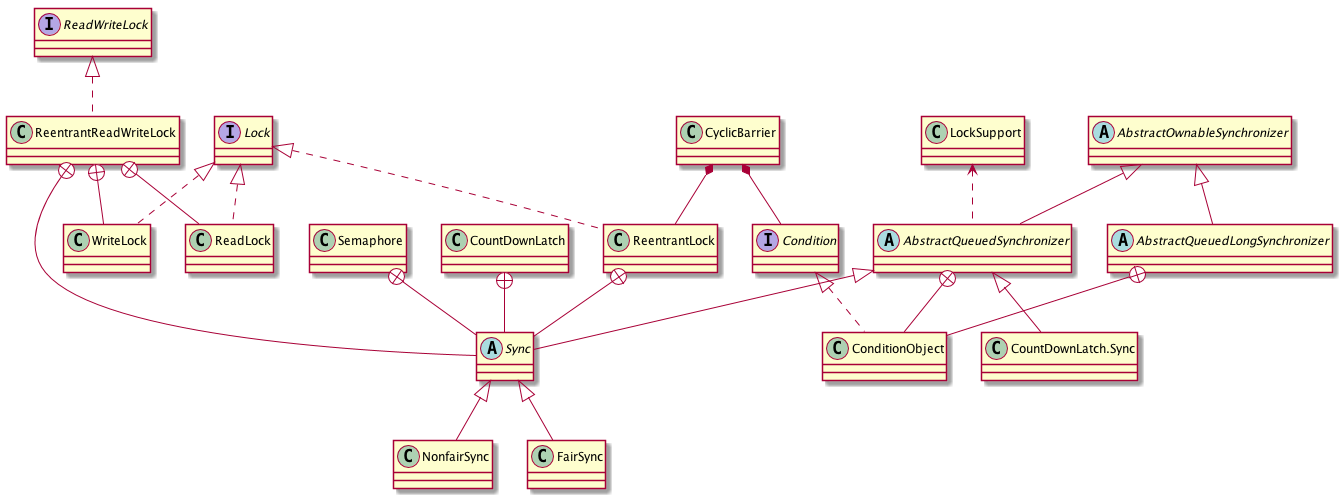
类图:
数据结构
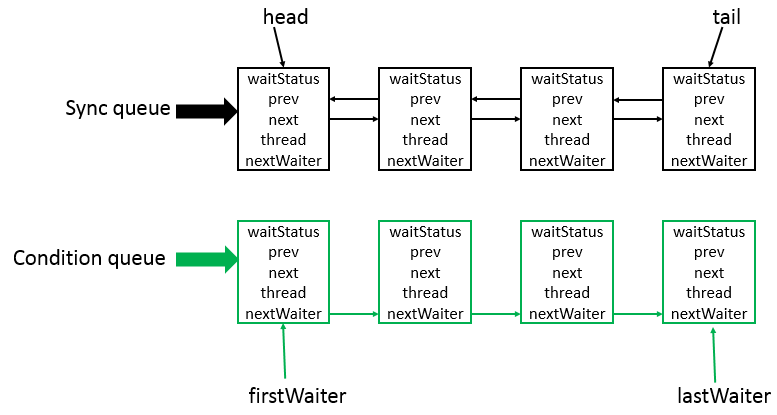
说明:
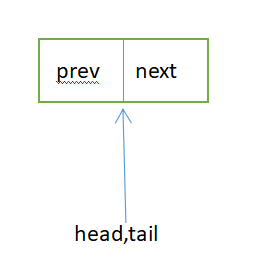
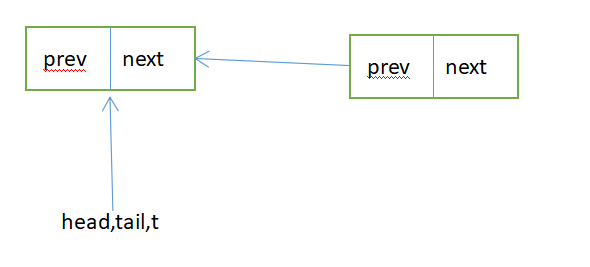
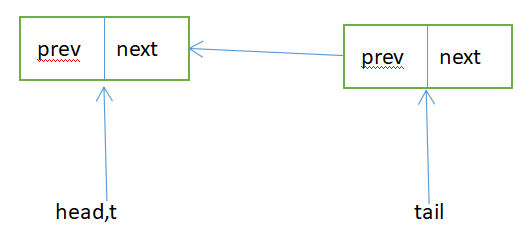
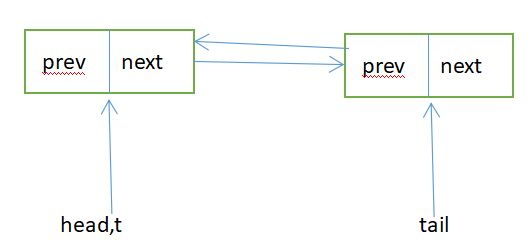
Sync queue,即同步队列,是双向链表,包括head结点和tail结点,head结点主要用作后续的调度。
Condition queue不是必须的,是一个单向链表,只有当使用Condition时,才会存在此单向链表,并且可能会有多个Condition queue。
注意:
AbstractQueuedLongSynchronizer 以 long 形式维护同步状态的一个 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 版本。
AbstractQueuedLongSynchronizer 具有的结构、属性和方法与 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 完全相同,但所有与状态相关的参数和结果都定义为 long 而不是 int。当创建需要 64 位状态的多级别锁和屏障等同步器时,就应当使用 AbstractQueuedLongSynchronizer。
源码:
package java.util.concurrent.locks;
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7373984972572414691L;//版本序列号
//头结点
private transient volatile Node head;
//尾结点
private transient volatile Node tail;
//状态
private volatile int state;
//自旋时间
static final long spinForTimeoutThreshold = 1000L;
//构造函数
protected AbstractQueuedSynchronizer() {
}
static final class Node {
// 模式,分为共享与独占
// 共享模式
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
// 独占模式
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
// 结点状态
// CANCELLED,值为1,表示当前的线程被取消 (取消状态)
// SIGNAL,值为-1,表示当前节点的后继节点包含的线程需要运行,也就是unpark (等待触发状态)
// CONDITION,值为-2,表示当前节点在等待condition,也就是在condition队列中 (等待条件状态)
// PROPAGATE,值为-3,表示当前场景下后续的acquireShared能够得以执行 (状态需要向后传播)
// 值为0,表示当前节点在sync队列中,等待着获取锁
static final int CANCELLED = 1;
static final int SIGNAL = -1;
static final int CONDITION = -2;
static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
// 结点状态
volatile int waitStatus;
// 前驱结点
volatile Node prev;
// 后继结点
volatile Node next;
// 结点所对应的线程
volatile Thread thread;
// 下一个等待者
Node nextWaiter;
// 结点是否在共享模式下等待
final boolean isShared() {
return nextWaiter == SHARED;
}
// 获取前驱结点,若前驱结点为空,抛出异常
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
// 保存前驱结点
Node p = prev;
if (p == null) // 前驱结点为空,抛出异常
throw new NullPointerException();
else // 前驱结点不为空,返回
return p;
}
// 无参构造函数
Node() {
}
// 构造函数
Node(Thread thread, Node mode) {
this.nextWaiter = mode;
this.thread = thread;
}
// 构造函数
Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) {
this.waitStatus = waitStatus;
this.thread = thread;
}
}
public class ConditionObject implements Condition, java.io.Serializable {
// 版本号
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1173984872572414699L;
// condition队列的头结点
private transient Node firstWaiter;
// condition队列的尾结点
private transient Node lastWaiter;
// 构造函数
public ConditionObject() {
}
// 添加新的waiter到wait队列
private Node addConditionWaiter() {
// 保存尾结点
Node t = lastWaiter;
// If lastWaiter is cancelled, clean out.
