十四周一次课
14.1NFS介绍
14.2NFS服务端安装配置
14.3NFS配置选项
14.1NFS介绍
NFS介绍
NFS是Network File System的缩写;这个文件系统是基于网路层面,通过网络层面实现数据同步
NFS最早由Sun公司开发,分2,3,4三个版本,2和3由Sun起草开发,4.0开始Netapp公司参与并主导开发,目前最新为4.1版本——>4.1版本是2010年出来还没更新过
NFS数据传输基于RPC协议,RPC为Remote Procedure Call的简写,意思为远程过程调用
服务端和客户端通信,A机器和B机器之间不能直接通信,需要借助RPC协议来实现
例子
1.服务端和客户端通信,A机器和B机器之间不能直接通信,需要借助RPC协议来实现
NFS应用场景是:A,B,C三台机器上需要保证被访问到的文件是一样的,A共享数据出来,B和C分别去挂载A共享的数据目录,从而B和C访问到的数据和A上的一致
NFS架构
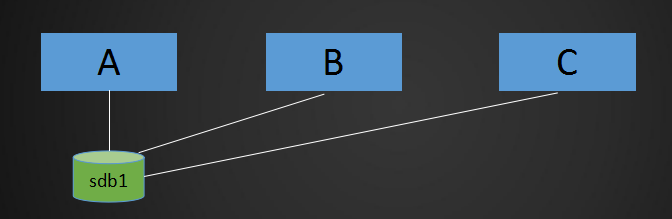
跑了一个网站,上面传输了很多图片,用户访问一个图片时,需要从A机器上去请求,但A机器负载高,为了分担负载,就多弄了两台机器,B机器C机器同时提供服务;正常的话,需要到A机器上才能拿到数据,但是B机器和C机器做了负载均衡,分担了相同的服务器,那么用户也有可能到B机器或者C机器上;那么用户请求到B机器上的时候,如何才能获取到A机器上的数据呢;要么把A机器的数据传输到B机器上,同时传输到C机器上,但是这个不能时时更新,(用户上传的数据是存放在A机器上,但用户请求的时候数据是请求到B机器上)这样A上的数据还没到B上面去,就会导致用户请求获取的数据访问不到,访问为空,为404;那么NFS服务就可以解决这个问题,将A机器的数据共享到B机器和C机器,通过NFS来实现。有NFS服务以后,上传到A机器上的数据,B机器或C机器上就能马上看到和调用。
例子:
总结,NFS就是实时同步
NFS原理图
服务端需要启动一个NFS服务,服务端要想给客户端提供服务,需要借助RPC协议,RPC协议是由rpcbind服务所实现的;在centos 5或者之前的版本叫portmap服务,centos6及之后的版本叫rpcbind服务,这两个都是一个服务,最终实现了RPC协议的通信,NFS服务默认不会监听任何端口(启动服务,但不会监听端口),最终监听端口,实现TCP/IP通信的过程是由rpcbind服务产生的RPC协议实现的,RPC协议默认监听的端口是111 端口;
整个流程为:服务端的NFS服务监听一个端口通过RPC协议监听的端口,再去告诉客户端RPC协议,然后NFS客户端通过本机的RPC端口回传数据信息到服务端NFS监听的端口,最终实现通信
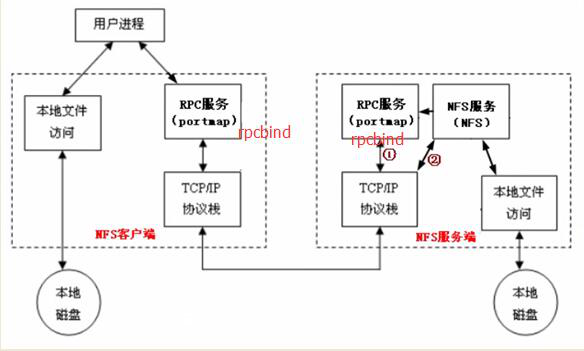
NFS服务需要借助RPC协议实现通信
14.2NFS服务端安装配置
NFS服务端安装配置目录概要
yum install -y nfs-utils rpcbind
vim /etc/exports //加入如下内容
/home/nfstestdir 192.168.133.1/24(rw,sync,all_squash,anonuid=1000,anongid=1000)
保存配置文件后,执行如下操作
mkdir /home/nfstestdir
chmod 777 /home/nfstestdir
systemctl start rpcbind
systemctl start nfs
systemctl enable rpcbind
systemctl enable nfs
NFS服务端安装配置
1.首先准备两台机器,一个作为服务端,一个作为客户端我这里准备两台虚拟机,A机器IP分别为192.168.11.136,B机器IP为192.168.11.138
A机器,查看IP
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# ifconfig
ens33: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.11.136 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.11.255
inet6 fe80::1eb9:8f9e:264a:7159 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:08:64:43 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 526 bytes 51443 (50.2 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 76 bytes 8818 (8.6 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
ens33:0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.11.139 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.11.255
ether 00:0c:29:08:64:43 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
ens37: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.233.130 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.233.255
inet6 fe80::8834:1ebf:d84b:7dc9 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:08:64:4d txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 464 bytes 47165 (46.0 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 768 bytes 133542 (130.4 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 16 bytes 1424 (1.3 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 16 bytes 1424 (1.3 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
B机器,查看IP
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# ifconfig
eno16777736: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.11.138 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.11.255
