虽然说app与网络打交道比较多但是本地存储数据库sqlite还是有它很重要的责任
那来一起学习一下sqlite吧
android的存储方式有如下几种
http://blog.csdn.net/a351945755/article/details/50900652
等我有时间就整理下
sharedpreferences
文件存储
sqlite数据库
contentprovider
网络我们来看看sqlite
他通过SQLiteOpenHelper这个抽象类;来创建和打开数据库
public class DBHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private static final String DATA_NAME = "jaytang.db";
private static final int version = 1;// 版本
private static final String TAG = "DBHelper";// 版本
public DBHelper(Context context) {
super(context, DATA_NAME, null, version);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/**
* 数据库第一次创建时回调该方法,一般做数据库的初始化操作 建表,添加数据等 SQLiteDatabase:增删查改
*/
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.v(TAG, "创建表");
db.execSQL("create table t_book(_id integer primary key autoincrement,name text,price integer)");
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}重写一个DBhelper来继承SQLiteOpenHelper
并重写他里面的方法;在oncreate方法里面新建一个表
db.execSQL("create table t_book(_id integer primary key autoincrement,name text,price integer)");
这样我们就新建了一个表了
可以在 project Explorer里面查看我们新建的数据库jaytang.db
再来写一个工具类来实现数据库的增删查改方法
通过数据库的辅助类SQLiteDatabase来操作
/**
* 操作数据库的工具类
*
* @author Jay-Tang
*
*/
public class DButils {
public static final String TABLE = "t_book";
public static final String ID = "id";
public static final String NAME = "name";
public static final String PRICE = "price";
private DBHelper dbhelper;
public DButils(Context context) {
dbhelper = new DBHelper(context);
}
// 保存操作
public int save(ContentValues values) {
// 通过数据库的辅助类来获取SQliteDatabase
// 没有设置成全局因为每个操作都要用
SQLiteDatabase db = dbhelper.getWritableDatabase();
/**
* 插入一条记录 表名 空字段回调:目的在于拼sql语句时不报错 第三个参数是键值对 插入字段的key和value
*/
long id = db.insert(TABLE, null, values);
db.close();
return (int) id;
}
// 删除操作
public int delete(int id) {
int effectNum = 0;
SQLiteDatabase db = dbhelper.getWritableDatabase();
/**
* 删除操作 表 条件 条件操作 源码是拼串构成的
*/
effectNum = db.delete(TABLE, ID + "=?",
new String[] { String.valueOf(id) });
db.close();
return effectNum;
}
// 更新要求ContentValues传一个id过来
public int update(ContentValues values) {
// 更新那个位置就传那个位置的id过来
String id = values.getAsString(ID);
// 影响的行数
int effecNums = 0;
SQLiteDatabase db = dbhelper.getWritableDatabase();
effecNums = db.update(TABLE, values, ID + "=" + id, null);
db.close();
return effecNums;
}
// 查询
public Cursor findcursor() {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbhelper.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.query(TABLE, null, null, null, null, null, null,
"price disc");
return cursor;
// 假如是返回游标不嫩关闭数据库
}
// 查询,返回的是list<map>
public List<Map<String, Object>> find() {
List<Map<String, Object>> data = null;
SQLiteDatabase db = dbhelper.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.query(TABLE, null, null, null, null, null, null,
"price disc");
// 假如有数据
if (cursor.getCount() > 0) {
data = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
}
// 遍历游标,把数据存放在list中
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put(ID, cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex(ID)));
map.put(NAME, cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex(NAME)));
map.put(PRICE, cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex(PRICE)));
data.add(map);
}
db.close();
return data;
}
public void pay() {
}
}上面的工具类DButils能基本实现增删改查的效果
//工具类是可以复用的 所以尽量写好,并且进行单元测试
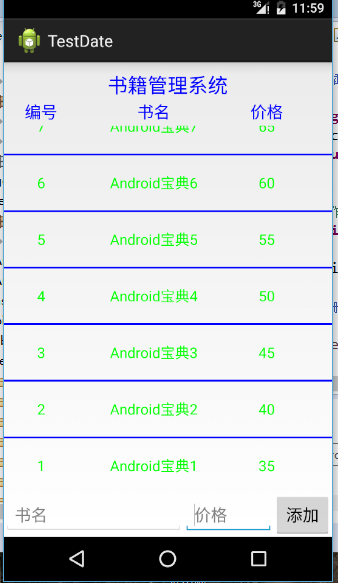
布局文件如下
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="书籍管理系统"
android:textColor="#0000ff"
android:textSize="22sp" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<TextView
style="@style/MyTitleStyle"
android:text="编号" />
<TextView
style="@style/MyTitleStyle"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:text="书名" />
<TextView
style="@style/MyTitleStyle"
android:text="价格" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_height="30dp"
android:src="@drawable/ic_menu_delete"
android:visibility="invisible" />
</LinearLayout>
<ListView
android:id="@android:id/list"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:divider="#0000ff"
android:dividerHeight="2dp" >
</ListView>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<EditText
android:id="@+id/name_et"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:hint="书名" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/price_et"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:hint="价格"
android:inputType="number" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="add"
android:text="添加" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>




















 604
604











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