if (t != null && t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) { // 尾结点不为空,并且尾结点的状态不为CONDITION
// 清除状态为CONDITION的结点
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
// 将最后一个结点重新赋值给t
t = lastWaiter;
}
// 新建一个结点
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), Node.CONDITION);
if (t == null) // 尾结点为空
// 设置condition队列的头结点
firstWaiter = node;
else // 尾结点不为空
// 设置为节点的nextWaiter域为node结点
t.nextWaiter = node;
// 更新condition队列的尾结点
lastWaiter = node;
return node;
}
private void doSignal(Node first) {
// 循环
do {
if ((firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null) // 该节点的nextWaiter为空
// 设置尾结点为空
lastWaiter = null;
// 设置first结点的nextWaiter域
first.nextWaiter = null;
} while (!transferForSignal(first) &&
(first = firstWaiter) != null); // 将结点从condition队列转移到sync队列失败并且condition队列中的头结点不为空,一直循环
}
private void doSignalAll(Node first) {
// condition队列的头结点尾结点都设置为空
lastWaiter = firstWaiter = null;
// 循环
do {
// 获取first结点的nextWaiter域结点
Node next = first.nextWaiter;
// 设置first结点的nextWaiter域为空
first.nextWaiter = null;
// 将first结点从condition队列转移到sync队列
transferForSignal(first);
// 重新设置first
first = next;
} while (first != null);
}
// 从condition队列中清除状态为CANCEL的结点
private void unlinkCancelledWaiters() {
// 保存condition队列头结点
Node t = firstWaiter;
Node trail = null;
while (t != null) { // t不为空
// 下一个结点
Node next = t.nextWaiter;
if (t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) { // t结点的状态不为CONDTION状态
// 设置t节点的额nextWaiter域为空
t.nextWaiter = null;
if (trail == null) // trail为空
// 重新设置condition队列的头结点
firstWaiter = next;
else // trail不为空
// 设置trail结点的nextWaiter域为next结点
trail.nextWaiter = next;
if (next == null) // next结点为空
// 设置condition队列的尾结点
lastWaiter = trail;
} else // t结点的状态为CONDTION状态
// 设置trail结点
trail = t;
// 设置t结点
t = next;
}
}
// 唤醒一个等待线程。如果所有的线程都在等待此条件,则选择其中的一个唤醒。在从 await 返回之前,该线程必须重新获取锁。
public final void signal() {
if (!isHeldExclusively()) // 不被当前线程独占,抛出异常
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
// 保存condition队列头结点
Node first = firstWaiter;
if (first != null) // 头结点不为空
// 唤醒一个等待线程
doSignal(first);
}
// 唤醒所有等待线程。如果所有的线程都在等待此条件,则唤醒所有线程。在从 await 返回之前,每个线程都必须重新获取锁。
public final void signalAll() {
if (!isHeldExclusively()) // 不被当前线程独占,抛出异常
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
// 保存condition队列头结点
Node first = firstWaiter;
if (first != null) // 头结点不为空
// 唤醒所有等待线程
doSignalAll(first);
}
// 等待,当前线程在接到信号之前一直处于等待状态,不响应中断
public final void awaitUninterruptibly() {
// 添加一个结点到等待队列
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
// 获取释放的状态
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
boolean interrupted = false;
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) { //
// 阻塞当前线程
LockSupport.park(this);
if (Thread.interrupted()) // 当前线程被中断
// 设置interrupted状态
interrupted = true;
}
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) || interrupted) //
selfInterrupt();
}
private static final int REINTERRUPT = 1;
private static final int THROW_IE = -1;
private int checkInterruptWhileWaiting(Node node) {
return Thread.interrupted() ?
(transferAfterCancelledWait(node) ? THROW_IE : REINTERRUPT) :
0;
}
private void reportInterruptAfterWait(int interruptMode)
throws InterruptedException {
if (interruptMode == THROW_IE)
throw new InterruptedException();
else if (interruptMode == REINTERRUPT)
selfInterrupt();
}
// 等待,当前线程在接到信号或被中断之前一直处于等待状态
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted()) // 当前线程被中断,抛出异常
throw new InterruptedException();
// 在wait队列上添加一个结点
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
//
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
int interruptMode = 0;
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
// 阻塞当前线程
LockSupport.park(this);
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0) // 检查结点等待时的中断类型
break;
}
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
if (node.nextWaiter != null) // clean up if cancelled
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
}
// 等待,当前线程在接到信号、被中断或到达指定等待时间之前一直处于等待状态
public final long awaitNanos(long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;
int interruptMode = 0;
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L) {
transferAfterCancelledWait(node);
break;
}
if (nanosTimeout >= spinForTimeoutThreshold)
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();
}
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
if (node.nextWaiter != null)
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
return deadline - System.nanoTime();
}
// 等待,当前线程在接到信号、被中断或到达指定最后期限之前一直处于等待状态
public final boolean awaitUntil(Date deadline)
throws InterruptedException {
long abstime = deadline.getTime();
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
boolean timedout = false;
int interruptMode = 0;
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
if (System.currentTimeMillis() > abstime) {
timedout = transferAfterCancelledWait(node);
break;
}
LockSupport.parkUntil(this, abstime);
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
}
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
if (node.nextWaiter != null)
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
return !timedout;
}
// 等待,当前线程在接到信号、被中断或到达指定等待时间之前一直处于等待状态。此方法在行为上等效于:awaitNanos(unit.toNanos(time)) > 0
public final boolean await(long time, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
long nanosTimeout = unit.toNanos(time);
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;
boolean timedout = false;
int interruptMode = 0;
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L) {
timedout = transferAfterCancelledWait(node);
break;
}
if (nanosTimeout >= spinForTimeoutThreshold)
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();
}
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
if (node.nextWaiter != null)
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
return !timedout;
}
final boolean isOwnedBy(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer sync) {
return sync == AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.this;
}
// 查询是否有正在等待此条件的任何线程
protected final boolean hasWaiters() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
for (Node w = firstWaiter; w != null; w = w.nextWaiter) {
if (w.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION)
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 返回正在等待此条件的线程数估计值
protected final int getWaitQueueLength() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
int n = 0;
for (Node w = firstWaiter; w != null; w = w.nextWaiter) {
if (w.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION)
++n;
}
return n;
}
// 返回包含那些可能正在等待此条件的线程集合
protected final Collection<Thread> getWaitingThreads() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
ArrayList<Thread> list = new ArrayList<Thread>();
for (Node w = firstWaiter; w != null; w = w.nextWaiter) {
if (w.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION) {
Thread t = w.thread;
if (t != null)
list.add(t);
}
}
return list;
}
}
//返回同步状态的当前值
protected final int getState() {
return state;
}
//设置同步状态的值
protected final void setState(int newState) {
state = newState;
}
//如果当前状态值等于预期值expect,则以原子方式将同步状态设置为给定的更新值update
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update);
}
// 入队列
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (; ; ) { // 无限循环,确保结点能够成功入队列
// 保存尾结点
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // 尾结点为空,即还没被初始化
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node())) // 头结点为空,并设置头结点为新生成的结点
tail = head; // 头结点与尾结点都指向同一个新生结点
} else { // 尾结点不为空,即已经被初始化过
// 将node结点的prev域连接到尾结点
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) { // 比较结点t是否为尾结点,若是则将尾结点设置为node
// 设置尾结点的next域为node
t.next = node;
return t; // 返回node节点的前一个节点
}
}
}
}
// 添加一个节点到队列的尾部,并返回这个节点
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 新生成一个结点,默认为独占模式
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// 保存尾结点
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) { // 尾结点不为空,即已经被初始化
// 将node结点的prev域连接到尾结点
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { // 比较pred是否为尾结点,是则将尾结点设置为node
// 设置尾结点的next域为node
pred.next = node;
return node; // 返回新生成的结点
}
}
enq(node); // 尾结点为空(即还没有被初始化过),或者是compareAndSetTail操作失败,则入队列
return node;//返回这个节点
}
private void setHead(Node node) {
head = node;
node.thread = null;
node.prev = null;
}
// 唤醒node的后继不为CANCELLED状态的节点
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
// 获取node结点的等待状态
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0) // 状态值小于0,为SIGNAL -1 或 CONDITION -2 或 PROPAGATE -3
// 比较并且设置结点等待状态,设置为0
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
// 获取node节点的下一个结点
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) { // 下一个结点为空或者下一个节点的等待状态大于0,即为CANCELLED
// s赋值为空
s = null;
// 从尾结点开始从后往前开始遍历
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0) // 找到等待状态小于等于0的结点,找到最前的状态小于等于0的结点
// 保存结点
s = t;
}
if (s != null) // 该结点不为为空,释放许可
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
private void doReleaseShared() {
for (; ; ) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue;
unparkSuccessor(h);
} else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue;
}
if (h == head)
break;
}
}
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate) {
Node h = head;
setHead(node);
if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ||
(h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0) {
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.isShared())
doReleaseShared();
}
}
// 取消继续获取(资源),将当前节点等待状态置为CANCELLED
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
// node为空,返回
if (node == null)
return;
// 设置node结点的thread为空
node.thread = null;
// 保存node的前驱结点
Node pred = node.prev;
while (pred.waitStatus > 0) // 找到node前驱结点中第一个状态小于0的结点,即不为CANCELLED状态的结点
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
// 获取pred结点的下一个结点
Node predNext = pred.next;
// 设置node结点的状态为CANCELLED
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
//此时node.prev指向了前驱节点中第一个不为CANCELLED的节点
//pred则指向了那个节点,predNext指向了那个节点的下一个节点
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) { // node结点为尾结点,则设置尾结点为pred结点
// 比较并设置predNext节点为null
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);
} else { // node结点不为尾结点,或者比较设置不成功
int ws;
//(pred结点不为头结点,并且pred结点的状态为SIGNAL)或者
// pred结点状态小于等于0(不为CANCELLED),并且比较并设置pred等待状态为SIGNAL成功,并且pred结点所封装的线程不为空
if (pred != head && ((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL || (ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) && pred.thread != null) {
Node next = node.next;//next指向node的后继节点
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0) // 若 next 不空并且状态不为CANCELLED
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next); // 比较并设置pred.next = next;
//此时pred.next指向了next,next.prev指向了pred
} else {//当前节点为头节点
unparkSuccessor(node); // 唤醒node的后继不为CANCELLED状态的节点
}
node.next = node; // help GC
}
}
// 当获取(资源)失败后,检查并且更新结点状态
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
// 获取前驱结点的状态
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) // 状态为SIGNAL,为-1
// 可以进行park操作
return true;
if (ws > 0) { // 表示状态为CANCELLED,为1
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0); // 找到pred结点前面最近的一个状态不为CANCELLED的结点
// 赋值pred结点的next域
pred.next = node;
} else { // 为PROPAGATE -3 或者是0 表示无状态,(为CONDITION -2时,表示此节点在condition queue中)
// 比较并设置前驱结点的状态为SIGNAL
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
// 不能进行park操作
return false;
}
static void selfInterrupt() {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
// 进行park操作并且返回该线程是否被中断
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
// 在许可可用之前禁用当前线程,并且设置了blocker
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted(); // 当前线程是否已被中断,并清除中断标记位
}
// sync队列中的结点在独占且忽略中断的模式下获取(资源)
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
// 标志
boolean failed = true;
try {
// 中断标志
boolean interrupted = false;
for (; ; ) { // 无限循环
// 获取node节点的前驱结点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { // 前驱为头结点并且成功获得锁
setHead(node); // 设置头结点
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false; // 设置标志
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
private void doAcquireInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (; ; ) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
private boolean doAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (; ; ) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return true;
}
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
nanosTimeout > spinForTimeoutThreshold)
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
private void doAcquireShared(int arg) {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (; ; ) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
if (interrupted)
selfInterrupt();
failed = false;
return;
}
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (; ; ) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
private boolean doAcquireSharedNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (; ; ) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return true;
}
}
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
nanosTimeout > spinForTimeoutThreshold)
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// 试图在独占模式下获取对象状态
protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//试图设置状态来反映独占模式下的一个释放
protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//试图在共享模式下获取对象状态
protected int tryAcquireShared(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//试图设置状态来反映共享模式下的一个释放
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//如果对于当前(正调用的)线程,同步是以独占方式进行的,则返回 true
protected boolean isHeldExclusively() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//以独占模式获取对象,忽略中断
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
//以独占模式获取对象,如果被中断则中止
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (!tryAcquire(arg))
doAcquireInterruptibly(arg);
}
//试图以独占模式获取对象,如果被中断则中止,如果到了给定超时时间,则会失败
public final boolean tryAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
return tryAcquire(arg) ||
doAcquireNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);
}
//以独占模式释放对象
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) { // 释放成功
// 保存头结点
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0) // 头结点不为空并且头结点状态不为0
unparkSuccessor(h); //释放头结点的后继结点
return true;
}
return false;
}
//以共享模式获取对象,忽略中断
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireShared(arg);
}
//以共享模式获取对象,如果被中断则中止
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
//试图以共享模式获取对象,如果被中断则中止,如果到了给定超时时间,则会失败
public final boolean tryAcquireSharedNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
return tryAcquireShared(arg) >= 0 ||
doAcquireSharedNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);
}
//以共享模式释放对象
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
//查询是否有正在等待获取的任何线程
public final boolean hasQueuedThreads() {
return head != tail;
}
//查询是否其他线程也曾争着获取此同步器;也就是说,是否某个 acquire 方法已经阻塞
public final boolean hasContended() {
return head != null;
}
//返回队列中第一个(等待时间最长的)线程,如果目前没有将任何线程加入队列,则返回 null.
