一、自适应直方图均衡化(Adaptive histgram equalization/AHE)
1.简述
自适应直方图均衡化(AHE)用来提升图像的对比度的一种计算机图像处理技术。和普通的直方图均衡算法不同,AHE算法通过计算图像的局部直方图,然后重新分布亮度来来改变图像对比度。因此,该算法更适合于改进图像的局部对比度以及获得更多的图像细节。
不过,AHE有过度放大图像中相同区域的噪音的问题,另外一种自适应的直方图均衡算法即限制对比度直方图均衡(CLAHE)算法能有限的限制这种不利的放大。
2. 算法的解释
普通的直方图均衡算法对于整幅图像的像素使用相同的直方图变换,对于那些像素值分布比较均衡的图像来说,算法的效果很好。然后,如果图像中包括明显比图像其它区域暗或者亮的部分,在这些部分的对比度将得不到有效的增强。
AHE算法通过对局部区域执行响应的直方图均衡来改变上述问题。该算法首先被开发出来适用于改进航天器驾驶舱的显示效果。其最简单的形式,就是每个像素通过其周边一个矩形范围内的像素的直方图进行均衡化。均衡的方式则完全同普通的均衡化算法:变换函数同像素周边的累积直方图函数(CDF)成比例。
图像边缘的像素需要特殊处理,因为边缘像素的领域不完全在图像内部。这个通过镜像图像边缘的行像素或列像素来解决。直接复制边缘的像素进行扩充是不合适的。因为这会导致带有剑锋的领域直方图。
3. AHE的属性
- 领域的大小是该方法的一个参数。领域小,对比度得到增强,领域大,则对比度降低。
- 当某个区域包含的像素值非常相似,其直方图就会尖状化,此时直方图的变换函数会将一个很窄范围内的像素映射到整个像素范围。这将使得某些平坦区域中的少量噪音经AHE处理后过度放大。
二、限制对比度自适应直方图均衡(Contrast Limited Adaptive histgram equalization/CLAHE)
1.简述
CLAHE同普通的自适应直方图均衡不同的地方主要是其对比度限幅。这个特性也可以应用到全局直方图均衡化中,即构成所谓的限制对比度直方图均衡(CLHE),但这在实际中很少使用。在CLAHE中,对于每个小区域都必须使用对比度限幅。CLAHE主要是用来克服AHE的过度放大噪音的问题。
这主要是通过限制AHE算法的对比提高程度来达到的。在指定的像素值周边的对比度放大主要是由变换函数的斜度决定的。这个斜度和领域的累积直方图的斜度成比例。CLAHE通过在计算CDF前用预先定义的阈值来裁剪直方图以达到限制放大幅度的目的。这限制了CDF的斜度因此,也限制了变换函数的斜度。直方图被裁剪的值,也就是所谓的裁剪限幅,取决于直方图的分布因此也取决于领域大小的取值。
通常,直接忽略掉那些超出直方图裁剪限幅的部分是不好的,而应该将这些裁剪掉的部分均匀的分布到直方图的其他部分。如下图所示。
2. 通过插值加快计算速度
如上所述的直接的自适应直方图,不管是否带有对比度限制,都需要对图像中的每个像素计算器领域直方图以及对应的变换函数,这使得算法及其耗时。
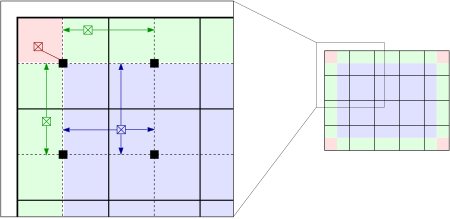
而插值使得上述算法效率上有极大的提升,并且质量上没有下降。首先,将图像均匀分成等份矩形大小,如下图的右侧部分所示(8行8列64个块是常用的选择)。然后计算个块的直方图、CDF以及对应的变换函数。这个变换函数对于块的中心像素(下图左侧部分的黑色小方块)是完全符合原始定义的。而其他的像素通过哪些于其临近的四个块的变换函数插值获取。位于图中蓝色阴影部分的像素采用双线性查插值,而位于便于边缘的(绿色阴影)部分采用线性插值,角点处(红色阴影处)直接使用块所在的变换函数。
CLAHE算法的源代码参考:

 View Code
View Code
/* * ANSI C code from the article * "Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization" * by Karel Zuiderveld, karel@cv.ruu.nl * in "Graphics Gems IV", Academic Press, 1994 * * * These functions implement Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization. * The main routine (CLAHE) expects an input image that is stored contiguously in * memory; the CLAHE output image overwrites the original input image and has the * same minimum and maximum values (which must be provided by the user). * This implementation assumes that the X- and Y image resolutions are an integer * multiple of the X- and Y sizes of the contextual regions. A check on various other * error conditions is performed. * * #define the symbol BYTE_IMAGE to make this implementation suitable for * 8-bit images. The maximum number of contextual regions can be redefined * by changing uiMAX_REG_X and/or uiMAX_REG_Y; the use of more than 256 * contextual regions is not recommended. * * The code is ANSI-C and is also C++ compliant. * * Author: Karel Zuiderveld, Computer Vision Research Group, * Utrecht, The Netherlands (karel@cv.ruu.nl) */ #ifdef BYTE_IMAGE typedef unsigned char kz_pixel_t; /* for 8 bit-per-pixel images */ #define uiNR_OF_GREY (256) #else typedef unsigned short kz_pixel_t; /* for 12 bit-per-pixel images (default) */ # define uiNR_OF_GREY (4096) #endif /******** Prototype of CLAHE function. Put this in a separate include file. *****/ int CLAHE(kz_pixel_t* pImage, unsigned int uiXRes, unsigned int uiYRes, kz_pixel_t Min, kz_pixel_t Max, unsigned int uiNrX, unsigned int uiNrY, unsigned int uiNrBins, float fCliplimit); /*********************** Local prototypes ************************/ static void ClipHistogram (unsigned long*, unsigned int, unsigned long); static void MakeHistogram (kz_pixel_t*, unsigned int, unsigned int, unsigned int, unsigned long*, unsigned int, kz_pixel_t*); static void MapHistogram (unsigned long*, kz_pixel_t, kz_pixel_t, unsigned int, unsigned long); static void MakeLut (kz_pixel_t*, kz_pixel_t, kz_pixel_t, unsigned int); static void Interpolate (kz_pixel_t*, int, unsigned long*, unsigned long*, unsigned long*, unsigned long*, unsigned int, unsigned int, kz_pixel_t*); /************** Start of actual code **************/ #include <stdlib.h> /* To get prototypes of malloc() and free() */ const unsigned int uiMAX_REG_X = 16; /* max. # contextual regions in x-direction */ const unsigned int uiMAX_REG_Y = 16; /* max. # contextual regions in y-direction */ /************************** main function CLAHE ******************/ int CLAHE (kz_pixel_t* pImage, unsigned int uiXRes, unsigned int uiYRes, kz_pixel_t Min, kz_pixel_t Max, unsigned int uiNrX, unsigned int uiNrY, unsigned int uiNrBins, float fCliplimit) /* pImage - Pointer to the input/output image * uiXRes - Image resolution in the X direction * uiYRes - Image resolution in the Y direction * Min - Minimum greyvalue of input image (also becomes minimum of output image) * Max - Maximum greyvalue of input image (also becomes maximum of output image) * uiNrX - Number of contextial regions in the X direction (min 2, max uiMAX_REG_X) * uiNrY - Number of contextial regions in the Y direction (min 2, max uiMAX_REG_Y) * uiNrBins - Number of greybins for histogram ("dynamic range") * float fCliplimit - Normalized cliplimit (higher values give more contrast) * The number of "effective" greylevels in the output image is set by uiNrBins; selecting * a small value (eg. 128) speeds up processing and still produce an output image of * good quality. The output image will have the same minimum and maximum value as the input * image. A clip limit smaller than 1 results in standard (non-contrast limited) AHE. */ { unsigned int uiX, uiY; /* counters */ unsigned int uiXSize, uiYSize, uiSubX, uiSubY; /* size of context. reg. and subimages */ unsigned int uiXL, uiXR, uiYU, uiYB; /* auxiliary variables interpolation routine */ unsigned long ulClipLimit, ulNrPixels;/* clip limit and region pixel count */ kz_pixel_t* pImPointer; /* pointer to image */ kz_pixel_t aLUT[uiNR_OF_GREY]; /* lookup table used for scaling of input image */ unsigned long* pulHist, *pulMapArray; /* pointer to histogram and mappings*/ unsigned long* pulLU, *pulLB, *pulRU, *pulRB; /* auxiliary