从操作配置文件properties中读取连接字符串,通过该字符串进行数据连接,需要写三个文件其中,两个是java类,一个是后缀名为.properties的文件,该文件放在src工作目录下。
需要准备的包:
https://github.com/chenhaoxiang/Java
后缀为.properties的文件此处为其取名为jdbc.properties,其中的代码如下:
##MySQL
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/hncu?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username=root
password=1234
##Oracle
#driver=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
#url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl
#username=scott
#password=tiger
可以配置多个数据库代码,形成框架,这里只配置了MySQL和Oracle数据库的、如果换数据库了,就把相应数据库的#号注释去掉,把原来的代码给用#号注释就可以了。
接下来用单例写一个Connection的工厂类ConnFactory.java:
package cn.hncu.util;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class ConnFactory {
private static Connection con = null;
//静态块
static{
try {
//读取配置文件
Properties p = new Properties();
p.load(ConnFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"));
String drive = p.getProperty("driver");
String url = p.getProperty("url");
String user = p.getProperty("username");
String password = p.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(drive);
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("配置文件出现异常", e);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Drive.Class文件出现异常", e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("数据库访问出现异常", e);
}
}
public static Connection getConnection(){
return con;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(getConnection());
}
}
演示Statement中的4个执行方法:
1, executeQuery()、
2, execute()、
3, executeUpdate()、
4, executeBatch()。
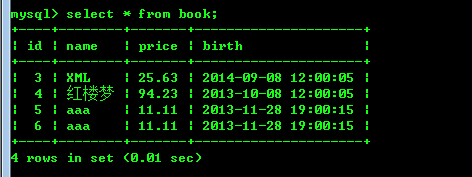
首先创建一个表格book:
create table book(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(30),
price numeric(5,2),
birth datetime
);
insert into book values(1,'Oracle',88.88,'2015-07-12 20:42:12');
insert into book values(2,'MySQL',38.66,'2015-07-12 19:22:12');
executeQuery()
@Test
public void results() throws SQLException{
Statement st = ConnFactory.getConnection().createStatement();
String sql = "select * from book";
ResultSet res = st.executeQuery(sql);
while(res.next()){
Integer id = res.getInt(1);
String name = res.getString(2);
double price = res.getDouble("price");
//注意!这个是获取日期时间型数据的方式
String birth = res.getDate(4)+" "+res.getTime(4);
System.out.println(id+","+name+","+price+","+birth);
}
ConnFactory.getConnection().close();
}只能执行查询语句
execute()
@Test
public void execute() throws SQLException{
Statement st = ConnFactory.getConnection().createStatement();
//测试语句:
//测试增加数据
//String sql = "insert into book(name,price,birth) values ('XML',23.30,'2014-09-08 12:00:05' )";
//测试删除数据
//String sql = "delete from book where id='2'";
//测试查询数据
String sql = "select * from book";
//如果第一个结果为一个结果集,则为 true。否则为 false。
boolean boo = st.execute(sql);
System.out.println(boo);
if(boo){
ResultSet rs = st.getResultSet();
while(rs.next()){
//这里就只输出2个示意一下了。
System.out.println(rs.getInt(1)+","+rs.getString(2));
}
}
ConnFactory.getConnection().close();
}增、删、改、查的语句都能够执行。只是查询时返回的结果是告诉成功与否,如果要获取查询结果,得另外用” st.getResultSet()”获取
executeUpdate()
@Test
public void executeUpdate() throws SQLException{
Statement st = ConnFactory.getConnection().createStatement();
//增加
String sql = "insert into book(name,price,birth) values('红楼梦',85.66,'2013-10-08 12:00:05' )";
//修改
//String sql="update book set price=price*1.1";
//删除
//String sql ="delete from book where id=1";
//查询--不能进行查询!!!
//String sql = "select * from book";
int num = st.executeUpdate(sql);//返回值是影响的行数
System.out.println(num);
}
只能增、删、改, 不能执行查询语句
executeBatch()
@Test
public void batchDemo() throws SQLException{
Connection con = ConnFactory.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into book(name,price ,birth) values ('aaa',11.11,'2013-11-28 19:00:15' )";
Statement st = con.createStatement();
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
if(i==2){
//错误的MySQL代码!
sql = "insert into book(name,price,birth) values('aaa','aa','2013-11-28 19:00:15' )";