// 在此实现中,该操作是以固定时间返回的,但是,如果其他线程目前正在并发修改该队列,则可能出现循环争用
public final Thread getFirstQueuedThread() {
// handle only fast path, else relay
return (head == tail) ? null : fullGetFirstQueuedThread();
}
private Thread fullGetFirstQueuedThread() {
Node h, s;
Thread st;
if (((h = head) != null && (s = h.next) != null &&
s.prev == head && (st = s.thread) != null) ||
((h = head) != null && (s = h.next) != null &&
s.prev == head && (st = s.thread) != null))
return st;
Node t = tail;
Thread firstThread = null;
while (t != null && t != head) {
Thread tt = t.thread;
if (tt != null)
firstThread = tt;
t = t.prev;
}
return firstThread;
}
//如果给定线程的当前已加入队列,则返回 true
public final boolean isQueued(Thread thread) {
if (thread == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev)
if (p.thread == thread)
return true;
return false;
}
final boolean apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive() {
Node h, s;
return (h = head) != null &&
(s = h.next) != null &&
!s.isShared() &&
s.thread != null;
}
//判断是否有其他线程等待获取的时间比当前线程更长
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
Node t = tail; // Read fields in reverse initialization order
Node h = head;
Node s;
return h != t &&
((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());
}
//返回等待获取的线程数估计值
public final int getQueueLength() {
int n = 0;
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (p.thread != null)
++n;
}
return n;
}
// 返回包含可能正在等待获取的线程 collection
public final Collection<Thread> getQueuedThreads() {
ArrayList<Thread> list = new ArrayList<Thread>();
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
Thread t = p.thread;
if (t != null)
list.add(t);
}
return list;
}
//返回包含可能正以独占模式等待获取的线程 collection
public final Collection<Thread> getExclusiveQueuedThreads() {
ArrayList<Thread> list = new ArrayList<Thread>();
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (!p.isShared()) {
Thread t = p.thread;
if (t != null)
list.add(t);
}
}
return list;
}
//返回包含可能正以共享模式等待获取的线程 collection
public final Collection<Thread> getSharedQueuedThreads() {
ArrayList<Thread> list = new ArrayList<Thread>();
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (p.isShared()) {
Thread t = p.thread;
if (t != null)
list.add(t);
}
}
return list;
}
//返回标识此同步器及其状态的字符串
public String toString() {
int s = getState();
String q = hasQueuedThreads() ? "non" : "";
return super.toString() +
"[State = " + s + ", " + q + "empty queue]";
}
final boolean isOnSyncQueue(Node node) {
if (node.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION || node.prev == null)
return false;
if (node.next != null) // If has successor, it must be on queue
return true;
return findNodeFromTail(node);
}
private boolean findNodeFromTail(Node node) {
Node t = tail;
for (; ; ) {
if (t == node)
return true;
if (t == null)
return false;
t = t.prev;
}
}
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
Node p = enq(node);
int ws = p.waitStatus;
if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL))
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread);
return true;
}
final boolean transferAfterCancelledWait(Node node) {
if (compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0)) {
enq(node);
return true;
}
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node))
Thread.yield();
return false;
}
final int fullyRelease(Node node) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
int savedState = getState();
if (release(savedState)) {
failed = false;
return savedState;
} else {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
}
}
//查询给定的 ConditionObject 是否使用了此同步器作为其锁
public final boolean owns(ConditionObject condition) {
return condition.isOwnedBy(this);
}
//查询是否有线程正在等待给定的、与此同步器相关的条件
public final boolean hasWaiters(ConditionObject condition) {
if (!owns(condition))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Not owner");
return condition.hasWaiters();
}
public final int getWaitQueueLength(ConditionObject condition) {
if (!owns(condition))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Not owner");
return condition.getWaitQueueLength();
}
//返回一个 collection,其中包含可能正在等待与此同步器有关的给定条件的那些线程
public final Collection<Thread> getWaitingThreads(ConditionObject condition) {
if (!owns(condition))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Not owner");
return condition.getWaitingThreads();
}
//Unsafe类实例
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
//state内存偏移地址
private static final long stateOffset;
//head内存偏移地址
private static final long headOffset;
//state内存偏移地址
private static final long tailOffset;
//tail内存偏移地址
private static final long waitStatusOffset;
//next内存偏移地址
private static final long nextOffset;
//静态初始化块
static {
try {
stateOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("state"));
headOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("head"));
tailOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("tail"));
waitStatusOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(Node.class.getDeclaredField("waitStatus"));
nextOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(Node.class.getDeclaredField("next"));
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new Error(ex);
}
}
private final boolean compareAndSetHead(Node update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, headOffset, null, update);
}
private final boolean compareAndSetTail(Node expect, Node update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, tailOffset, expect, update);
}
private static final boolean compareAndSetWaitStatus(Node node, int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(node, waitStatusOffset,
expect, update);
}
private static final boolean compareAndSetNext(Node node, Node expect, Node update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(node, nextOffset, expect, update);
}
}类 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
所有已实现的接口:
为实现依赖于先进先出 (FIFO) 等待队列的阻塞锁和相关同步器(信号量、事件,等等)提供一个框架。
此类支持默认的 独占 模式和 共享 模式之一,或者二者都支持。
- 处于独占模式下时,其他线程试图获取该锁将无法取得成功。
- 在共享模式下,多个线程获取某个锁可能(但不是一定)会获得成功。
只支持独占模式或者只支持共享模式的子类不必定义支持未使用模式的方法。
使用
在ReentrantLock,Semaphore,CountDownLatch,ReentrantReadWriteLock中都用到了继承自AQS的Sync内部类。
AQS根据模式的不同:独占(EXCLUSIVE)和共享(SHARED)模式。
- 独占:只有一个线程能执行。如ReentrantLock。
- 共享:多个线程可同时执行。如Semaphore,可以设置指定数量的线程共享资源。
为了将此类用作同步器的基础,需要适当地重新定义以下方法。实现以下方法,主要是通过使用 getState()、setState(int) 、compareAndSetState(int, int) 方法来检查、修改同步状态来实现。
tryAcquire(int)//独占模式下获取锁的方法tryRelease(int)//独占模式下解锁的方法tryAcquireShared(int)//共享模式下获取锁的方法tryReleaseShared(int)//共享模式下解锁的方法isHeldExclusively()//判断是否为持有独占锁
默认情况下,每个方法都抛出 UnsupportedOperationException。这些方法的实现,在内部必须是线程安全的,通常应该很短并且不被阻塞。其他所有方法都被声明为final,因为它们无法保证是各不相同的。
示例:
对应的类根据不同的模式,来实现对应的方法。例如:独占锁只需实现tryAcquire(int)、tryRelease(int)、isHeldExclusively(),而不必要实现tryAcquireShared(int)、tryReleaseShared(int)。
以下是一个非重入的互斥锁类,它使用值 0 表示未锁定状态,使用 1 表示锁定状态。
class Mutex implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
// Our internal helper class
private static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
// Report whether in locked state
protected boolean isHeldExclusively() {
return getState() == 1;
}
// Acquire the lock if state is zero
public boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
assert acquires == 1; // Otherwise unused
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Release the lock by setting state to zero
protected boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
assert releases == 1; // Otherwise unused
if (getState() == 0) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
setState(0);
return true;
}
// Provide a Condition
Condition newCondition() { return new ConditionObject(); }
// Deserialize properly
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
setState(0); // reset to unlocked state
}
}
// The sync object does all the hard work. We just forward to it.