pointers interpolation */ if (uiNrX > uiMAX_REG_X) return -1; /* # of regions x-direction too large */ if (uiNrY > uiMAX_REG_Y) return -2; /* # of regions y-direction too large */ if (uiXRes % uiNrX) return -3; /* x-resolution no multiple of uiNrX */ if (uiYRes & uiNrY) return -4; /* y-resolution no multiple of uiNrY */ if (Max >= uiNR_OF_GREY) return -5; /* maximum too large */ if (Min >= Max) return -6; /* minimum equal or larger than maximum */ if (uiNrX < 2 || uiNrY < 2) return -7;/* at least 4 contextual regions required */ if (fCliplimit == 1.0) return 0; /* is OK, immediately returns original image. */ if (uiNrBins == 0) uiNrBins = 128; /* default value when not specified */ pulMapArray=(unsigned long *)malloc(sizeof(unsigned long)*uiNrX*uiNrY*uiNrBins); if (pulMapArray == 0) return -8; /* Not enough memory! (try reducing uiNrBins) */ uiXSize = uiXRes/uiNrX; uiYSize = uiYRes/uiNrY; /* Actual size of contextual regions */ ulNrPixels = (unsigned long)uiXSize * (unsigned long)uiYSize; if(fCliplimit > 0.0) { /* Calculate actual cliplimit */ ulClipLimit = (unsigned long) (fCliplimit * (uiXSize * uiYSize) / uiNrBins); ulClipLimit = (ulClipLimit < 1UL) ? 1UL : ulClipLimit; } else ulClipLimit = 1UL<<14; /* Large value, do not clip (AHE) */ MakeLut(aLUT, Min, Max, uiNrBins); /* Make lookup table for mapping of greyvalues */ /* Calculate greylevel mappings for each contextual region */ for (uiY = 0, pImPointer = pImage; uiY < uiNrY; uiY++) { for (uiX = 0; uiX < uiNrX; uiX++, pImPointer += uiXSize) { pulHist = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiY * uiNrX + uiX)]; MakeHistogram(pImPointer,uiXRes,uiXSize,uiYSize,pulHist,uiNrBins,aLUT); ClipHistogram(pulHist, uiNrBins, ulClipLimit); MapHistogram(pulHist, Min, Max, uiNrBins, ulNrPixels); } pImPointer += (uiYSize - 1) * uiXRes; /* skip lines, set pointer */ } /* Interpolate greylevel mappings to get CLAHE image */ for (pImPointer = pImage, uiY = 0; uiY <= uiNrY; uiY++) { if (uiY == 0) { /* special case: top row */ uiSubY = uiYSize >> 1; uiYU = 0; uiYB = 0; } else { if (uiY == uiNrY) { /* special case: bottom row */ uiSubY = uiYSize >> 1; uiYU = uiNrY-1; uiYB = uiYU; } else { /* default values */ uiSubY = uiYSize; uiYU = uiY - 1; uiYB = uiYU + 1; } } for (uiX = 0; uiX <= uiNrX; uiX++) { if (uiX == 0) { /* special case: left column */ uiSubX = uiXSize >> 1; uiXL = 0; uiXR = 0; } else {








 自适应直方图均衡化(AHE)是一种提升图像对比度的技术,但可能导致噪声放大。限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化(CLAHE)通过对比度限幅解决了这一问题。CLAHE通过预先定义的阈值裁剪直方图并均匀分布裁剪部分,限制了像素值的放大,有效抑制了噪声。文章介绍了CLAHE的原理、实现方法以及与AHE的区别,并提供了VB和C#的实现示例。
自适应直方图均衡化(AHE)是一种提升图像对比度的技术,但可能导致噪声放大。限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化(CLAHE)通过对比度限幅解决了这一问题。CLAHE通过预先定义的阈值裁剪直方图并均匀分布裁剪部分,限制了像素值的放大,有效抑制了噪声。文章介绍了CLAHE的原理、实现方法以及与AHE的区别,并提供了VB和C#的实现示例。

 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 3064
3064

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








