Debug
debug的入口在CtsConsole类,所以我们把第一个断点打在249行:
Console console = new CtsConsole();按F6再按F5进入到Console.startConsole方法中。
按F5进入GlobalConfiguration.createGlobalConfiguration方法中。
该方法内主要是读取全局配置文件并设置IGlobalConfiguration接口对象sInstance。主要方法为95行读取文件的getGlobalConfigPath():
private static String getGlobalConfigPath() throws ConfigurationException {
String path = System.getenv(GLOBAL_CONFIG_VARIABLE);
if (path != null) {
// don't actually check for accessibility here, since the variable
// might be specifying
// a java resource rather than a filename. Even so, this can help
// the user figure out
// which global config (if any) was picked up by TF.
System.err
.format("Attempting to use global config \"%s\" from variable $%s.\n",
path, GLOBAL_CONFIG_VARIABLE);
return path;
}
File file = new File(GLOBAL_CONFIG_FILENAME);
if (file.exists()) {
path = file.getPath();
System.err.format(
"Attempting to use auto detected global config \"%s\".\n",
path);
System.err.flush();
return path;
}
// FIXME: search in tradefed.sh launch dir (or classpath?) return null; }
首先推断是否设置了全局配置文件的系统变量,假设没有设置,那直接在当前文件文件夹下找tf_global_config.xml文件。
非常显然,本程序这些都没有。所以该方法返回的结果应该是null。回到了createGlobalConfiguration(String[] args)方法中:
if (globalConfigPath != null) {
// Found a global config file; attempt to parse and use it
sInstance = configFactory.createGlobalConfigurationFromArgs(
ArrayUtil.buildArray(new String[] { globalConfigPath },
args), nonGlobalArgs);
System.err.format("Success! Using global config \"%s\"\n",
globalConfigPath);
} else {
// Use default global config
sInstance = new GlobalConfiguration();
nonGlobalArgs = Arrays.asList(args);
}
return nonGlobalArgs;由于返回的路径为null。所以直接跳转到else语句块中,new一个新对象,没有设置不论什么属性。最后将命令行參数封装在list中返回,然后console设置參数,终于启动线程来运行任务。所以第二个断点要打在Console的run方法里。然后按F8进入run方法。
run方法中先做一些參数的推断,假设为空。启动CommandScheduler线程。里面会去从运行队列中拿出队首元素。假设取得的队列为空就会结束。
假设參数不为空。除了启动CommandScheduler线程外还会运行其它的操作,例如以下:
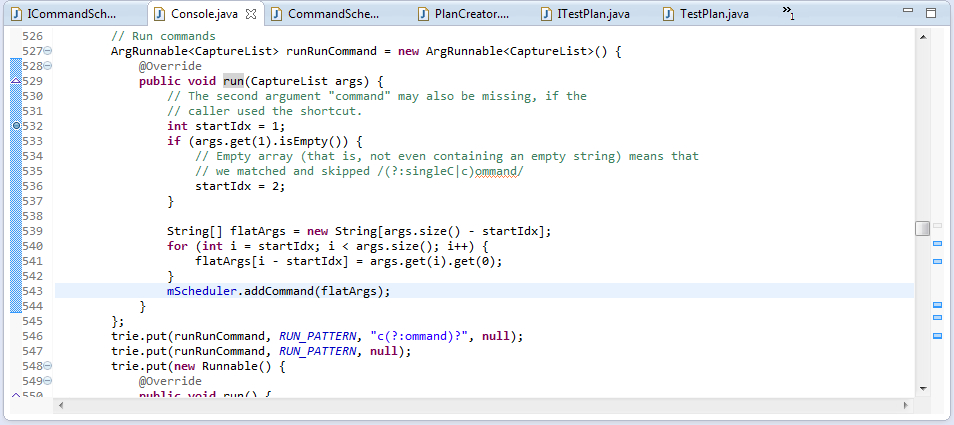
public void run() {
List<String> arrrgs = mMainArgs;
// Fallback, in case this isn't set already
if (mScheduler == null) {
mScheduler = new CommandScheduler();
}
try {
// Check System.console() since jline doesn't seem to consistently know whether or not
// the console is functional.
if (!isConsoleFunctional()) {
if (arrrgs.isEmpty()) {
printLine("No commands for non-interactive mode; exiting.");
// FIXME: need to run the scheduler here so that the things blocking on it
// FIXME: will be released.
mScheduler.start();
mScheduler.await();
return;
} else {
printLine("Non-interactive mode: Running initial command then exiting.");
mShouldExit = true;
}
}
// Wait for the CommandScheduler to start. It will hold the JVM open (since the Console
// thread is a Daemon thread), and also we require it to have started so that we can
// start processing user input.
mScheduler.start();
mScheduler.await();
String input = "";
CaptureList groups = new CaptureList();
String[] tokens;
// Note: since Console is a daemon thread, the JVM may exit without us actually leaving
// this read loop. This is by design.
do {
if (arrrgs.isEmpty()) {
input = getConsoleInput();
if (input == null) {
// Usually the result of getting EOF on the console
printLine("");
printLine("Received EOF; quitting...");
mShouldExit = true;
break;
}
tokens = null;
try {
tokens = QuotationAwareTokenizer.tokenizeLine(input);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
printLine(String.format("Invalid input: %s.", input));
continue;
}
if (tokens == null || tokens.length == 0) {
continue;
}
} else {
printLine(String.format("Using commandline arguments as starting command: %s",
arrrgs));
if (mConsoleReader != null) {
// Add the starting command as the first item in the console history
// FIXME: this will not properly escape commands that were properly escaped
// FIXME: on the commandline. That said, it will still be more convenient
// FIXME: than copying by hand.