private final Sync sync = new Sync();
public void lock() { sync.acquire(1); }
public boolean tryLock() { return sync.tryAcquire(1); }
public void unlock() { sync.release(1); }
public Condition newCondition() { return sync.newCondition(); }
public boolean isLocked() { return sync.isHeldExclusively(); }
public boolean hasQueuedThreads() { return sync.hasQueuedThreads(); }
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
}
public boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
} 以下是一个锁存器类,它类似于 CountDownLatch,除了只需要触发单个 signal 之外。因为锁存器是非独占的,所以它使用 shared 的获取和释放方法。
class BooleanLatch {
private static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
boolean isSignalled() { return getState() != 0; }
protected int tryAcquireShared(int ignore) {
return isSignalled()? 1 : -1;
}
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int ignore) {
setState(1);
return true;
}
}
private final Sync sync = new Sync();
public boolean isSignalled() { return sync.isSignalled(); }
public void signal() { sync.releaseShared(1); }
public void await() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
}
嵌套类摘要:
class | AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 的 Condition 实现是 Lock 实现的基础。 |
构造方法摘要:
protected | AbstractQueuedSynchronizer() 创建具有初始同步状态 0 的新 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 实例。 |
方法摘要
void | acquire(int arg) 以独占模式获取对象,忽略中断。 |
void | acquireInterruptibly(int arg) 以独占模式获取对象,如果被中断则中止。 |
void | acquireShared(int arg) 以共享模式获取对象,忽略中断。 |
void | acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) 以共享模式获取对象,如果被中断则中止。 |
protected boolean | compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) 如果当前状态值等于预期值,则以原子方式将同步状态设置为给定的更新值。 |
Collection<Thread> | getExclusiveQueuedThreads() 返回包含可能正以独占模式等待获取的线程 collection。 |
Thread | getFirstQueuedThread() 返回队列中第一个(等待时间最长的)线程,如果目前没有将任何线程加入队列,则返回 null. 在此实现中,该操作是以固定时间返回的,但是,如果其他线程目前正在并发修改该队列,则可能出现循环争用。 |
Collection<Thread> | getQueuedThreads() 返回包含可能正在等待获取的线程 collection。 |
int | getQueueLength() 返回等待获取的线程数估计值。 |
Collection<Thread> | getSharedQueuedThreads() 返回包含可能正以共享模式等待获取的线程 collection。 |
protected int | getState() 返回同步状态的当前值。 |
Collection<Thread> | getWaitingThreads(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject condition) 返回一个 collection,其中包含可能正在等待与此同步器有关的给定条件的那些线程。 |
int | getWaitQueueLength(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject condition) 返回正在等待与此同步器有关的给定条件的线程数估计值。 |
boolean | hasContended() 查询是否其他线程也曾争着获取此同步器;也就是说,是否某个 acquire 方法已经阻塞。 |
boolean | hasQueuedThreads() 查询是否有正在等待获取的任何线程。 |
boolean | hasWaiters(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject condition) 查询是否有线程正在等待给定的、与此同步器相关的条件。 |
protected boolean | isHeldExclusively() 如果对于当前(正调用的)线程,同步是以独占方式进行的,则返回 true。 |
boolean | isQueued(Thread thread) 如果给定线程的当前已加入队列,则返回 true。 |
boolean | owns(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject condition) 查询给定的 ConditionObject 是否使用了此同步器作为其锁。 |
boolean | release(int arg) 以独占模式释放对象。 |
boolean | releaseShared(int arg) 以共享模式释放对象。 |
protected void | setState(int newState) 设置同步状态的值。 |
String | toString() 返回标识此同步器及其状态的字符串。 |
protected boolean | tryAcquire(int arg) 试图在独占模式下获取对象状态。 |
boolean | tryAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) 试图以独占模式获取对象,如果被中断则中止,如果到了给定超时时间,则会失败。 |
protected int | tryAcquireShared(int arg) 试图在共享模式下获取对象状态。 |
boolean | tryAcquireSharedNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) 试图以共享模式获取对象,如果被中断则中止,如果到了给定超时时间,则会失败。 |
protected boolean | tryRelease(int arg) 试图设置状态来反映独占模式下的一个释放。 |
protected boolean | tryReleaseShared(int arg) 试图设置状态来反映共享模式下的一个释放。 |
从类 java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractOwnableSynchronizer 继承的方法:
getExclusiveOwnerThread, setExclusiveOwnerThread
从类 java.lang.Object 继承的方法:
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, wait, wait, wait
实现原理:
为了便于理解,将根据ReentrantLock 源码的调用,来讲解 AbstractOwnableSynchronizer。由于ReentrantLock 仅仅使用了独占锁,因此关于共享锁,本文将不做解析。
在AQS的结构中,内部类Node 是队列Sync的 主要结构。其中,node结构中的变量waitStatus则表示当前被封装成Node结点的等待状态,共有4种取值CANCELLED、SIGNAL、CONDITION、PROPAGATE。
- CANCELLED:值为1,在同步队列中等待的线程等待超时或被中断,需要从同步队列中取消该Node的结点,其结点的waitStatus为CANCELLED,即结束状态,进入该状态后的结点将不会再变化。
- SIGNAL:值为-1,被标识为该等待唤醒状态的后继结点,当其前继结点的线程释放了同步锁或被取消,将会通知该后继结点的线程执行。说白了,就是处于唤醒状态,只要前继结点释放锁,就会通知标识为SIGNAL状态的后继结点的线程执行。
- CONDITION:值为-2,与Condition相关,该标识的结点处于等待队列中,结点的线程等待在Condition上,当其他线程调用了Condition的signal()方法后,CONDITION状态的结点将从等待队列转移到同步队列中,等待获取同步锁。
- PROPAGATE:值为-3,与共享模式相关,在共享模式中,该状态标识结点的线程处于可运行状态。
- 0状态:值为0,代表初始化状态。当构造器没有指定 waitStatus 的值时,waitStatus会被默认初始化为0.
对于pre和next,分别指向当前Node结点的前驱结点和后继结点,thread变量存储的请求锁的线程。nextWaiter,与Condition相关,代表等待队列中的后继结点。
lock():尝试获取失败就挂起等待,即使发生中断,也只是进行了记录,不会抛出异常并再次尝试获取锁,获取失败继续挂起等待。
分为非公平和公平的实现。
非公平的实现:
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))//恰好存在可用的锁
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());//直接占用独占锁
else//否则就去等待队列中取出一个线程获得独占锁
acquire(1);
可以发现,若当前锁是可用的,则该线程直接占用独占锁,而不执行AbstractOwnableSynchronizer的方法acquire(1);
公平的实现:
acquire(1);
那么有必要分析 acquire(1) (从等待队列中取一个线程获得独占锁):
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
tryAcquire(arg) 尝试去获取锁,获取成功返回true;获取不成功,则继续执行 acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg) 将当前线程添加到队列中,Node.EXCLUSIVE 表示获取独占锁;
需要注意:在AbstractOwnableSynchronizer中的tryAcquire(int arg)将抛出一个UnsupportedOperationException异常;所以才必须要求在AbstractOwnableSynchronizer的子类中,实现tryAcquire(int arg)方法。
在非公平的实现中,tryAcquire的实现:
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {//锁的状态为可用
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);//继承至AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {//当前线程持有独占锁
int nextc = c + acquires;//增加重入次数
if (nextc < 0) // 越界
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
在公平的实现中,tryAcquire的实现:
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {//锁的状态为可用
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);//继承至AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {//当前线程持有独占锁
int nextc = c + acquires;//增加重入次数
if (nextc < 0)// 越界
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
可以发现两者的不同之处,仅仅在于:hasQueuedPredecessors():
Node t = tail; // 尾节点
Node h = head;//头节点
Node s;
return h != t && ((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());//返回true条件:
- h!=t,h.next=null 说明head 和 tail 都还没初始化;此处需要后续操作初始化head、tail,并将当前节点设为第一个节点且获取到锁
- h!=t,h.next!=null,h.next.thread != Thread.currentThread() 说明 当前节点不是队列的第一个节点
当tryAcquire(arg) 返回true,则lock()获取独占锁的操作执行完毕;对于非公平实现,tryAcquire(arg)返回false,则表示当前独占锁被其他线程独占;对于公平实现,tryAcquire(arg)返回false,则表示当前独占锁被其他线程独占或者当前线程不是队列中的第一个节点或者队列还未初始化。
对于tryAcquire(arg)返回false,将继续执行acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg);
先分析addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE):
// 添加一个节点到队列的尾部,并返回这个节点
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 新生成一个结点,默认为独占模式,即 node.nextWaiter为 nullNode node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// 获取尾结点的引用
Node pred = tail;//插入队列尾部,并维持调整tail指向当前插入的node节点(和enq的第二次循环操作一样,不再重复解读)
if (pred != null) { // 尾结点不为空,即已经被初始化
// 将node结点的prev域连接到尾结点
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { // 比较pred是否为尾结点,是则将尾结点设置为node
// 设置尾结点的next域为node
pred.next = node;
return node; // 返回新生成的结点
}
}
enq(node); // 尾结点为空(即还没有被初始化过),或者是compareAndSetTail操作失败,在enq 执行插入队列和初始化操作
return node;
}
尾节点未初始化或 compareAndSetTail操作失败,再次尝试将node节点加入到队列的尾部:
//返回 node节点的前一个节点
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (; ; ) { // 无限循环,确保结点能够成功入队列
