演示效果如下:
另外在竖屏的时候是这样的效果:
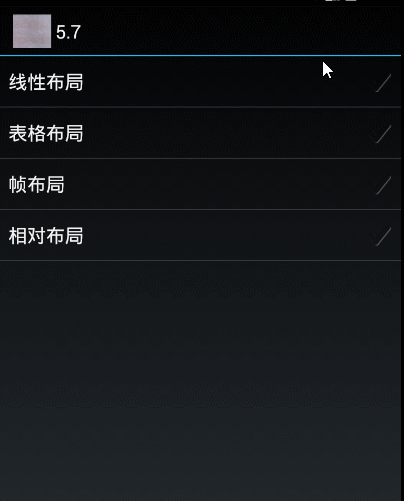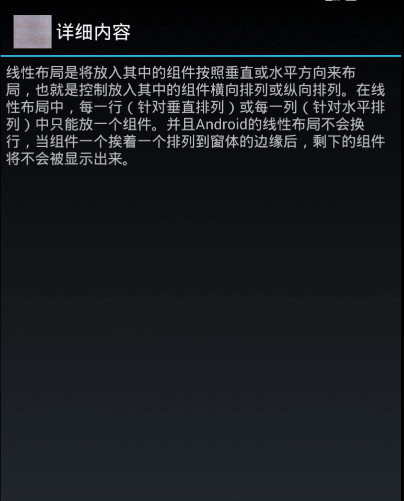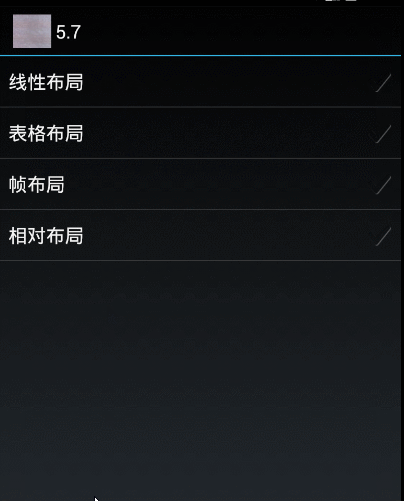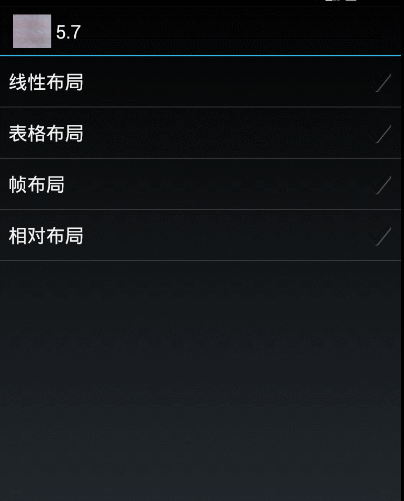
布局文件如下:
可以看出有两个资源文件,一个是处理横屏一个是竖屏
第一个:
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
android:id="@+id/titles"
android:layout_width="0px"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
class="com.xuliugen.frag.ListFragment" />
第二个:
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
android:id="@+id/titles"
android:layout_width="0px"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
class="com.xuliugen.frag.ListFragment" />
android:id="@+id/detail"
android:layout_width="0px"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:background="?android:attr/detailsElementBackground" />
类代码
Data.java
public final class Data {
// 标题
public static final String[] TITLES = { "线性布局", "表格布局", "帧布局", "相对布局"
};
// 详细内容
public static final String[] DETAIL = {
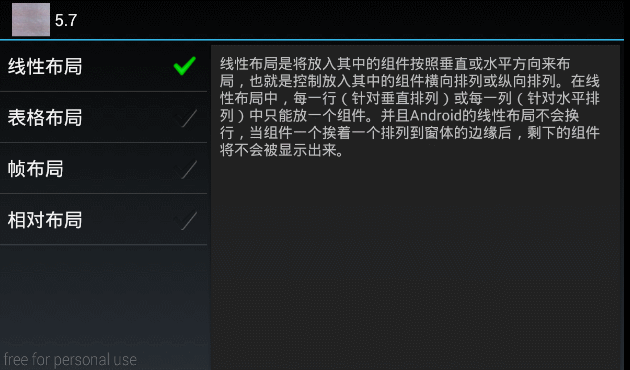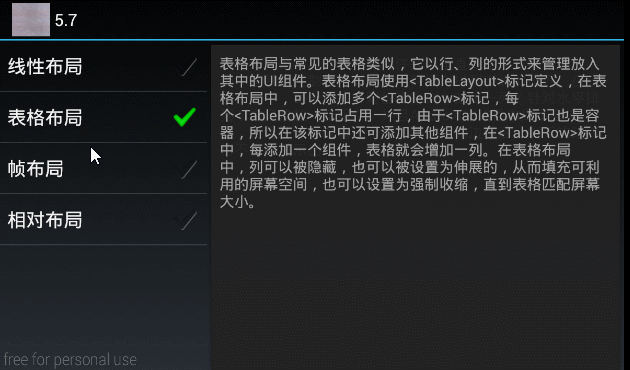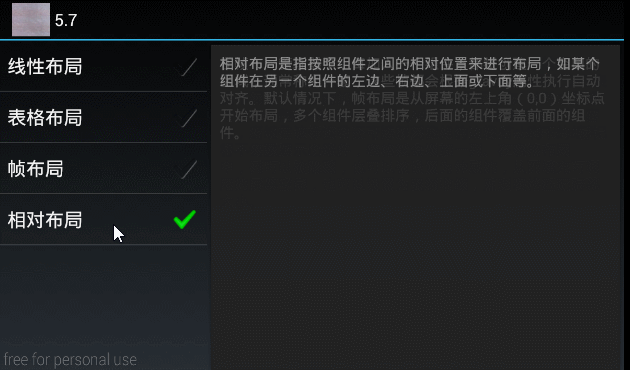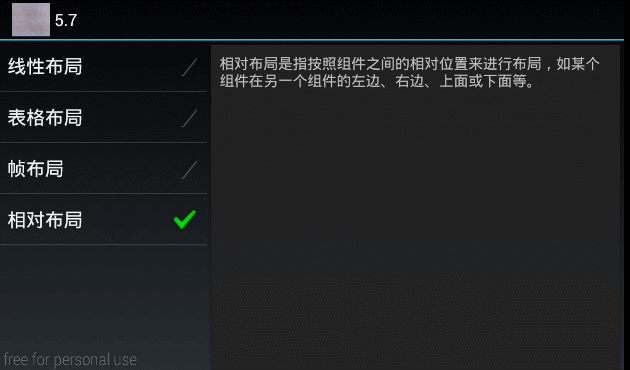
"线性布局是将放入其中的组件按照垂直或水平方向来布局,也就是控制放入其中的组件横向排列或纵向排列。"
+ "在线性布局中,每一行(针对垂直排列)或每一列(针对水平排列)中只能放一个组件。"
+ "并且Android的线性布局不会换行,当组件一个挨着一个排列到窗体的边缘后,剩下的组件将不会被显示出来。",
"表格布局与常见的表格类似,它以行、列的形式来管理放入其中的UI组件。"
+ "表格布局使用标记定义,在表格布局中,可以添加多个标记,"
+ "每个标记占用一行,由于标记也是容器,所以在该标记中还可添加其他组件,"
+ "在标记中,每添加一个组件,表格就会增加一列。在表格布局中,列可以被隐藏,"
+ "也可以被设置为伸展的,从而填充可利用的屏幕空间,也可以设置为强制收缩,直到表格匹配屏幕大小。",
"在帧布局管理器中,每加入一个组件,都将创建一个空白的区域,通常称为一帧,"
+ "这些帧都会根据gravity属性执行自动对齐。默认情况下,帧布局是从屏幕的左上角(0,0)坐标点开始布局,"
+ "多个组件层叠排序,后面的组件覆盖前面的组件。",
"相对布局是指按照组件之间的相对位置来进行布局,如某个组件在另一个组件的左边、右边、上面或下面等。" };
}
DetailFragment.java
package com.xuliugen.frag;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ScrollView;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class DetailFragment extends Fragment {
// 创建一个DetailFragment的新实例,其中包括要传递的数据包
public static DetailFragment newInstance(int index) {
