VFS中还有2个专门针对文件系统的2个对象,
- struct file_system_type: 用来描述文件系统的类型(比如ext3,ntfs等等)
- struct vfsmount : 描述一个安装文件系统的实例
file_system_type 结构体位于:<linux/fs.h>
struct file_system_type {
const char *name; /* 文件系统名称 */
int fs_flags; /* 文件系统类型标志 */
/* 从磁盘中读取超级块,并且在文件系统被安装时,在内存中组装超级块对象 */
int (*get_sb) (struct file_system_type *, int,
const char *, void *, struct vfsmount *);
/* 终止访问超级块 */
void (*kill_sb) (struct super_block *);
struct module *owner; /* 文件系统模块 */
struct file_system_type * next; /* 链表中下一个文件系统类型 */
struct list_head fs_supers; /* 超级块对象链表 */
/* 下面都是运行时的锁 */
struct lock_class_key s_lock_key;
struct lock_class_key s_umount_key;
struct lock_class_key i_lock_key;
struct lock_class_key i_mutex_key;
struct lock_class_key i_mutex_dir_key;
struct lock_class_key i_alloc_sem_key;
};每种文件系统,不管由多少个实例安装到系统中,还是根本没有安装到系统中,都只有一个 file_system_type 结构。
======================================================================================================================
当文件系统被实际安装时,会在安装点创建一个 vfsmount 结构体。
结构体代表文件系统的实例,也就是文件系统被安装几次,就会创建几个 vfsmount
vfsmount 的定义参见:<linux/mount.h>
struct vfsmount {
struct list_head mnt_hash; /* 散列表 */
struct vfsmount *mnt_parent; /* 父文件系统,也就是要挂载到哪个文件系统 */
struct dentry *mnt_mountpoint; /* 安装点的目录项 */
struct dentry *mnt_root; /* 该文件系统的根目录项 */
struct super_block *mnt_sb; /* 该文件系统的超级块 */
struct list_head mnt_mounts; /* 子文件系统链表 */
struct list_head mnt_child; /* 子文件系统链表 */
int mnt_flags; /* 安装标志 */
/* 4 bytes hole on 64bits arches */
const char *mnt_devname; /* 设备文件名 e.g. /dev/dsk/hda1 */
struct list_head mnt_list; /* 描述符链表 */
struct list_head mnt_expire; /* 到期链表的入口 */
struct list_head mnt_share; /* 共享安装链表的入口 */
struct list_head mnt_slave_list;/* 从安装链表 */
struct list_head mnt_slave; /* 从安装链表的入口 */
struct vfsmount *mnt_master; /* 从安装链表的主人 */
struct mnt_namespace *mnt_ns; /* 相关的命名空间 */
int mnt_id; /* 安装标识符 */
int mnt_group_id; /* 组标识符 */
/*
* We put mnt_count & mnt_expiry_mark at the end of struct vfsmount
* to let these frequently modified fields in a separate cache line
* (so that reads of mnt_flags wont ping-pong on SMP machines)
*/
atomic_t mnt_count; /* 使用计数 */
int mnt_expiry_mark; /* 如果标记为到期,则为 True */
int mnt_pinned; /* "钉住"进程计数 */
