus<string> stringAdd;
string s1 = "aaa";
string s2 = "bbb";
string s3 = stringAdd(s1, s2);
cout<<"s3:"<<s3<<endl;
vector<string> v1;
v1.push_back("bbb");
v1.push_back("aaa");
v1.push_back("ccc");
v1.push_back("zzz");
v1.push_back("ccc");
v1.push_back("ccc");
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end(), greater<string>()); //降序排列;
vector<string>::iterator it;
for(it = v1.begin(); it != v1.end(); it++){
cout<<*it<<endl;
}
//求“ccc”出现的字符串的个数;
string sc = "ccc"; //函数适配器:将函数和参数强行绑定;
//equal_to<string>有2个参数,left参数来自容器,right参数来自sc,
//bind2nd就是函数适配器:把预定义函数对象和第二个参数进行绑定;`
int num = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), bind2nd(equal_to<string>(), sc));
cout<<"num:"<<num<<endl;
}
int main(void){
main21();
return 0;
}(2)、运行结果:
3、STL算法--for_each()
(1)、代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
using namespace std;
void printV(vector<int> &v){
vector<int>::iterator it;
for(it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++){
cout<<*it<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
void showElem(int &n){
cout<<n<<" ";
}
class MyShow{
public:
MyShow(){
num = 0;
}
void operator()(int &n){
num++;
cout<<n<<" ";
}
void printNum(){
cout<<"num :"<<num<<endl;
}
private:
int num;
};
int main(void){
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(3);
v1.push_back(5);
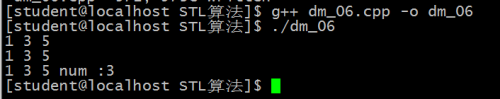
printV(v1);
//第三个参数是:函数对象/回掉函数
//for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), showElem); //利用的是回调函数
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), MyShow()); //利用的是函数对象(这个类中重载了())
//函数的返回值是函数对象
cout<<endl;
MyShow my1 = for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), MyShow()); //利用的是函数对象(这个类中重载了())
my1.printNum();
return 0;
}(2)、运行结果:
4、for_each()和transform()的区别
(1)、代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
using namespace std;
void showElem(int &n){
cout<<n<<" ";
}
int showElem2(int &n){
cout<<n<<" ";
return n;
}
//for_each和transform的本质区别:
//结论:
//1、一般情况下,for_each所使用的函数对象,参数是引用,没有返回值;
//2、transform所使用的函数对象,参数一般不使用引用,而是还有返回值;
int main(void){
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(3);
v1.push_back(5);
vector<int> v2 = v1;
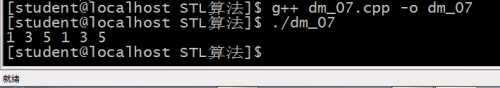
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), showElem);
transform(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v2.begin(), showElem2);//transform对回调函数的要求;返回值必须有
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}运行结果:
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/wait0804/1876418





















 360
360











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