final String cmd = ArrayUtil.join(" ", arrrgs);
mConsoleReader.getHistory().addToHistory(cmd);
}
tokens = arrrgs.toArray(new String[0]);
//置空
arrrgs = Collections.emptyList();
}
Runnable command = mCommandTrie.retrieve(groups, tokens);
if (command != null) {
executeCmdRunnable(command, groups);
} else {
printLine(String.format(
"Unable to handle command '%s'. Enter 'help' for help.", tokens[0]));
}
RunUtil.getDefault().sleep(100);
} while (!mShouldExit);
} catch (Exception e) {
printLine("Console received an unexpected exception (shown below); shutting down TF.");
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
mScheduler.shutdown();
// Make sure that we don't quit with messages still in the buffers
System.err.flush();
System.out.flush();
}
}上面这段代码主要看846行左右的
executeCmdRunnable(command, groups);我们来看这种方法里面的实现:
/**
* Execute a command.
* <p />
* Exposed for unit testing
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
void executeCmdRunnable(Runnable command, CaptureList groups) {
if (command instanceof ArgRunnable) {
// FIXME: verify that command implements ArgRunnable<CaptureList> instead
// FIXME: of just ArgRunnable
((ArgRunnable<CaptureList>)command).run(groups);
} else {
command.run();
}
}会发现程序会跳转到
((ArgRunnable<CaptureList>)command).run(groups);然后再按F5就跳转不进去了。这个时候程序进入到了
所以在这个地方打个断点。又一次启动debug,会进入到这个地方。该方法调用了CommandScheduler.addCommand方法,进入该方法
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public boolean addCommand(String[] args, long totalExecTime) {
try {
//得到cts配置文件的信息
IConfiguration config = getConfigFactory().createConfigurationFromArgs(args);
//打印帮助信息,仅仅打印Importance类型的option信息
if (config.getCommandOptions().isHelpMode()) {
getConfigFactory().printHelpForConfig(args, true, System.out);
System.out.flush();
//打印全部option信息
} else if (config.getCommandOptions().isFullHelpMode()) {
getConfigFactory().printHelpForConfig(args, false, System.out);
} else if (config.getCommandOptions().isDryRunMode()) {
if (config.getCommandOptions().isNoisyDryRunMode()) {
CLog.logAndDisplay(LogLevel.DEBUG, "DRY RUN: %s", Arrays.toString(args));
} else {
CLog.d("Dry run mode; skipping adding command: %s", Arrays.toString(args));
}
} else {
config.validateOptions();
if (config.getCommandOptions().runOnAllDevices()) {
addCommandForAllDevices(totalExecTime, args);
} else {
CommandTracker cmdTracker = createCommandTracker(args);
cmdTracker.incrementExecTime(totalExecTime);
ExecutableCommand cmdInstance = createExecutableCommand(cmdTracker, config, false);
addExecCommandToQueue(cmdInstance, 0);
}
return true;
}
} catch (ConfigurationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// FIXME: do this with jline somehow for ANSI support
// note: make sure not to log (aka record) this line, as (args) may contain passwords.
System.out.println(String.format("Error while processing args: %s",
Arrays.toString(args)));
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.out.println();
}
return false;
}
先来看第一行代码:
IConfiguration config = getConfigFactory().createConfigurationFromArgs(args);该方法会依据參数中的第二个參数来找到config文件夹下的xml文件,读取里面的内容,然后配置CTS框架的9大组件(这个内容放在下一篇文章讲)。
得到Config对象后,会推断是全设备执行还是单个设备执行,默认是全设备执行。假设是单设备执行,须要指定设备的sn号,框架依据SN号来找到设备。最后将执行计划放入到队列中。
到此任务的加入就完毕了。任务队列不断的接受新的任务,然后CommandScheduler的run方法里有一个循环。每次都取第一个任务出来运行。
try {
// Notify other threads that we're running.
mRunLatch.countDown();
IDeviceManager manager = getDeviceManager();
while (!isShutdown()) {
ExecutableCommand cmd = dequeueConfigCommand();
if (cmd != null) {
IDeviceSelection options = cmd.getConfiguration().getDeviceRequirements();
ITestDevice device = manager.allocateDevice(0, options);
if (device != null) {
// Spawn off a thread to perform the invocation
InvocationThread invThread = startInvocation(manager, device, cmd);
addInvocationThread(invThread);
if (cmd.isLoopMode()) {
addNewExecCommandToQueue(cmd.getCommandTracker());
}
} else {
// no device available for command, put back in queue
// increment exec time to ensure fair scheduling among commands when devices
// are scarce
cmd.getCommandTracker().incrementExecTime(1);
addExecCommandToQueue(cmd, NO_DEVICE_DELAY_TIME);
//CLog.logAndDisplay(LogLevel.ERROR,String.format("Can't find device %s.",options.getSerials()));
}
}
}
mCommandTimer.shutdown();
CLog.i("Waiting for invocation threads to complete");
List<InvocationThread> threadListCopy;
synchronized (this) {
threadListCopy = new ArrayList<InvocationThread>(mInvocationThreads.size());
threadListCopy.addAll(mInvocationThreads);
}
for (Thread thread : threadListCopy) {
waitForThread(thread);
}
closeRemoteClient();
if (mRemoteManager != null) {
mRemoteManager.cancel();
}
exit(manager);
cleanUp();
CLog.logAndDisplay(LogLevel.INFO, "All done");
} finally {
// Make sure that we don't quit with messages still in the buffers
System.err.flush();
System.out.flush();
}到此任务的加入就算讲完了。 下一篇文章解析一下是怎样解析配置文件的。
版权声明:本文博客原创文章,博客,未经同意,不得转载。


























 1276
1276

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








