相对布局管理器指的是參考某一其它控件进行摆放,能够通过控制,将组件摆放在一个指定參考组件的上、下、左、右等位置,这些能够直接通过各个组件提供的属性完毕。
以下介绍一下各个方法的基本使用
|
No.
|
属性名称
|
相应的规则常量
|
描写叙述
|
|
1
|
android:layout_below
|
RelativeLayout.BELOW
|
摆放在指定组件的下边
|
|
2
|
android:layout_toLeftOf
|
RelativeLayout.LEFT_OF
|
摆放在指定组件的左边
|
|
3
|
android:layout_toRightOf
|
RelativeLayout.RIGHT_OF
|
摆放在指定组件的右边
|
|
4
|
android:layout_alignTop
|
RelativeLayout.ALIGN_TOP
|
以指定组件为參考进行上对齐
|
|
5
|
android:layout_alignBottom
|
RelativeLayout.ALIGN_BOTTOM
|
以指定组件为參考进行下对齐
|
|
6
|
android:layout_alignLeft
|
RelativeLayout.ALIGN_LEFT
|
以指定组件为參考进行左对齐
|
|
7
|
android:layout_alignRight
|
RelativeLayout.ALIGN_RIGHT
|
以指定组件为參考进行右对齐
|
<span style="font-size:18px;"><RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:textAlignment="center"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:ems="10" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/editText1"
android:layout_below="@+id/editText1"
android:ems="10"
android:inputType="textPassword" >
<requestFocus />
</EditText>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/editText1"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:text="账号" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:text="password"
android:textAlignment="center" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_marginLeft="23dp"
android:layout_marginTop="36dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/textView2"
android:text="登 录" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/button1"
android:layout_marginLeft="14dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/button1"
android:autoLink="web"
android:linksClickable="true"
android:text="忘记password"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceSmall"
android:textSize="10dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
</span>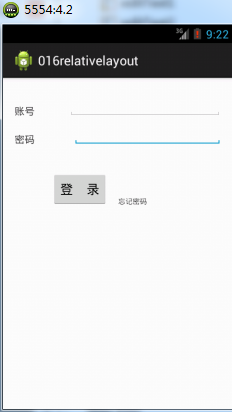
使用相对布局是眼下基本的布局方式,它比其它方式都方便快捷,能够再可视化界面直接拖拽就可以。
…………………………………………………………毫无美感的切割线…………………………………………………………
使用动态表布局实现和前面的是一样的,不常使用在这里不再赘述,有兴趣的读者能够自己尝试。
须要使用下面几个方法。
|
1
|
public RelativeLayout.LayoutParams (int w, int h)
|
构造
|
指定RelativeLayout布局的宽度和高度
|
|
2
|
public void addRule (int verb, int anchor)
|
普通
|
添加指定的參数规则
|
|
3
|
public int[] getRules ()
|
普通
|
取得一个组件的所有參数规则
|
下节预报:使用嵌套布局实现计算器界面






















 1044
1044

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