// 保存尾结点
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // 尾结点为空,即还没被初始化(第一次循环执行)
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node())) // 头结点为空,并设置头结点为新生成的结点
tail = head; // 头结点与尾结点都指向同一个新生成的结点
} else { // 尾结点不为空,即已经被初始化过(第二次循环执行)
// 将node结点的prev域连接到尾结点
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) { // 比较结点t是否为尾结点,若是则将尾结点设置为node,即如果t==tail,则tail=node
// 设置尾结点的next域为node
t.next = node;
return t; // 返回node节点的前一个节点
}
}
}
}
接着分析 acquireQueued(当前线程的节点, arg),由于已添加节点到队列中,接下来就是要让node节点的线程挂起。
在node的插入过程,之前没有阻塞的线程可能已经执行完成,所以要判断该node的前一个节点pred是否为head节点,
如果pred == head,表明当前节点是队列中第一个“有效的”节点,因此再次尝试tryAcquire获取锁,
1、如果成功获取到锁,表明之前的线程已经执行完成,当前线程不需要挂起。
2、如果获取失败,表示之前的线程还未完成,至少还未修改state值。此时将执行挂起操作,直到被持有锁的线程释放时的唤醒操作唤醒,或者被其他线程中断,才会继续尝试获取锁。
然后一直循环下去,直到成功获取锁为止。(lock()获取锁的请求是无法被中断的)
// sync队列中的结点在独占且忽略中断的模式下获取(资源)
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
//获得失败标志
boolean failed = true;
try {
// 中断标志
boolean interrupted = false;
for (; ; ) {
// 获取node节点的前驱结点p
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { // 若p为头结点,即node为第一个‘有效’节点;再次执行tryAcquire 成功获得锁,则当前线程不需要挂起。
setHead(node); // 将头结点指向node
p.next = null; // 释放头节点的链接。help GC
failed = false; // 设置获得失败标志为false,即获得锁成功
return interrupted;//当前线程,不再阻塞,才返回true
}
//shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire判断节点p是否应当挂起,并且进行一些删除CANCELLED状态节点和设置waitStatus的操作;
//符合挂起当前线程的条件之后,执行parkAndCheckInterrupt()挂起当前线程。
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;//执行到此处,表明中断已发生。由于lock()设计本身就是不响应中断的。因此只是使用 interrupted 进行了中断记录。没有做任何异常抛出处理,循环将继续进行。
}
} finally {
if (failed)//如果执行出错,则执行清理操作(基本上都不会执行到此处)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
//pred为node的前继节点,需要注意:addWaiter刚添加的节点的waitStatus一定为0
//如果pred的waitStatus == 0,则通过CAS指令修改waitStatus为Node.SIGNAL。
//如果pred的waitStatus > 0,表明pred的线程状态为CANCELLED,需从队列中删除。
//如果pred的waitStatus==-1 (SIGNAL),则通过LockSupport.park()方法把当前线程挂起,并等待被唤醒
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
// 获取结点p的等待状态
int ws = pred.waitStatus;//节点p符合条件,直接返回
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) // 状态为SIGNAL,为-1
// 可以进行park操作
return true;
if (ws > 0) { // 表示状态为CANCELLED,为1
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0); // 找到pred结点前面最近的一个状态不为CANCELLED的结点
// 赋值pred结点的next域
pred.next = node;//此时pred和node节点将直接相连,之前的中间节点将无法再次被访问到
} else { // 为PROPAGATE -3 或者是0 表示无状态,(为CONDITION -2时,表示此节点在condition queue中)
// 比较并设置前驱结点的状态为SIGNAL
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
// 不能进行park操作
return false;
}
假设锁已被某线程占用,当前线程执行lock()方法,对于循环,第一次执行shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire之前,内存地址529的waitStatus为0:
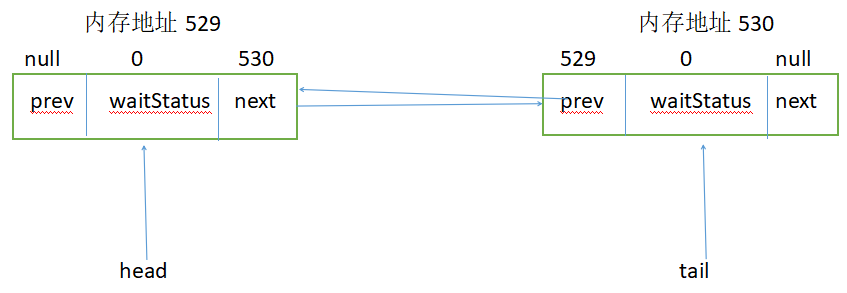
执行之后,内存地址529的waitStatus为-1:
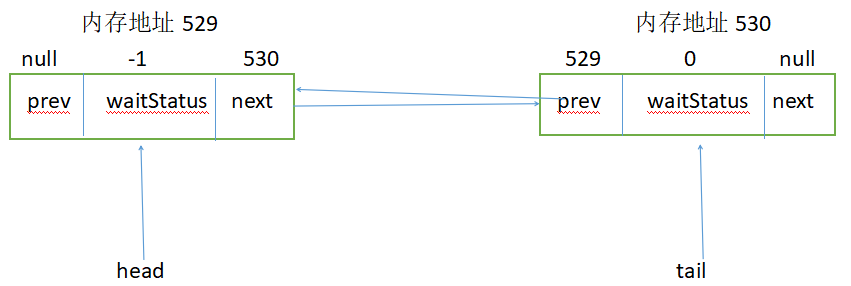
此时,返回false。在循环中,第二次执行shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire,由于node节点的前继节点的等待状态为-1,此处直接返回true。之后将执行parkAndCheckInterrupt(),将当前线程挂起。
需要注意:LockSupport.park() 除了 可以被 LockSupport.unpark() 唤醒,还支持对中断的响应.
// 进行挂起操作,当被 unpark() 唤醒时,返回false;当被中断时,返回false
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
// 在许可可用之前禁用当前线程,并且设置了blocker( park 方法 支持中断检测 )
LockSupport.park(this);//当前线程被挂起,之前的循环将不再继续执行了,直到unpark 或者 中断发生。
return Thread.interrupted(); // 返回当前线程中断状态值,并重置中断标记位(只有发生了中断,才会返回true)
}
如果执行出错,则执行清理操作cancelAcquire():
// 取消继续获取(资源),将当前节点等待状态置为CANCELLED
//此时node.prev指向了前驱节点中第一个不为CANCELLED的节点
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
// node为空,返回
if (node == null)
return;
// 设置node结点的thread为空
node.thread = null;
// 保存node的前驱结点
Node pred = node.prev;
while (pred.waitStatus > 0) // 找到node前驱结点中第一个状态小于0的结点,即不为CANCELLED状态的结点
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
// 获取pred结点的下一个结点
Node predNext = pred.next;
// 设置node结点的状态为CANCELLED
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
//pred则指向了那个节点,predNext指向了那个节点的下一个节点
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) { // node结点为尾结点,则设置尾结点为pred指向的结点
// 如果predNext是pred的下一个节点,那么pred.next置为null(符合尾节点的条件:尾节点的next域为null)
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);//此时,pred指向的节点为队列的尾节点;node.prev、predNext.prev 和 pred 均指向当前最新的尾节点;虽然没有将node.prev置为null,但是对于tail节点之后的节点是无法继续被访问到的,所以不需要置为null。
} else { // node结点不为尾结点
int ws;
//(pred结点不为头结点,并且pred结点的状态为SIGNAL)或者
// pred结点状态小于等于0(不为CANCELLED),设置pred等待状态为SIGNAL,并且pred结点所封装的线程不为空
if (pred != head && ((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL || (ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) && pred.thread != null) {
Node next = node.next;//next指向node的后继节点
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0) // 若 next 不空并且状态不为CANCELLED(由于已经确认了node 不是尾节点,所以此处只是进行了二次判断:node节点存在不为CANCELLED的后续节点)
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next); // 比较并设置pred.next = next;
//此时pred.next指向了next,next.prev指向了pred,从而跳过node,将上一个节点与下一个节点直接连接,虽然没有将node.prev仍指向pred,但是对于pred节点之后的节点是只能访问到next,因此node节点将无法被访问到,所以不需要置为null。
} else {//node节点为第一个有效节点,即head指针指向 node节点的前继节点;取消node节点的等待资格,需要通过重新唤醒node的后继节点,使得唤醒之后,将头指针指向唤醒的那个节点,从而node节点不再被访问的到。
unparkSuccessor(node); // 唤醒node的后继不为CANCELLED状态的第一个节点,此时node的等待状态为1
}
node.next = node; // node的next指向自身,help GC
}
}
// 唤醒node的后继不为CANCELLED状态的第一个节点
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
// 获取node结点的等待状态
int ws = node.waitStatus;//只要不是取消状态,则重新将等待状态值置为0,使得后续被唤醒的节点和当前节点重新公平竞争锁
if (ws < 0) // 状态值小于0,为SIGNAL -1 或 CONDITION -2 或 PROPAGATE -3
// 比较并且设置结点等待状态,设置为0
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);// 获取node节点的下一个结点
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) { // 下一个结点为null,则node为尾节点;下一个节点的等待状态大于0,即为CANCELLED;这两种情况的出现,都表示目前队列里面出现了错误;因为CANCELLED节点不应该被再次访问得到。此时,通过从尾节点向前遍历尝试找到一个可用的节点并唤醒,唤醒的节点在获得锁之后,会移动头指针指向被唤醒的节点;有可能会舍弃一部分可用的节点,但是这种做法也行之有效地快速修复了队列的错误。如果没有找到一个可用的节点,则证明此时不需要进行任何唤醒的操作。
// s赋值为空
s = null;
// 从尾结点开始从后往前开始遍历
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0) // 找到等待状态小于等于0的结点,找到最前的状态小于等于0的结点
// 保存结点
s = t;
}
if (s != null) // 该结点不为为空,唤醒节点s
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
当acquireQueued()在挂起等待锁的过程中出现了中断,返回true,将执行selfInterrupt()方法恢复线程的中断状态为true,以免中断状态丢失,使得无法被更高的调用栈得知曾经发生过中断请求:
static void selfInterrupt() {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();//设置当前线程的中断状态为true
}
lock()方法就分析完毕。
lockInterruptibly():如果当前线程被中断,直接抛出异常。未被中断,则尝试获取锁:获取成功,执行完毕;获取失败,则挂起等待。等待过程中被中断,将抛出异常,退出锁的队列且执行完毕;若是被释放锁的线程唤醒,将再次尝试获取锁,失败则再次挂起。
支持中断的独占锁获取(公平和非公平之分体现在调用tryAcquire(arg) 时 )
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
}
//以独占模式获取对象,如果被中断则中止
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())//抛出异常
throw new InterruptedException();
if (!tryAcquire(arg))//尝试调用tryAcquire获取锁(有公平和非公平之分)
doAcquireInterruptibly(arg);//对于非公平实现,tryAcquire(arg)返回false,则表示当前独占锁被其他线程独占;对于公平实现,tryAcquire(arg)返回false,则表示当前独占锁被其他线程独占或者当前线程不是队列中的第一个节点或者队列还未初始化。
}
使用tryAcquire(arg) 获取失败,则执行 doAcquireInterruptibly(arg);
private void doAcquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);//添加当前线程节点到队列中
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (; ; ) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();//得到前继节点
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {// 若p为头结点,即node为第一个‘有效’节点;再次执行tryAcquire 成功获得锁,则当前线程不需要挂起。
setHead(node);// 将头结点指向node
p.next = null; // 释放头节点的链接。help GC
failed = false;// 设置获得失败标志为false,即获得锁成功
return;
}//shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire判断节点p是否应当阻塞;parkAndCheckInterrupt() 正常被唤醒,将返回false
