题解:
判断一个链表是不是回文的,这里要求O(n)时间复杂度和O(1)的空间时间复杂度,总共想了三种办法,三种办法都用到了两个指针,符合题目要求的只有最后一种。
第一种办法:用数组倒着存前半段的链表的值,然后和后半段链表的值进行比较。这种解法运行的时间最久可能是因为数组倒着插入比较耗时。
代码:
[java] view plain copy
- //用数组实现 o(n/2)空间
- public static boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
- // ArrayList<Integer> nodeVal=new ArrayList<>();
- LinkedList<Integer> nodeVal=new LinkedList<>();
- if(head==null||head.next==null)
- return true;
- ListNode slow=head;
- ListNode fast=head;
- nodeVal.add(0,slow.val);
- while(fast.next!=null&&fast.next.next!=null)
- {
- fast=fast.next.next;
- slow=slow.next;
- nodeVal.add(0,slow.val);
- }
- ListNode cur=slow;
- if(fast.next!=null)//链表长度为偶数
- cur=slow.next;
- int i=0;
- while(cur!=null)
- {
- if(nodeVal.get(i)!=cur.val)
- return false;
- cur=cur.next;
- i++;
- }
- return true;
- }
第二种解法:在第一种的思路的基础上,我们要实现一个倒序,我们干嘛不用现成的数据结构-栈,于是把链表前半段压栈,然后出栈和后面的链表依次比较,这种运行时间最短,但因为用到了栈还是不符合题目要求。
代码:
[java] view plain copy
- //用栈实现
- public static boolean isPalindrome2(ListNode head) {
- Stack<ListNode> stack=new Stack<>();
- ListNode slow=head;
- ListNode fast=head;
- if(fast==null||fast.next==null)//0个节点或是1个节点
- return true;
- stack.push(slow);
- while(fast.next!=null&&fast.next.next!=null)
- {
- fast=fast.next.next;
- slow=slow.next;
- stack.push(slow);
- }
- if(fast.next!=null)//链表长度为偶数
- slow=slow.next;
- ListNode cur=slow;
- while(cur!=null)
- {
- if(cur.val!=stack.pop().val)
- return false;
- cur=cur.next;
- }
- return true;
- }
第三种:我们这样想,我们可不可以不借助外在的存储实现倒序呢,其实是可以的,链表反转的时候我们就没有借助外在存储。思路是把后半段的原地链表反转然后和前半段进行比较(当然你也可以反转前半段)运行时间稍微比第二种慢一些,但是符合题目O(1)空间复杂度的要求
代码:
[java] view plain copy
- //链表原地转置实现o(1)空间复杂度
- public static boolean isPalindrome3(ListNode head) {
- ListNode slow=head;
- ListNode fast=head;
- if(fast==null||fast.next==null)//0个节点或是1个节点
- return true;
- while(fast.next!=null&&fast.next.next!=null)
- {
- fast=fast.next.next;
- slow=slow.next;
- }
- //对链表后半段进行反转
- ListNode midNode=slow;
- ListNode firNode=slow.next;//后半段链表的第一个节点
- ListNode cur=firNode.next;//插入节点从第一个节点后面一个开始
- firNode.next=null;//第一个节点最后会变最后一个节点
- while(cur!=null)
- {
- ListNode nextNode=cur.next;//保存下次遍历的节点
- cur.next=midNode.next;
- midNode.next=cur;
- cur=nextNode;
- }
- //反转之后对前后半段进行比较
- slow=head;
- fast=midNode.next;
- while(fast!=null)
- {
- if(fast.val!=slow.val)
- return false;
- slow=slow.next;
- fast=fast.next;
- }
- return true;
- }
快行指针找到链表中间结点
1. 反转前半部分看是否和后半部分一样
2. 将前半部分入栈,迭代访问剩下的一半结点,每次的栈顶元素一样则是回文链表
[java] view plain copy
- import java.util.Stack;
- public class isHuiWen {
- public boolean isPalinddrome(LinkedListNode head) {
- LinkedListNode fast = head;
- LinkedListNode slow = head;
- Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
- while( fast != null && fast.next != null ) {
- stack.push(slow.data);
- slow = slow.next;
- fast = fast.next.next;
- }
- //如果链表有奇数个元素,那么fast这时不为空,则比较后半段时跳过中间元素
- if ( fast != null ) {
- slow = slow.next;
- }
- while (slow != null) {
- int top = stack.pop().intValue();
- //如果不相同,则不是回文
- if (top != slow.data) {
- return false;
- }
- slow= slow.next;
- }
- return true;
- }
- }
递归的解法:
[java] view plain copy
- class Result{
- public LinkedListNode node;
- public boolean result;
- }
- Result isPalindromeRecurse(LinkedListNode head, int length) {
- if (head == null || length == 0) {
- return new Result(null, true);
- }
- else if(length == 1) {
- return new Result(head.next,true);
- }
- else if(length == 2) {
- return new Result(head.next.next, head.data == head.next.data);
- }
- Result res = isPalindromeRecurse(head.next, length -2);
- if(!res.result || res.node == null){
- return res;
- }
- else{
- res.result = head.data == res.node.data;
- res.node = res.node.next;
- return res;
- }
- }
- boolean isPalinddrome(LinkedListNode head) {
- Result p = isPalindromeRecurse(head, listSize(head));
- return p.result;
- }
思路:
1 Iterative,利用栈,把链表前半段存入栈,再逐个弹栈和链表后半段比较。注意链表长度为奇数的情况!要跳过中间节点!
2 递归!
