这场还是tourist出题,我当时大晚上做完1题滚粗了
一个节点下面必须k叉的,直接统计就好了,但是has at least 3 leaf children,所以需要<=3,我没考虑这个啊
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int N=100005; int n,fa[N],use[N],f; int main() { scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=2; i<=n; i++) scanf("%d",&fa[i]),use[fa[i]]=1; for(int i=n; i>=1; i--) if(!use[i])use[fa[i]]++; for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) if(use[i]>0&&use[i]<4)f=1; if(!f)puts("Yes"); else puts("No"); return 0; }
我直接dfs也要区分节点啊,所以+1好了,就和上面的一样正确了
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int N=1005; vector<int>V[N]; int F[N]; void dfs(int x) { for(auto X:V[x]) { if(V[X].size())dfs(X); else F[x]++; } F[x]++; } int main() { int n,f=1; scanf("%d",&n); for(int u=2,v;u<=n;u++) scanf("%d",&v),V[v].push_back(u); dfs(1); for(int i=1;i<=n&&f;i++) if(F[i]&&F[i]<4)f=0; printf("%s",f?"YES":"NO"); return 0; }
A New Year party is not a New Year party without lemonade! As usual, you are expecting a lot of guests, and buying lemonade has already become a pleasant necessity.
Your favorite store sells lemonade in bottles of n different volumes at different costs. A single bottle of type i has volume 2i - 1 liters and costs ci roubles. The number of bottles of each type in the store can be considered infinite.
You want to buy at least L liters of lemonade. How many roubles do you have to spend?
The first line contains two integers n and L (1 ≤ n ≤ 30; 1 ≤ L ≤ 109) — the number of types of bottles in the store and the required amount of lemonade in liters, respectively.
The second line contains n integers c1, c2, ..., cn (1 ≤ ci ≤ 109) — the costs of bottles of different types.
Output a single integer — the smallest number of roubles you have to pay in order to buy at least L liters of lemonade.
4 12
20 30 70 90
150
4 3
10000 1000 100 10
10
4 3
10 100 1000 10000
30
5 787787787
123456789 234567890 345678901 456789012 987654321
44981600785557577
In the first example you should buy one 8-liter bottle for 90 roubles and two 2-liter bottles for 30 roubles each. In total you'll get 12 liters of lemonade for just 150 roubles.
In the second example, even though you need only 3 liters, it's cheaper to buy a single 8-liter bottle for 10 roubles.
In the third example it's best to buy three 1-liter bottles for 10 roubles each, getting three liters for 30 roubles.
模拟题,看样例猜题意看题目一条龙
#include <iostream> using namespace std; long long n,l,d,a[35],i,c,s=1e18; int main() { cin>>n>>l>>a[0]; for(int i=1; i<n; i++) cin>>a[i],a[i]=min(a[i-1]*2,a[i]); for(int i=n-1; i>=0; i--) { d=(1<<i); c+=a[i]*(l/d); l%=d; s=min(s,c+(l!=0)*a[i]); } cout<<s; }







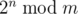 ,
,
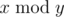 denotes the remainder of division of
denotes the remainder of division of 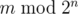 .
.
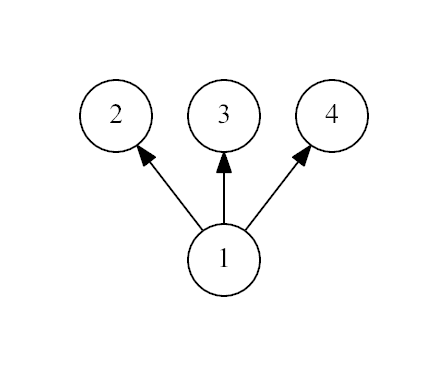














 1527
1527

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