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();//发生中断,则抛出异常
}
} finally {
if (failed)//如果发生中断抛出异常,则执行清理操作
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
发生中断时,抛出异常之后,将执行cancelAcquire(node) :(释放node节点) 把node的等待状态值变为CANCELLED;如果node节点为尾节点,则node的前继节点为新的尾节点;如果node节点为中间节点,则让前继节点和后继节点直接连接;如果node节点为第一个有效的节点,则需要唤醒后继节点。
lockInterruptibly()方法分析完毕。
tryLock():只尝试获取一次。仅在调用时锁未被另一个线程保持的情况下,才获取该锁;获取失败就直接返回。
公平和非公平此处实现一致,均调用Sync的nonfairTryAcquire,也就是tryLock()只有非公平的实现:
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();//当前线程
int c = getState();//得到锁状态
if (c == 0) {//没有加锁
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {//如果锁状态修改成功,则设置
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);//记录占用当前独占锁的thread对象实例
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {//当前线程已拥有独占锁
int nextc = c + acquires;//增加重入次数
if (nextc < 0) // 重入次数小于0,越界 overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);//修改状态
return true;
}
return false;
}
tryLock() 实现比较简单。线程只会尝试获取一次锁时,即使获取失败也不会将线程节点加入队列。
tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit):若线程被中断,则直接抛出异常,否则尝试获取一次锁,获取仍然失败,则挂起指定的时间。挂起的期间,若被释放锁的线程给唤醒,则再次尝试,尝试成功,则返回true;尝试失败,将判断是否已超时:未超时,则继续挂起剩余的等待时间;已超时,则返回false执行完毕。挂起期间,接收到中断信号,则抛出异常且执行结束。
公平和非公平之分体现在调用tryAcquire(arg) 时:
public final boolean tryAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())//中断,则抛出异常
throw new InterruptedException();
return tryAcquire(arg) || doAcquireNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);//尝试获取锁,若获取不成功,则执行doAcquireNanos
}
对于非公平实现,tryAcquire(arg)返回false,则表示当前独占锁被其他线程独占;对于公平实现,tryAcquire(arg)返回false,则表示当前独占锁被其他线程独占或者当前线程不是队列中的第一个节点或者队列还未初始化。
private boolean doAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException {
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)//毫秒数小于0,则无需等待。等价于tryLock(),由于已经尝试了获取1次,直接返回false
return false;
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;//记录最终结束的系统时间
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);//执行addWaiter 添加当前线程节点到队列中
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (; ; ) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();//获得当前的前继节点
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {//如果当前节点是第一个有效节点,则尝试获取锁,而不需要挂起
setHead(node);//获得锁成功,修改头节点指向
p.next = null; //释放前继节点, help GC
failed = false;//成功
return true;//成功
}
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();//得到当前剩余时间
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)//没有剩余时间,返回false
return false;
//shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) 执行了清理CANCELLED状态节点的操作,判断node是否需要挂起
//只有剩余的等待时间大于了本身的挂起和唤醒操作的时间,才需要执行挂起;否则,继续尝试获取就行。
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && nanosTimeout > spinForTimeoutThreshold)
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);//挂起指定秒数后唤醒。支持中断响应
if (Thread.interrupted())//检测到中断信号,则抛出异常
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)//如果发生中断抛出异常,则执行清理操作
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
unlock():释放锁资源。没有公平和非公平之分,公平和非公平只体现在锁的获取策略上。
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {//先修改锁的状态值,记录独占锁的对象实例置为null
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)//队列已经初始化,且曾经执行过锁的获取或中断操作
unparkSuccessor(h);//唤醒头节点不为CANCELLED状态的后继节点
return true;//返回结果值
}
return false;//操作失败(当前线程也许并非存有锁的线程)
}
tryRelease(arg):默认的实现是抛出 UnsupportedOperationException 异常。因此子类必须要重写tryRelease(arg),此处没有公平和非公平之分:
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;//重入次数减1
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())//如果当前线程不是独占锁的所有者,则抛出异常
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false; //是否应当释放独占锁资源
if (c == 0) {//重入次数为0,表示应该释放所占资源
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);//记录独占锁的对象实例置为null
}
setState(c);//重新设置状态值
return free;//返回是否进行了释放所占资源操作
}
成功释放独占锁之后,还需要唤醒不为CANCELLED状态的后继节点,使其能够重新尝试获取锁资源:
// 唤醒node的后继不为CANCELLED状态的节点
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
// 获取node结点的等待状态
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0) // 状态值小于0,为SIGNAL -1 或 CONDITION -2 或 PROPAGATE -3
// 比较并且设置结点等待状态,设置为0
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);// 获取node节点的下一个结点
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) { // 下一个结点为空或者下一个节点的等待状态大于0,即为CANCELLED
// s赋值为空
s = null;
// 从尾结点开始从后往前开始遍历
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0) // 找到等待状态小于等于0的结点,找到最前的状态小于等于0的结点
// 保存结点
s = t;
}
if (s != null) // 该结点不为为空,唤醒该节点
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
newCondition():返回 ConditionObject 对象实例
final ConditionObject newCondition() {
return new ConditionObject();
}
构造函数本身什么也没有执行:
public ConditionObject() { }
具体的操作,均包含在signal、signalAll、await等方法之中。
getHoldCount():返回当前线程在某一个锁上的状态值。持有时,即在lock、lockInterruptibly、tryLock方法执行之前,一定返回0;在其之后,则会返回重入次数。
public int getHoldCount() {
return sync.getHoldCount();//执行内部类sync的getHoldCount()
}
final int getHoldCount() {
return isHeldExclusively() ? getState() : 0;//若当前线程持有独占锁,则返回state,否则返回0
}
protected final boolean isHeldExclusively() {
return getExclusiveOwnerThread() == Thread.currentThread();//返回当前线程的内存地址是否等于记录占用独占锁的Thread对象实例的内存地址
}
isHeldByCurrentThread():当前线程是否持有独占锁,持有,返回true;否则,返回false
public boolean isHeldByCurrentThread() {
return sync.isHeldExclusively();//执行内部类sync的isHeldExclusively()
}
isLocked():锁资源是否被任意的线程所持有
public boolean isLocked() {
return sync.isLocked();//执行内部类sync的isLocked()
}
final boolean isLocked() {
return getState() != 0;//状态值为0,则表示锁资源可用,返回false;否则,表示锁已被某个线程独占,返回true
}
isFair():返回当前创建的对象实例是否为公平锁对象实例。true:公平锁;false:不公平锁
public final boolean isFair() {
return sync instanceof FairSync;//使用instanceof关键字来比较当前对象实例sync的类是否为FairSync
}
getOwner():得到占用锁资源的线程对象实例
protected Thread getOwner() {
return sync.getOwner();//执行内部类sync的getOwner()
}
final Thread getOwner() {
return getState() == 0 ? null : getExclusiveOwnerThread();//锁为可用状态,返回null;锁为占用状态,返回记录占用锁的Thread对象实例
}
hasQueuedThreads():返回true,表示队列存在等待获取锁的线程节点;返回false,表示队列中不存在等待获取锁的线程节点。
public final boolean hasQueuedThreads() {
return sync.hasQueuedThreads();//执行内部类sync的hasQueuedThreads()
}
public final boolean hasQueuedThreads() {
return head != tail;//若头指针等于尾指针,即当前只存在一个节点,而该节点的线程正持有锁对象,将返回false,表示不存在等待获取锁的线程;若是在head和tail未初始化时,即两个都是null,此时返回false,仍正确表示出不存在等待获取锁的线程。
}
hasQueuedThread(Thread thread):返回true,代表thread对象存在于等待获取锁的队列之中,返回false,代表thread对象不存在于等待获取锁的队列之中。
public final boolean hasQueuedThread(Thread thread) {
return sync.isQueued(thread);//执行内部类sync的isQueued(thread)
}
public final boolean isQueued(Thread thread) {
if (thread == null)//处理空指针异常问题
throw new NullPointerException();
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev)//从队列尾部开始遍历
if (p.thread == thread)//若队列的线程对象实例和想要查询的线程对象实例内存地址相等,则代表找到了
return true;
return false;
}
getQueueLength():得到队列中的节点数
public final int getQueueLength() {
return sync.getQueueLength();
}
从尾指针向前遍历队列并计数,返回计数结果。
public final int getQueueLength() {
int n = 0;
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (p.thread != null)
++n;
}
return n;
}
getQueuedThreads():得到队列中的thread对象实例集合
protected Collection<Thread> getQueuedThreads() {
return sync.getQueuedThreads();
}
从尾指针向前遍历队列并添加到ArrayList集合中,返回ArrayList集合。
public final Collection<Thread> getQueuedThreads() {
ArrayList<Thread> list = new ArrayList<Thread>();
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
Thread t = p.thread;
if (t != null)//只要节点的对象实例不为空,就添加到集合中
list.add(t);
}
return list;
}
hasWaiters(Condition condition):在条件队列condition上,是否存在等待的线程。存在,返回true;不存在,返回false.
