这个题重要的是看n,m的范围,(1 ≤ n,m ≤ 108).这里n是很大的,当n>2^63-1时long long也放不下,可是m<=1e8,也就是2^n>m时m mod (2^n)=0,当n>=27时,2^n>1e8也就是一定比m大,其余情况直接算
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<math.h>
#include<iomanip>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define M 32000
int main()
{
int n,m;
//int t=pow(2,27);
//printf("%d\n",t);
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
if(n>=27)
printf("%d\n",m);
else
{
int t=pow(2,n);
printf("%d\n",m%t);
}
return 0;
}题意:有一个n个节点的有根树,只有一个根,下面给出了除根节点外每个节点的父节点,问除叶节点外是否所有节点都至少有3个是叶节点的子节点。
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<math.h>
#include<iomanip>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define M 1005
int n;
vector<int> p[M];
int num[M];
int main()
{
int i,j,t,k;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&t);
p[i].push_back(t);
num[t]++;
}
bool flag=true;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int res=0;
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
for(k=0;k<p[j].size();k++)
{
if(p[j][k]==i&&num[j]==0)
{
res++;
break;
}
}
}
if(num[i]!=0&&res<3)
{
flag=false;
break;
}
}
if(flag)
printf("Yes\n");
else
printf("No\n");
return 0;
}A New Year party is not a New Year party without lemonade! As usual, you are expecting a lot of guests, and buying lemonade has already become a pleasant necessity.
Your favorite store sells lemonade in bottles of n different volumes at different costs. A single bottle of type i has volume 2i - 1 liters and costs ci roubles. The number of bottles of each type in the store can be considered infinite.
You want to buy at least L liters of lemonade. How many roubles do you have to spend?
The first line contains two integers n and L (1 ≤ n ≤ 30; 1 ≤ L ≤ 109) — the number of types of bottles in the store and the required amount of lemonade in liters, respectively.
The second line contains n integers c1, c2, ..., cn (1 ≤ ci ≤ 109) — the costs of bottles of different types.
Output a single integer — the smallest number of roubles you have to pay in order to buy at least L liters of lemonade.
4 12 20 30 70 90
150
4 3 10000 1000 100 10
10
4 3 10 100 1000 10000
30
5 787787787 123456789 234567890 345678901 456789012 987654321
44981600785557577
In the first example you should buy one 8-liter bottle for 90 roubles and two 2-liter bottles for 30 roubles each. In total you'll get 12 liters of lemonade for just 150 roubles.
In the second example, even though you need only 3 liters, it's cheaper to buy a single 8-liter bottle for 10 roubles.
In the third example it's best to buy three 1-liter bottles for 10 roubles each, getting three liters for 30 roubles.
题意:有n种装lemonade的瓶子,分别为1~n,第i种瓶子的容量为2^(i-1)升价格为c[i],问至少买L升最少花多少钱。
可以将每种瓶子对应的容量的最优价格先求出来,再贪心,下面两个代码都是在Standings上看的代码,都很巧妙,
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<math.h>
#include<iomanip>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define M 35
int n;
ll L,c[M],ans;
int main()
{
int i;
scanf("%d%I64d",&n,&L);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%I64d",&c[i]);
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
c[i]=min(c[i],2*c[i-1]);
for(i=n-2;i>=0;i--) //这个for循环不加也能AC
c[i]=min(c[i],c[i+1]);
ll ans=4e18,res=0;
for(i=n-1;i>=0;i--)
{
res+=c[i]*(L>>i); //(L>>i)就是L/2^(i-1)
ans=min(ans,res+c[i]);
L%=(1ll<<i);
}
printf("%I64d\n",min(ans,res));
return 0;
}#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define M 35
int n;
ll c[M],L,ans;
int main()
{
int i;
scanf("%d%I64d",&n,&L);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%I64d",&c[i]);
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++)
c[i+1]=min(c[i+1],2*c[i]);
for(i=n-2;i>=0;i--)
c[i]=min(c[i],c[i+1]);
ll ans=4e18;
ll sum=0;
for(i=n-1;i>=0;i--)
{
int need=L/(1<<i);
sum+=(ll)need*c[i];
L-=need<<i;
ans=min(ans,sum+(L>0)*c[i]);
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}







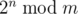 ,
,
 denotes the remainder of division of
denotes the remainder of division of 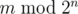 .
.




















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