DetailFragment f = new DetailFragment();
// 将index作为一个参数传递
Bundle bundle = new Bundle(); // 实例化一个Bundle对象
bundle.putInt("index", index); // 将索引值添加到Bundle对象中
f.setArguments(bundle); // 将bundle对象作为Fragment的参数保存
return f;
}
public int getShownIndex() {
return getArguments().getInt("index", 0); // 获取要显示的列表项索引
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
if (container == null) {
return null;
}
ScrollView scroller = new ScrollView(getActivity()); // 创建一个滚动视图
TextView text = new TextView(getActivity()); // 创建一个文本框对象
text.setPadding(10, 10, 10, 10); // 设置内边距
scroller.addView(text); // 将文本框对象添加到滚动视图中
text.setText(Data.DETAIL[getShownIndex()]); // 设置文本框中要显示的文本
return scroller;
}
}
ListFragment.java
package com.xuliugen.frag;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
public class ListFragment extends android.app.ListFragment {
boolean dualPane; // 是否在一屏上同时显示列表和详细内容
int curCheckPosition = 0; // 当前选择的索引位置
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
setListAdapter(new ArrayAdapter(getActivity(),
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_checked, Data.TITLES)); // 为列表设置适配器
View detailFrame = getActivity().findViewById(R.id.detail); // 获取布局文件中添加的FrameLayout帧布局管理器
dualPane = detailFrame != null
&& detailFrame.getVisibility() == View.VISIBLE; // 判断是否在一屏上同时显示列表和详细内容
if (savedInstanceState != null) {
curCheckPosition = savedInstanceState.getInt("curChoice", 0); // 更新当前选择的索引位置
}
if (dualPane) { // 如果在一屏上同时显示列表和详细内容
getListView().setChoiceMode(ListView.CHOICE_MODE_SINGLE); // 设置列表为单选模式
showDetails(curCheckPosition); // 显示详细内容
}
}
// 重写onSaveInstanceState()方法,保存当前选中的列表项的索引值
@Override
public void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState) {
super.onSaveInstanceState(outState);
outState.putInt("curChoice", curCheckPosition);
}
// 重写onListItemClick()方法
@Override
public void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) {
showDetails(position); // 调用showDetails()方法显示详细内容
}
void showDetails(int index) {
