In the C++ programming language, a reference is a simple reference datatype that is less powerful but safer than the pointer type inherited from C. The name C++ reference may cause confusion, as in computer science a reference is a general concept datatype, with pointers and C++ references being specific reference datatype implementations. The definition of a reference in C++ is such that it does not need to exist. It can be implemented as a new name for an existing object (similar to rename keyword in Ada).
C++ references differ from pointers in several essential ways:
It is not possible to refer directly to a reference object after it is defined; any occurrence of its name refers directly to the object it references.
Once a reference is created, it cannot be later made to reference another object; it cannot be reseated. This is often done with pointers.
References cannot be null, whereas pointers can; every reference refers to some object, although it may or may not be valid. Note that for this reason, containers of references are not allowed.
References cannot be uninitialized. Because it is impossible to reinitialize a reference, they must be initialized as soon as they are created. In particular, local and global variables must be initialized where they are defined, and references which are data members of class instances must be initialized in the initializer list of the class's constructor.
References can be thought of as "Symbolic links" in file system terminology. Symbolic links can be modified as though they were the file they were linked to and when a symbolic link is deleted the original file remains. Similarly, references can be deleted (whether by going out of scope or explicitly being removed if they were allocated in heap) and the original object that was referenced remains. Similarly, once a symbolic link has been created it can never be changed.
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
void fun(int &a, int &b);
int main(void)
{
int x = 10;
int y = 20;
cout << x << "," << y << endl;
fun(x, y);
cout << x << "," << y << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void fun(int &a, int &b)
{
int c = 0;
c = a;
a = b;
b = c;
}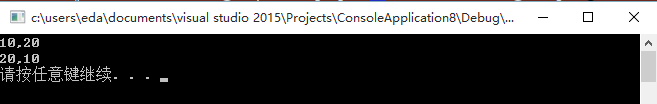
程序利用引用实现了数据的互换。引用可以简单理解为是变量的一个别名,对别名的操作同样也会作用到原变量之上。






















 1575
1575

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