public boolean hasWaiters(Condition condition) {
if (condition == null)//处理空指针问题
throw new NullPointerException();
if (!(condition instanceof AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject))//判断参数类型是否合法
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not owner");
return sync.hasWaiters((AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject)condition);//执行ReentrantLock内部类Sync的hasWaiters方法
}
public final boolean hasWaiters(ConditionObject condition) {
if (!owns(condition))//判断是否由同一个AQS对象创建出的condition
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Not owner");
return condition.hasWaiters();//执行AQS内部类condition的hasWaiters()
}
从firstWaiter 开始遍历当前condition的所有节点,只要状态为等待状态,返回true,否则,返回false:
protected final boolean hasWaiters() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())//是否持有当前独占锁
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
for (Node w = firstWaiter; w != null; w = w.nextWaiter) {
if (w.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION)
return true;
}
return false;
}
getWaitQueueLength(Condition condition):在条件队列condition上的节点数
public int getWaitQueueLength(Condition condition) {
if (condition == null)//处理空指针问题
throw new NullPointerException();
if (!(condition instanceof AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject))//判断参数类型是否合法
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not owner");
return sync.getWaitQueueLength((AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject)condition);//执行ReentrantLock内部类Sync的getWaitQueueLength方法
}
public final int getWaitQueueLength(ConditionObject condition) {
if (!owns(condition))//判断是否由同一个AQS对象创建出的condition
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Not owner");
return condition.getWaitQueueLength();//执行AQS内部类condition的getWaitQueueLength()
}
从firstWaiter 开始遍历当前condition的所有节点,只要状态为等待状态,则计数一次,返回最终的计数值:
protected final int getWaitQueueLength() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())//是否持有当前独占锁
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
int n = 0;
for (Node w = firstWaiter; w != null; w = w.nextWaiter) {
if (w.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION)
++n;
}
return n;
}
getWaitingThreads(Condition condition):在条件队列condition上的thread对象实例集合
protected Collection<Thread> getWaitingThreads(Condition condition) {
if (condition == null)//处理空指针问题
throw new NullPointerException();
if (!(condition instanceof AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject))//判断参数类型是否合法
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not owner");
return sync.getWaitingThreads((AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject)condition);//执行ReentrantLock内部类Sync的getWaitingThreads方法
}
public final Collection<Thread> getWaitingThreads(ConditionObject condition) {
if (!owns(condition))//判断是否由同一个AQS对象创建出的condition
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Not owner");
return condition.getWaitingThreads();//执行AQS内部类condition的getWaitingThreads()
}
从firstWaiter 开始遍历当前condition的所有节点,只要状态为等待状态且thread对象实例不为null,则添加到集合中,返回最终的ArrayList对象集合:
protected final Collection<Thread> getWaitingThreads() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())//是否持有当前独占锁
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
ArrayList<Thread> list = new ArrayList<Thread>();
for (Node w = firstWaiter; w != null; w = w.nextWaiter) {
if (w.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION) {
Thread t = w.thread;
if (t != null)
list.add(t);
}
}
return list;
}
getState
protected final int getState()
返回同步状态的当前值。此操作具有 volatile 读的内存语义。
setState
protected final void setState(int newState)
设置同步状态的值。此操作具有 volatile 写的内存语义。
参数:
newState - 新的状态值
compareAndSetState
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update)
如果当前状态值等于预期值,则以原子方式标题 4将同步状态设置为给定的更新值。此操作具有 volatile 读和写的内存语义。
参数:
expect - 预期值
update - 新值
返回:
如果成功,则返回 true。返回 false 指示实际值与预期值不相等。
tryAcquire
protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg)
试图在独占模式下获取对象状态。此方法应该查询是否允许它在独占模式下获取对象状态,如果允许,则获取它。
此方法总是由执行 acquire 的线程来调用。如果此方法报告失败,则 acquire 方法可以将线程加入队列(如果还没有将它加入队列),直到获得其他某个线程释放了该线程的信号。可以用此方法来实现 Lock.tryLock() 方法。
默认实现将抛出 UnsupportedOperationException。
参数:
arg - acquire 参数。该值总是传递给 acquire 方法的那个值,或者是因某个条件等待而保存在条目上的值。该值是不间断的,并且可以表示任何内容。
返回:
如果成功,则返回 true。在成功的时候,此对象已经被获取。
抛出:
IllegalMonitorStateException - 如果正在进行的获取操作将在非法状态下放置此同步器。必须以一致的方式抛出此异常,以便同步正确运行。
UnsupportedOperationException - 如果不支持独占模式
tryRelease
protected boolean tryRelease(int arg)
试图设置状态来反映独占模式下的一个释放。
此方法总是由正在执行释放的线程调用。
默认实现将抛出 UnsupportedOperationException。
参数:
arg - release 参数。该值总是传递给 release 方法的那个值,或者是因某个条件等待而保存在条目上的当前状态值。该值是不间断的,并且可以表示任何内容。
返回:
如果此对象现在处于完全释放状态,从而使等待的线程都可以试图获得此对象,则返回 true;否则返回 false。
抛出:
IllegalMonitorStateException - 如果正在进行的释放操作将在非法状态下放置此同步器。必须以一致的方式抛出此异常,以便同步正确运行。
UnsupportedOperationException - 如果不支持独占模式
tryAcquireShared
protected int tryAcquireShared(int arg)
试图在共享模式下获取对象状态。此方法应该查询是否允许它在共享模式下获取对象状态,如果允许,则获取它。
此方法总是由执行 acquire 线程来调用。如果此方法报告失败,则 acquire 方法可以将线程加入队列(如果还没有将它加入队列),直到获得其他某个线程释放了该线程的信号。
默认实现将抛出 UnsupportedOperationException。
参数:
arg - acquire 参数。该值总是传递给 acquire 方法的那个值,或者是因某个条件等待而保存在条目上的值。该值是不间断的,并且可以表示任何内容。
返回:
在失败时返回负值;如果共享模式下的获取成功但其后续共享模式下的获取不能成功,则返回 0;如果共享模式下的获取成功并且其后续共享模式下的获取可能够成功,则返回正值,在这种情况下,后续等待线程必须检查可用性。(对三种返回值的支持使得此方法可以在只是有时候以独占方式获取对象的上下文中使用。)在成功的时候,此对象已被获取。
抛出:
IllegalMonitorStateException - 如果正在进行的获取操作将在非法状态下放置此同步器。必须以一致的方式抛出此异常,以便同步正确运行。
UnsupportedOperationException - 如果不支持共享模式
tryReleaseShared
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int arg)
试图设置状态来反映共享模式下的一个释放。
此方法总是由正在执行释放的线程调用。
默认实现将抛出 UnsupportedOperationException。
参数:
arg - release 参数。该值总是传递给 release 方法的那个值,或者是因某个条件等待而保存在条目上的当前状态值。该值是不间断的,并且可以表示任何内容。
返回:
如果此对象现在处于完全释放状态,从而使正在等待的线程都可以试图获得此对象,则返回 true;否则返回 false
抛出:
IllegalMonitorStateException - 如果正在进行的释放操作将在非法状态下放置此同步器。必须以一致的方式抛出此异常,以便同步正确运行
UnsupportedOperationException - 如果不支持共享模式
isHeldExclusively
protected boolean isHeldExclusively()
如果对于当前(正调用的)线程,同步是以独占方式进行的,则返回 true。此方法是在每次调用非等待 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject 方法时调用的。(等待方法则调用 release(int)。)