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:feaa:97e3 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:aa:97:e3 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 743172 bytes 1002507382 (956.0 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 262681 bytes 20781578 (19.8 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 0 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 36 bytes 1968 (1.9 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 36 bytes 1968 (1.9 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
2.将A机器作为服务端,并安装两个包,分别为 nfs-utils 和 rpcbind
yum install -y nfs-utils rpcbind
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# yum install -y nfs-utils rpcbind
3.将B机器作为客户端,安装 nfs-utils 包
每次刚开机运行yum的时候都会很慢,因为需要重新生成一个缓存文件
有时yum安装的时候很慢,我们可以先禁掉,进入到/etc/yum.repos.d/目录下,将目录下的epel.repo文件改个名字,重新安装即可
yum install -y nfs-utils
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# yum install -y nfs-utils
4.在安装完成后,需要去A机器中 /etc/exports 编辑配置文件
vim /etc/exports //加入如下内容
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# vim /etc/exports
/home/nfstestdir 192.168.11.0/24(rw,sync,all_squash,anonuid=1000,anongid=1000)
5.下面就可以启动服务了,启动服务前需要先创建分享的目录,并设置权限
6.在A机器上创建分享的目录
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# mkdir /home/nfstestdir
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
7.并设置成777的权限,这里设置777权限是为了方便接下里的实验
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# chmod 777 !$
chmod 777 /home/nfstestdir
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
8.启动 rpcbind ,再启动前查看A机器上监听的端口,就会看到启动了1/systemd,这是centos7系统的一个特性——>111端口是rpcbind服务监听的
用ps可以查看服务已经启动,因为有这个服务,所以监听了111端口
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# netstat -lntp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1/systemd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 802/nginx: master p
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 788/sshd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 890/master
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:443 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 802/nginx: master p
tcp6 0 0 :::111 :::* LISTEN 1/systemd
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 788/sshd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 890/master
tcp6 0 0 :::3306 :::* LISTEN 1037/mysqld
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# ps aux |grep rpc
root 378 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 12:38 0:00 [rpciod]
root 1324 0.0 0.0 112660 980 pts/0 R+ 19:38 0:00 grep --color=auto rpc
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
9.再到B机器上查看下端口,会看到也启动了rpcbind
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# netstat -lntp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2420/master
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1/systemd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1275/sshd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 2420/master
tcp6 0 0 :::111 :::* LISTEN 1/systemd
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 1275/sshd
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# ps aux |grep rpc
root 378 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 12:38 0:00 [rpciod]
root 1324 0.0 0.0 112660 980 pts/0 R+ 19:38 0:00 grep --color=auto rpc
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
10.在A机器启动了rpcbind,下面就可以启动nfs服务,在使用ps查看
systemctl start nfs