定义递归函数为 Result rec(LinkedListNode head, int length) 意义为 传入链表头结点和链表长度,返回该链表的尾节点的下一个节点
Result是一个Wrapper 类,包含了node和当前是否match的判断
递归的关键是要清楚递归函数的每一个参数的意义是什么,还有返回值的意义是什么!!!
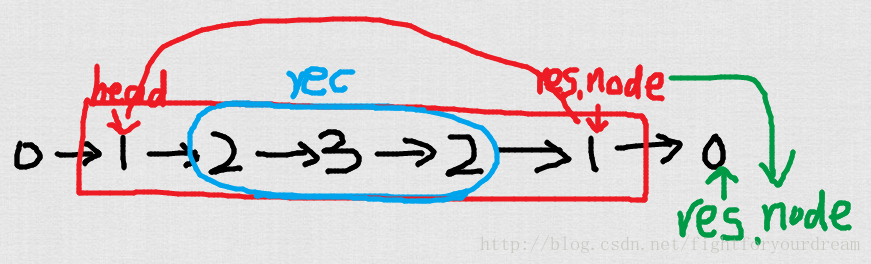
如下图:假设在递归的某一个阶段,要比较前半段的那个1和后半段的那个1是否相等:
根据递归可以得到蓝色部分的返回值Result,包含了一个res.node和match值。res.node的意义就是该子链表的尾节点的下一个节点,即后半段的1!
然后我们可以把head指向的1和res.node指向的1比较。如果相同则设置match为true,并且更新本层递归(红色区域)的返回值为本层子链表的尾节点(1)的下一个节点(0),作为res.node返回。
[java] view plain copy
- package LinkLists;
- import java.util.Stack;
- import CtCILibrary.LinkedListNode;
- public class S2_7 {
- // 利用栈,把链表前半段存入栈,再逐个弹栈和链表后半段比较
- public static boolean isPalindrome(LinkedListNode head) {
- LinkedListNode fast = head;
- LinkedListNode slow = head;
- Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
- while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
- stack.push(slow.data);
- slow = slow.next;
- fast = fast.next.next;
- }
- if (fast != null) { // 只有当链表长度为奇数时,fast才不会为null
- slow = slow.next; // 这时要跳过中间节点
- }
- while (slow != null) { // 边弹栈边比较
- int top = stack.pop().intValue();
- if (top != slow.data) {
- return false;
- }
- slow = slow.next;
- }
- return true;
- }
- // 递归
- public static boolean isPalindrome2(LinkedListNode head) {
- int size = 0;
- LinkedListNode n = head;
- while (n != null) {
- size++;
- n = n.next;
- }
- Result p = rec(head, size);
- return p.match;
- }
- // 传入链表头结点和链表长度,返回该链表的尾节点的下一个节点
- public static Result rec(LinkedListNode head, int length) {
- if (head == null || length == 0) { // 空链表,肯定是回文
- return new Result(null, true);
- } else if (length == 1) { // 只有1个节点,肯定是回文
- return new Result(head.next, true);
- } else if (length == 2) { // 有两个节点,如果相同则是回文
- return new Result(head.next.next, head.data == head.next.data);
- }
- Result res = rec(head.next, length-2); // 长度缩小2的子链表问题,res存放子问题的结果和子链表尾节点的下一个节点
- if(!res.match || res.node==null) { // 不match
- return res;
- } else{
- res.match = head.data == res.node.data; // 比较当前节点和尾节点是否相等
- res.node = res.node.next; // 更新返回值,即该链表的尾节点的下一个节点
- return res;
- }
- }
- static class Result {
- public LinkedListNode node;
- public boolean match;
- public Result(LinkedListNode n, boolean res) {
- node = n;
- match = res;
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int length = 10;
- LinkedListNode[] nodes = new LinkedListNode[length];
- for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
- nodes[i] = new LinkedListNode(i >= length / 2 ? length - i - 1 : i, null, null);
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
- if (i < length - 1) {
- nodes[i].setNext(nodes[i + 1]);
- }
- if (i > 0) {
- nodes[i].setPrevious(nodes[i - 1]);
- }
- }
- // nodes[length - 2].data = 9; // Uncomment to ruin palindrome
- LinkedListNode head = nodes[0];
- System.out.println(head.printForward());
- System.out.println(isPalindrome2(head));
- }
- }






















 568
568











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