int mnt_ghosts; /* "镜像"引用计数 */
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
int *mnt_writers; /* 写者引用计数 */
#else
int mnt_writers; /* 写者引用计数 */
#endif
};文件系统和进程相关的数据结构
以上介绍的都是在内核角度看到的 VFS 各个结构,所以结构体中包含的属性非常多。
而从进程的角度来看的话,大多数时候并不需要那么多的属性,所有VFS通过以下3个结构体和进程紧密联系在一起。
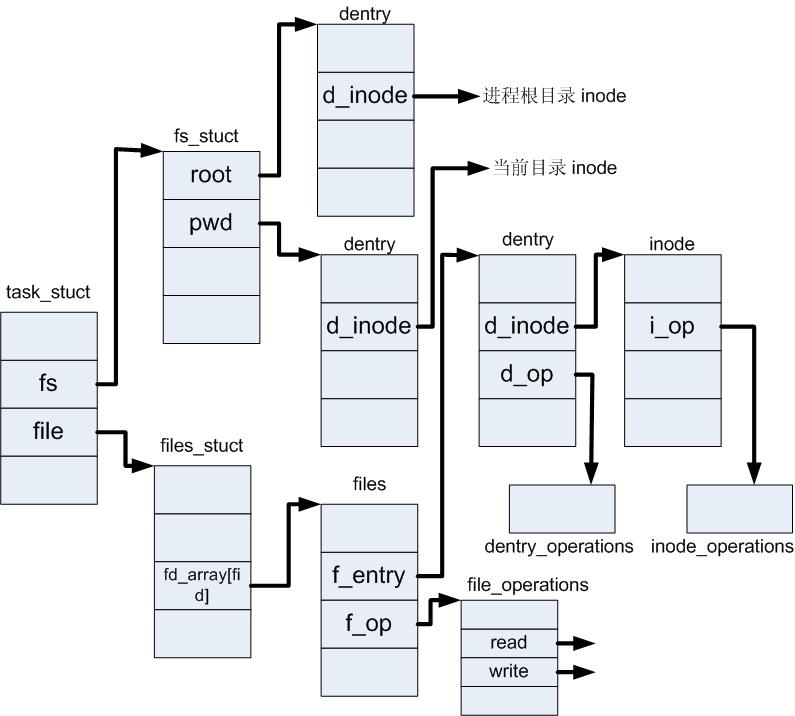
- struct files_struct :由进程描述符中的 files 目录项指向,所有与单个进程相关的信息(比如打开的文件和文件描述符)都包含在其中。
- struct fs_struct :由进程描述符中的 fs 域指向,包含文件系统和进程相关的信息。
- struct mmt_namespace :由进程描述符中的 mmt_namespace 域指向。
struct files_struct 位于:<linux/fdtable.h>
//文件描述表
struct fdtable {
unsigned int max_fds;
struct file ** fd; /* current fd array */
fd_set *close_on_exec;
fd_set *open_fds;
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct fdtable *next;
};
/*
* Open file table structure
*/
struct files_struct {
atomic_t count; /* 使用计数 */
struct fdtable *fdt; /* 指向其他fd表的指针 */
struct fdtable fdtab;/* 基 fd 表 进程的关联的所有文件数组*/
spinlock_t file_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp; /* 单个文件的锁 */
int next_fd; /* 缓存下一个可用的fd */
struct embedded_fd_set close_on_exec_init; /* exec()时关闭的文件描述符链表 */
struct embedded_fd_set open_fds_init; /* 打开的文件描述符链表 */
struct file * fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT]; /* 缺省的文件对象数组 NR_OPEN_DEFAULT在64位系统中等于64*/
};-
task_struct-> files_struct-> fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT]是一个struct file 数组 ,进程打开文件小于64个文件时
-
task_struct->files_struct->fdtable->fd 是一个struct file 数组,进程打开文件大于64个文件
当新打开文件时,就会新建一个struct file结构体,然后将这个结构体会赋值给上面的指针。
struct fs_struct 位于:<linux/fs_struct.h>
struct fs_struct {
int users; /* 用户数目 */
rwlock_t lock; /* 保护结构体的读写锁 */
int umask; /* 掩码 */
int in_exec; /* 当前正在执行的文件 */
struct path root, pwd; /* 根目录路径和当前工作目录路径 */
};struct mmt_namespace 位于:<linux/mmt_namespace.h>
但是在2.6内核之后似乎没有这个结构体了,而是用 struct nsproxy 来代替。
以下是 struct task_struct 结构体中关于文件系统的3个属性。
struct task_struct 的定义位于:<linux/sched.h>
/* filesystem information */
struct fs_struct *fs;
/* open file information */
struct files_struct *files; //进程打开文件
/* namespaces */
struct nsproxy *nsproxy;





















 871
871











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