}
st.addBatch(sql);
}
sql = "update book set price = price* where price<30";
st.addBatch(sql);
int a[] = st.executeBatch();
for(int x:a){
System.out.println(x);
}
ConnFactory.getConnection().close();
}//执行批处理—自己本身不带事务,如果其中某条sql语句挂了,则后续的sql执行失败,前面的还是有效的。如果要事务,另外再采用:con.setAutoCommit(false)+try-cacth+ rollback/commit
PrepareStatement:
java,servlet中的PreparedStatement 接口继承了Statement,并与之在两方面有所不同:有人主张,在JDBC应用中,如果你已经是稍有水平开发者,你就应该始终以PreparedStatement代替Statement.也就是说,在任何时候都不要使用Statement。
PreparedStatement 实例包含已编译的 SQL 语句。这就是使语句“准备好”。包含于 PreparedStatement 对象中的 SQL 语句可具有一个或多个 IN 参数。IN参数的值在 SQL 语句创建时未被指定。相反的,该语句为每个 IN 参数保留一个问号(“?”)作为占位符。每个问号的值必须在该语句执行之前,通过适当的setXXX 方法来提供。
优点:
一.代码的可读性和可维护性.
虽然用PreparedStatement来代替Statement会使代码多出几行,但这样的代码无论从可读性还是可维护性上来说.都比直接用Statement的代码高很多档次:
示例:
stmt.executeUpdate("insertintotb_name(col1,col2,col2,col4)values('"+var1+"','"+var2+"',"+var3+",'"+var4+"')");
perstmt=con.prepareStatement("insertintotb_name(col1,col2,col2,col4)values(?,?,?,?)");
perstmt.setString(1,var1);
perstmt.setString(2,var2);
perstmt.setString(3,var3);
perstmt.setString(4,var4);
perstmt.executeUpdate();二.PreparedStatement尽最大可能提高性能.
每一种数据库都会尽最大努力对预编译语句提供最大的性能优化.因为预编译语句有可能被重复调用.所以语句在被DB的编译器编译后的执行代码被缓存下来,那么下次调用时只要是相同的预编译语句就不需要编译,只要将参数直接传入编译过的语句执行代码中(相当于一个涵数)就会得到执行.这并不是说只有一个Connection中多次执行的预编译语句被缓存,而是对于整个DB中,只要预编译的语句语法和缓存中匹配.那么在任何时候就可以不需要再次编译而可以直接执行.而statement的语句中,即使是相同一操作,而由于每次操作的数据不同所以使整个语句相匹配的机会极小,几乎不太可能匹配.比如:
insertintotb_name(col1,col2)values('11','22');
insertintotb_name(col1,col2)values('11','23'); 即使是相同操作但因为数据内容不一样,所以整个个语句本身不能匹配,没有缓存语句的意义.事实是没有数据库会对普通语句编译后的执行代码缓存.
当然并不是所以预编译语句都一定会被缓存,数据库本身会用一种策略,比如使用频度等因素来决定什么时候不再缓存已有的预编译结果.以保存有更多的空间存储新的预编译语句.
三.最重要的一点是极大地提高了安全性.
即使到目前为止,仍有一些人连基本的恶义SQL语法都不知道.
String sql="select * from tb_name where name='"+varname+"' and passwd='"+varpasswd+"'";如果我们把[‘or’1’=’1]作为varpasswd传入进来.用户名随意,看看会成为什么?
select * from tb_name =' 随意 ' and passwd='' or '1'='1';因为’1’=’1’肯定成立,所以可以任何通过验证.更有甚者:
把[';drop table tb_name;]作为varpasswd传入进来,则:
select * from tb_name=' 随意 ' and passwd='' ; drop table tb_name;有些数据库是不会让你成功的,但也有很多数据库就可以使这些语句得到执行.
而如果你使用预编译语句.你传入的任何内容就不会和原来的语句发生任何匹配的关系.只要全使用预编译语句,你就用不着对传入的数据做任何过虑.而如果使用普通的statement,有可能要对drop,;等做费尽心机的判断和过虑.
模拟用户登录:
这里如果用普通的statement是很容易被黑的。
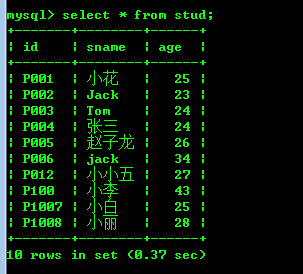
stud表:
模拟用户输入id和name登录:
@Test //不会被黑:如输入name值为: a' or '1'='1
public void login() throws SQLException{
Connection con = ConnFactory.getConnection();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String id = sc.next();
String name = sc.next();
System.out.println(id+","+name);
//创建预处理语句对象
String sql = "select count(*) from stud where id=? and sname =?";
//凡是用户输入的地方,用“?”号(称为占位符)填入
PreparedStatement pst = con.prepareStatement(sql);
//给占位符设置值---设置参数
pst.setString(1, id);//给第一个?号参数设置值
pst.setString(2, name);//给第二个?号参数设置值
ResultSet rs = pst.executeQuery();//这里不能传参数sql
rs.next();//因为这里查询到的肯定只有一个数目,只要接一个参数就可以了
int n = rs.getInt(1);
if(n<=0){
System.out.println("登录失败...");
}else{
System.out.println("登录成功...");
}
con.close();
}这样的话,无论用户输入啥符号都不管用了,必须输入正确的id和name。
PreparedStatement 执行批处理
@Test
public void preBatchDemo() throws SQLException{
Connection con = ConnFactory.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into book(name,price,birth) values(?,?,'2013-11-28 19:00:15' )";
PreparedStatement pst = con.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
pst.setString(1, "bb"+i);
pst.setDouble(2, 25+i);
pst.addBatch();
}
sql="update book set price = price*1.1 where price<30";
pst.addBatch(sql);
int a[] = pst.executeBatch();
for(int x:a){
System.out.println(x);
}
ConnFactory.getConnection().close();
}转载请附上原文链接:
http://blog.csdn.net/qq_26525215/article/details/52153452








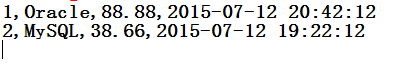
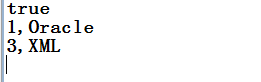














 312
312

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