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# systemctl start nfs
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# ps aux |grep nfs
root 1352 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 19:40 0:00 [nfsd4_callbacks]
root 1358 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 19:40 0:00 [nfsd]
root 1359 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 19:40 0:00 [nfsd]
root 1360 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 19:40 0:00 [nfsd]
root 1361 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 19:40 0:00 [nfsd]
root 1362 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 19:40 0:00 [nfsd]
root 1363 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 19:40 0:00 [nfsd]
root 1364 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 19:40 0:00 [nfsd]
root 1365 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 19:40 0:00 [nfsd]
root 1369 0.0 0.0 112660 980 pts/0 R+ 19:40 0:00 grep --color=auto nfs
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
11.同时也可以在A机器上ps aux |grep rpc查询,在启动nfs服务的时候,它会自动帮你启动rpc相关的一些服务
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# ps aux |grep rpc
root 378 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 12:38 0:00 [rpciod]
rpcuser 1338 0.0 0.1 42376 1756 ? Ss 19:40 0:00 /usr/sbin/rpc.statd
rpc 1340 0.0 0.1 64956 1356 ? Ss 19:40 0:00 /sbin/rpcbind -w
root 1341 0.0 0.0 42564 948 ? Ss 19:40 0:00 /usr/sbin/rpc.mountd
root 1342 0.0 0.0 43816 540 ? Ss 19:40 0:00 /usr/sbin/rpc.idmapd
root 1371 0.0 0.0 112664 980 pts/0 R+ 19:41 0:00 grep --color=auto rpc
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
12.而在客户端B机器上是没有的这些服务的
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# !ps
ps aux |grep rpc
root 535 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 00:23 0:00 [rpciod]
rpc 2642 0.0 0.1 64896 1040 ? Ss 03:37 0:00 /sbin/rpcbind -w
root 2649 0.0 0.0 112660 976 pts/0 R+ 03:42 0:00 grep --color=auto rpc
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
13.如果想让nfs开机启动,还需要执行systemctl enable nfs 命令,在服务端A机器上调用
systemctl enable nfs 开机启动nfs
systemctl disable nfs 关闭开机启动
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# systemctl enable nfs
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nfs-server.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nfs-server.service.
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
14.3NFS配置选项
NFS配置选项
rw 读写
ro 只读
sync 同步模式,内存数据实时写入磁盘,相应的就会降低磁盘效率
async 非同步模式,它会每隔一段时间才会将数据刷新到磁盘
优势:能够保证磁盘的效率
劣势:万一断电,就会有可能丢失一部分数据
no_root_squash 客户端挂载NFS共享目录后,root用户不受约束,权限很大
NFS,要想在客户端上去使用服务端上共享的目录,需要去把它挂载到客户端上的一个挂载点,那就跟本地上的目录是一样的,在操作本地的目录时候,肯定会有一些权限设置,如果加上no_root_squash,这样root用户去共享目录下读写文件的时候,就不会受到限制(就相当于root用户在本地上读写)
root_squash 与上面选项相对,客户端上的root用户受到约束,被限定成某个普通用户
all_squash 客户端上所有用户(包括root用户)在使用NFS共享目录时都被限定为一个普通用户
anonuid/anongid 和上面几个选项搭配使用,定义被限定用户的uid和gid
客户端上挂载
1.首先在客户端B机器上安装了rpcbind,它是由nfs-utils 这个包自动安装的
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# yum install -y nfs-utils
2.在B机器上安装完成后不需要启动任何服务
3.在B机器上执行 showmount -e 命令
showmount -e 192.168.11.136 //查看在NFS服务端是否有权限
该ip为NFS服务端ip
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# showmount -e 192.168.11.136
clnt_create: RPC: Port mapper failure - Unable to receive: errno 113 (No route to host)
