今天在看源码的时候看到了一个类叫AtomicInteger,所以决定探索一番。
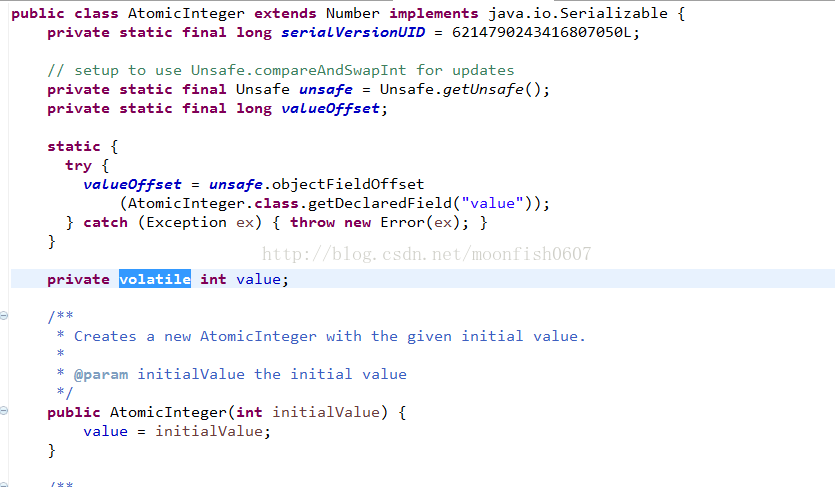
从源码中看出,AtomicInteger继承自Number类,值得注意的是其中的value属性是用volatile关键字修饰的,这个关键字在java 1.5之前经常容易引发一些意想不到的错误,之后得到了优化,才得以重生。这里先简单的说下volatile关键字吧,被其修饰的变量当线程前来访问的时候,会去读取该变量被修改后的值,从而达到维持有序性的目的。volatile有两个有两个特性,被其修饰的变量对所有线程可见,另一个则是禁止了指令的重排序优化。至于对volatile关键字具体分析要放到另外的篇幅里面了。
下面回到AtomicIntger类,举几个例子来表明其用处。
package test;
public class Test1 {
static int num;
static boolean flag;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = getThread();
t1.start();
Thread t2 = getThread();
t2.start();
while (true) {
if(!t1.isAlive() && !t2.isAlive()){
System.out.println("最终计算结果为:" + num);
break;
}
}
}
public static Thread getThread() {
return new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
num++;
}
Thread.yield();
}
});
}
}
这是一个简单多线程同时对一个变量进行操作的例子,我们可以在控制台看到如下打印:

从系统打印可以看出,因为同一个数据被多个线程同时操作,并且没有做任何处理,从而导致了程序错误。传统的解决方法是在操作处加上synchronized关键字从而避免并发线程同时访问,代码如下:
package test;
public class Test1 {
static int num;
static boolean flag;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = getThread();
t1.start();
Thread t2 = getThread();
t2.start();
while (true) {
if(!t1.isAlive() && !t2.isAlive()){
System.out.println("最终计算结果为:" + num);
break;
}
}
}
public static Thread getThread() {
return new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (Test1.class) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
num++;
}
}
Thread.yield();
}
});
}
}
执行上述代码可以看到如下打印:

下面将尝试使用AtomicInteger来取代使用synchronized关键字的使用,代码如下:
package test;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class Test1 {
static AtomicInteger ato = new AtomicInteger(0);
static boolean flag;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = getThread();
t1.start();
Thread t2 = getThread();
t2.start();
while (true) {
if(!t1.isAlive() && !t2.isAlive()){
System.out.println("最终计算结果为:" + ato.get());
break;
}
}
}
public static Thread getThread() {
return new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
ato.incrementAndGet();
}
Thread.yield();
}
});
}
}
控制台输出如下:

由此可见,AtomicInteger是可以线程安全的进行加减操作,非常适合高并发的情况。但因为其内部使用了volatile关键字,使得jvm的一些优化功能被停用了,所以还是需要根据实际场景来使用。





















 1500
1500











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