curCheckPosition = index; // 更新保存当前索引位置的变量的值为当前选中值
if (dualPane) { // 当在一屏上同时显示列表和详细内容时
getListView().setItemChecked(index, true); // 设置选中列表项为选中状态
DetailFragment details = (DetailFragment) getFragmentManager()
.findFragmentById(R.id.detail); // 获取用于显示详细内容的Fragment
if (details == null || details.getShownIndex() != index) { // 如果如果
details = DetailFragment.newInstance(index); // 创建一个新的DetailFragment实例用于显示当前选择项对应的详细内容
// 要在activity中管理fragment, 需要使用FragmentManager
FragmentTransaction ft = getFragmentManager()
.beginTransaction();// 获得一个FragmentTransaction的实例
ft.replace(R.id.detail, details); // 替换原来显示的详细内容
ft.setTransition(FragmentTransaction.TRANSIT_FRAGMENT_FADE); // 设置转换效果
ft.commit(); // 提交事务
}
} else { // 在一屏上只能显示列表或详细内容中的一个内容时
// 使用一个新的Activity显示详细内容
Intent intent = new Intent(getActivity(),
MainActivity.DetailActivity.class); // 创建一个Intent对象
intent.putExtra("index", index); // 设置一个要传递的参数
startActivity(intent); // 开启一个指定的Activity
}
}
}
MainActivity.java
package com.xuliugen.frag;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.res.Configuration;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
// 创建一个继承Activity的内部类,用于在手机界面中,通过Activity显示详细内容
public static class DetailActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 判断是否为横屏,如果为横屏,则结束当前Activity,准备使用Fragment显示详细内容
if (getResources().getConfiguration().orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE) {
finish(); // 结束当前Activity
return;
}
if (savedInstanceState == null) { //
// 在初始化时插入一个显示详细内容的Fragment
DetailFragment details = new DetailFragment();// 实例化DetailFragment的对象
details.setArguments(getIntent().getExtras()); // 设置要传递的参数
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.add(android.R.id.content, details).commit(); // 添加一个显示详细内容的Fragment
}
}
}
}
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,谢谢大家对脚本之家的支持。如果你想了解更多相关内容请查看下面相关链接





















 2149
2149











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








