转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_26525215
本文源自【大学之旅_谙忆的博客】
用AspectJExpressionPointcut实现的切点比JdkRegexpMethodPointcut实现切点的好处就是,在设置切点的时候可以用切点语言来更加精确的表示拦截哪个方法!
可以精确到返回参数,参数类型,方法名。
当然,也可以模糊匹配。
这里用纯Java的方式和配置xml的方法都来演示一遍。
需要的包什么的就不解释了,如不动,请参考前面的。
首先,准备好原型对象Person
package cn.hncu.spring3x.aop.aspectj;
public class Person {
public int run(){
System.out.println("我在run...");
return 0;
}
public void run(int i){
System.out.println("我在run...<"+i+">");
}
public void say(){
System.out.println("我在say...");
}
public void sayHi(String name){
System.out.println("Hi,"+name+",你好");
}
public int say(String name, int i){
System.out.println(name+ "----"+ i);
return 0;
}
}
然后,用两种方式来拦截这个对象。
纯Java方式实现
4步曲:
1、声明出代理工厂。
2、设置切点
3、设置通知
4、为工厂添加切面
请记住:切面=切点+通知
AspectjDemo
package cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj;
import org.aopalliance.aop.Advice;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.aop.Advisor;
import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJExpressionPointcut;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor;
public class AspectjDemo {
@Test
public void demo(){
ProxyFactoryBean factory = new ProxyFactoryBean();
factory.setTarget(new Person());
//声明一个aspectj切点
AspectJExpressionPointcut cut = new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
//设置需要拦截的方法-用切点语言来写
cut.setExpression("execution( int cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj.Person.run() )");//拦截:空参返回值为int的run方法
Advice advice = new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("放行前拦截...");
Object obj = invocation.proceed();//放行
System.out.println("放行后拦截...");
return obj;
}
};
//切面=切点+通知
Advisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(cut,advice);
factory.addAdvisor(advisor);
Person p = (Person) factory.getObject();
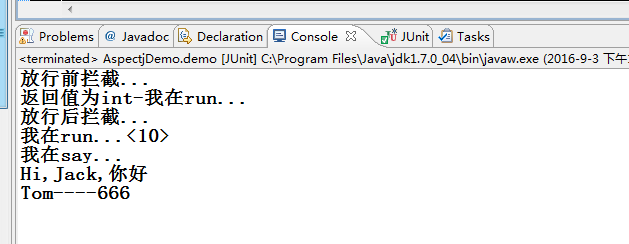
p.run();
p.run(10);
p.say();
p.sayHi("Jack");
p.say("Tom", 666);
}
}
运行结果:
切点语言:
AspectJExpressionPointcut对象在调用:
setExpression时,这个方法的参数就是使用切点语言的。
切点语言格式:
execution ( 返回类型 方法路径.方法名(参数) )例子:
//声明一个aspectj切点
AspectJExpressionPointcut cut = new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
cut.setExpression("execution( int cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj.Person.run() )");//拦截:空参返回值为int的run方法
cut.setExpression("execution( void cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj.Person.*() )");//拦截:空参空返回值的任意方法
cut.setExpression("execution (void cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj.Person.*(String))");//拦截:只有1个String类型参数,空返回值的任意方法
cut.setExpression("execution( void cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj.Person.*(*) )");//拦截:有1个参数(类型不限),空返回值的任意方法
cut.setExpression("execution( void cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj.Person.*(*,*) )");//拦截:有2个参数(类型不限),空返回值的任意方法
cut.setExpression("execution( void cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj.Person.*(..) )");//拦截:任意(个数和类型)参数,空返回值的任意方法
cut.setExpression("execution( int cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj.Person.*(*,..) )");//拦截:至少有1个参数(类型不限),返回值类型是int的任意方法
cut.setExpression("execution( * cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj.Person.*(*,..) )");//拦截:至少有1个参数(类型不限),返回值类型任意的方法
cut.setExpression("execution( * cn.hncu..*son.*(*,..) )");//拦截:cn.hncu包下,类名以"son"结束,至少有1个参数(类型不限),返回值类型任意的方法里面的参数是可以匹配正则表达式的。
“.”代表除\r\n外的任意字符。
“*”代表0个或多个。
由于切点语言无法定义指定的多个返回值,所以,例如:
如果需要拦截void和int返回值方法,则可以通过定义2个切点解决。
xml配置AOP拦截
AroundAdvice
package cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
public class AroundAdvice implements MethodInterceptor{
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("前面拦截....");
Object resObj = invocation.proceed();//放行
System.out.println("后面拦截.....");
return resObj;
}
}
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd">
<!-- 自动代理 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator"></bean>
<bean id="p" class="cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj.Person"></bean>
<!-- 切面=切点+通知 (把切点和通知写成内部bean)-->
<bean id="cut" class="org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJExpressionPointcut">
<!-- 拦截:cn.hncu包下,类名以"son"结束,至少有1个参数(类型不限),返回值类型任意的方法 -->
<property name="expression" value="execution( * cn.hncu..*son.*(*,..) )"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="advisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="pointcut" ref="cut"></property>
<property name="advice">
<bean id="advice" class="cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj.AroundAdvice"></bean>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>中间也可以这样配置:
<!-- 自动代理 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator"></bean>
<bean id="p" class="cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj.Person"></bean>
<!-- 切面=切点+通知 (※※采用面向切点语言进行配置切面)-->
<bean id="advisor" class="org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJExpressionPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="expression" value="execution( * cn.hncu..*son.*(*,..) )"></property>
<property name="advice">
<bean id="advice" class="cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj.AroundAdvice"></bean>
</property>
</bean>测试类:
package cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AspectjXmlDemo {
@Test
public void demo1(){
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/hncu/xmlImpl/aspectj/aspectj.xml");
Person p = ctx.getBean(Person.class);
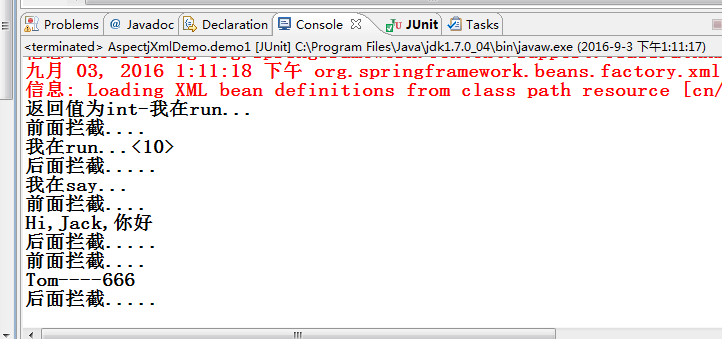
p.run();
p.run(10);
p.say();
p.sayHi("Jack");
p.say("Tom", 666);
}
}
测试结果
在本例:xml配置与纯Java方式相比,即把通过Java代码new出来的对象,通过xml配置来造对象。
如果是开发项目,用Spring的框架,我们的一些通过xml注入的对象就只需要依赖xml文件了。
而依赖xml的依赖不叫依赖,也就是独立了。
本文章由[谙忆]编写, 所有权利保留。
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_26525215
本文源自【大学之旅_谙忆的博客】





















 915
915

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