默认实现将抛出 UnsupportedOperationException。此方法只是 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject 方法内进行内部调用,因此,如果不使用条件,则不需要定义它。
返回:
如果同步是以独占方式进行的,则返回 true;其他情况则返回 false
抛出:
UnsupportedOperationException - 如果不支持这些条件
acquire
public final void acquire(int arg)
以独占模式获取对象,忽略中断。通过至少调用一次 tryAcquire(int) 来实现此方法,并在成功时返回。否则在成功之前,一直调用 tryAcquire(int) 将线程加入队列,线程可能重复被阻塞或不被阻塞。可以使用此方法来实现 Lock.lock() 方法。
参数:
arg - acquire 参数。此值被传送给 tryAcquire(int),但它是不间断的,并且可以表示任何内容。
acquireInterruptibly
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException
以独占模式获取对象,如果被中断则中止。通过先检查中断状态,然后至少调用一次 tryAcquire(int) 来实现此方法,并在成功时返回。否则在成功之前,或者线程被中断之前,一直调用 tryAcquire(int) 将线程加入队列,线程可能重复被阻塞或不被阻塞。可以使用此方法来实现 Lock.lockInterruptibly() 方法。
参数:
arg - acquire 参数。此值被传送给 tryAcquire(int),但它是不间断的,并且可以表示任何内容。
抛出:
InterruptedException - 如果当前线程被中断
tryAcquireNanos
public final boolean tryAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException
试图以独占模式获取对象,如果被中断则中止,如果到了给定超时时间,则会失败。通过先检查中断状态,然后至少调用一次 tryAcquire(int) 来实现此方法,并在成功时返回。否则,在成功之前、线程被中断之前或者到达超时时间之前,一直调用 tryAcquire(int) 将线程加入队列,线程可能重复被阻塞或不被阻塞。可以用此方法来实现 Lock.tryLock(long, TimeUnit) 方法。
参数:
arg - acquire 参数。此值被传送给 tryAcquire(int),但它是不间断的,并且可以表示任何内容。
nanosTimeout - 等待的最长时间,以毫微秒为单位
返回:
如果获取对象,则返回 true,如果超时,则返回 false
抛出:
InterruptedException - 如果当前线程被中断
release
public final boolean release(int arg)
以独占模式释放对象。如果 tryRelease(int) 返回 true,则通过消除一个或多个线程的阻塞来实现此方法。可以使用此方法来实现 Lock.unlock() 方法
参数:
arg - release 参数。此值被传送给 tryRelease(int),但它是不间断的,并且可以表示任何内容。
返回:
从 tryRelease(int) 返回的值
acquireShared
public final void acquireShared(int arg)
以共享模式获取对象,忽略中断。通过至少先调用一次 tryAcquireShared(int) 来实现此方法,并在成功时返回。否则在成功之前,一直调用 tryAcquireShared(int) 将线程加入队列,线程可能重复被阻塞或不被阻塞。
参数:
arg - acquire 参数。此值被传送给 tryAcquireShared(int),但它是不间断的,并且可以表示任何内容。
acquireSharedInterruptibly
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException
以共享模式获取对象,如果被中断则中止。通过先检查中断状态,然后至少调用一次 tryAcquireShared(int) 来实现此方法,并在成功时返回。否则在成功或线程被中断之前,一直调用 tryAcquireShared(int) 将线程加入队列,线程可能重复被阻塞或不被阻塞。
参数:
arg - acquire 参数。此值被传送给 tryAcquireShared(int),但它是不间断的,并且可以表示任何内容。
抛出:
InterruptedException - 如果当前线程被中断
tryAcquireSharedNanos
public final boolean tryAcquireSharedNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException
试图以共享模式获取对象,如果被中断则中止,如果到了给定超时时间,则会失败。通过先检查中断状态,然后至少调用一次 tryAcquireShared(int) 来实现此方法,并在成功时返回。否则在成功之前、线程被中断之前或者到达超时时间之前,一直调用 tryAcquireShared(int) 将线程加入队列,线程可能重复被阻塞或不被阻塞。
参数:
arg - acquire 参数。此值被传送给 tryAcquireShared(int),但它是不间断的,并且可以表示任何内容。
nanosTimeout - 等待的最长时间,以毫微秒为单位
返回:
如果获取对象,则返回 true,如果超时,则返回 false
抛出:
InterruptedException - 如果当前线程被中断
releaseShared
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg)
以共享模式释放对象。如果 tryReleaseShared(int) 返回 true,则通过消除一个或多个线程的阻塞来实现该方法。
参数:
arg - release 参数。此值被传送给 tryReleaseShared(int),但它是不间断的,并且可以表示任何内容。
返回:
从 tryReleaseShared(int) 中返回的值
hasQueuedThreads
public final boolean hasQueuedThreads()
查询是否有正在等待获取的任何线程。注意,随时可能因为中断和超时而导致取消操作,返回 true 并不能保证其他任何线程都将获取对象。
在此实现中,该操作是以固定时间返回的。
返回:
如果可能有其他线程正在等待获取锁,则返回 true。
hasContended
public final boolean hasContended()
查询是否其他线程也曾争着获取此同步器;也就是说,是否某个 acquire 方法已经阻塞。
在此实现中,该操作是以固定时间返回的。
返回:
如果曾经出现争用,则返回 true
getFirstQueuedThread
public final Thread getFirstQueuedThread()
返回队列中第一个(等待时间最长的)线程,如果目前没有将任何线程加入队列,则返回 null.
在此实现中,该操作是以固定时间返回的,但是,如果其他线程目前正在并发修改该队列,则可能出现循环争用。
返回:
队列中第一个(等待时间最长的)线程,如果目前没有将任何线程加入队列,则返回 null
isQueued
public final boolean isQueued(Thread thread)
如果给定线程的当前已加入队列,则返回 true。
该实现将遍历队列,以确定给定线程是否存在。
参数:
thread - 线程
返回:
如果给定线程在队列中,则返回 true
抛出:
NullPointerException - 如果 thread 为 null
getQueueLength
public final int getQueueLength()
返回等待获取的线程数估计值。该值只能是一个估计值,因为在此方法遍历内部数据结构时,线程的数量可能发生大的变化。该方法是为用来监视系统状态而设计的,不是为同步控制设计的。
返回:
正等待获取的线程估计数
getQueuedThreads
public final Collection<Thread> getQueuedThreads()
返回包含可能正在等待获取的线程 collection。因为在构造该结果时,实际线程 set 可能发生大的变化,所以返回的 collection 只是尽最大努力获得的一个估计值。返回 collection 的元素并不是以特定顺序排列的。此方法是为促进子类的构造而设计的,这些子类提供了大量的监视设施。
返回:
线程的 collection
getExclusiveQueuedThreads
public final Collection<Thread> getExclusiveQueuedThreads()
返回包含可能正以独占模式等待获取的线程 collection。此方法具有与 getQueuedThreads() 相同的属性,除了它只返回那些因独占获取而等待的线程。
返回:
线程的 collection
getSharedQueuedThreads
public final Collection<Thread> getSharedQueuedThreads()
返回包含可能正以共享模式等待获取的线程 collection。此方法具有与 getQueuedThreads() 相同的属性,除了它只返回那些因共享获取而等待的线程。
返回:
线程的 collection
toString
public String toString()
返回标识此同步器及其状态的字符串。此状态被括号括起来,它包括字符串 "State =",后面是 getState() 的当前值,再后面是 "nonempty" 或 "empty",这取决于队列是否为空。
覆盖:
返回:
标识此同步器及其状态的字符串
owns
public final boolean owns(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject condition)
查询给定的 ConditionObject 是否使用了此同步器作为其锁。
参数:
condition - 条件
返回:
如果具备此条件,则返回 true
抛出:
NullPointerException - 如果 condition 为 null
hasWaiters
public final boolean hasWaiters(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject condition)
查询是否有线程正在等待给定的、与此同步器相关的条件。注意,因为随时可能发生超时和中断,所以返回 true 并不能保证将来某个 signal 将唤醒任何线程。此方法主要是为了监视系统状态而设计的。
参数:
condition - 条件
返回:
如果有正在等待的线程,则返回 true
抛出:
IllegalMonitorStateException - 如果不进行独占同步
IllegalArgumentException - 如果给定的 condition 与此同步器无关
NullPointerException - 如果 condition 为 null
getWaitQueueLength
public final int getWaitQueueLength(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject condition)
返回正在等待与此同步器有关的给定条件的线程数估计值。注意,因为随时可能发生超时和中断,所以估计值只是实际等待线程的数量上限。此方法是为监视系统状态而设计的,不是为同步控制设计的。
参数:
condition - 条件
返回:
等待线程的估计数
抛出:
IllegalMonitorStateException - 如果不进行独占同步
IllegalArgumentException - 如果给定的 condition 与此同步器无关
NullPointerException - 如果 condition 为 null
getWaitingThreads
public final Collection<Thread> getWaitingThreads(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject condition)
返回一个 collection,其中包含可能正在等待与此同步器有关的给定条件的那些线程。因为在构造该结果时,实际线程 set 可能发生大的变化,所以返回的 collection 只是尽最大努力获得的一个估计值。返回 collection 的元素并不是以特定顺序排列的。
参数:
condition - 条件
返回:
线程的 collection
抛出:
IllegalMonitorStateException - 如果不进行独占同步
IllegalArgumentException - 如果给定的 condition 与此同步器无关
NullPointerException - 如果 condition 为 null























 980
980











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