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
4.这时候会看到报错了,RPC: Port mapper failure说明网络不通,无法与192.168.11.136端口通信
不能通信的两种情况
要么是对方没有开启rpcbind的服务,没有监听111端口
要么是防火墙导致的原因
5.因为之前在服务端已经开启了rpcbind服务,那这时只能说明是防火墙导致的,所以要想让NFS实现正常的通信,还需要把防火墙关闭,因为NFS服务比较特殊,虽然rpc可以通信,就算iptables把111端口放行但NFS也不一定能正常通信,因为它们使用了一个不固定的端口
6.这时先把A机器服务端和B机器客户端,防火墙关闭,命令systemctl stop firewalld
A机器关闭防火墙
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# getenforce
Disabled
A机器清空iptables规则
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# iptables -F
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
B机器关闭防火墙
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# getenforce
Enforcing
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# setenforce 0
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# getenforce
Permissive
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
7.这时再去B机器客户端来showmount -e 192.168.11.136 ,这时会看到可以能show到远程服务端192.168.11.136这台机器,它共享的目录是/home/nfstestdir
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# showmount -e 192.168.11.136
Export list for 192.168.11.136:
/home/nfstestdir 192.168.11.0/24
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
8.这时候在B机器客户端上来挂载了,然后查看——>挂载的时间可能有点慢
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# mount -t nfs 192.168.11.136:/home/nfstestdir /mnt/
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda3 18G 4.8G 14G 27% /
devtmpfs 485M 0 485M 0% /dev
tmpfs 490M 0 490M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 490M 6.7M 484M 2% /run
tmpfs 490M 0 490M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 197M 75M 122M 39% /boot
192.168.11.136:/home/nfstestdir 16G 6.7G 9.1G 43% /mnt
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
9.这个就是远程NFS服务端共享的目录
10.这时到B机器客户端共享的目录下创建文件
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# cd /mnt/
[root@tianqi-01 mnt]# ls
[root@tianqi-01 mnt]# touch aminglinux.111
[root@tianqi-01 mnt]# ll
total 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 tianqi tianqi 0 Mar 26 20:29 aminglinux.111
[root@tianqi-01 mnt]#
11.到A机器的服务端查看,可以看到文件的属主和属组都为1000
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# ll /home/nfstestdir/
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 mysql mysql 0 Mar 26 20:29 aminglinux.111
[root@tianqi-01 ~]# tail /etc/passwd
polkitd:x:999:997:User for polkitd:/:/sbin/nologin
postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin
sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin
ntp:x:38:38::/etc/ntp:/sbin/nologin
mysql:x:1000:1000::/home/mysql:/bin/bash
tianqi:x:1001:1001::/home/tianqi:/bin/bash
php-fpm:x:1002:1002::/home/php-fpm:/bin/bash
rpc:x:32:32:Rpcbind Daemon:/var/lib/rpcbind:/sbin/nologin
rpcuser:x:29:29:RPC Service User:/var/lib/nfs:/sbin/nologin
nfsnobody:x:65534:65534:Anonymous NFS User:/var/lib/nfs:/sbin/nologin
[root@tianqi-01 ~]#
原因是配置 /etc/exports文件时,配置了anonuid=1000,anongid=1000
客户端显示1000用户是因为客户端机器上并没有1000权限的用户
同样,服务端显示mysql,是因为服务端上的机器mysql 就是1000权限的用户
总结
在/etc/exports文件中的/home/nfstestdir 192.168.11.0/24(rw,sync,all_squash,anonuid=1000,anongid=1000) ,其中ip与(rw之间不能有空格, 否则客户端挂载的目录会变成只读..
友情推荐:http://www.apelearn.com阿铭linux
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/13184900/2091350





















 5万+
5万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








