学了Spring操作 JDBC 之后,当然要学怎么整合Hibernate了,这个例子的整合步骤,xml配置等等都可以应用到实际开发中,毕竟现在企业开发绝大多数都是SpringMvc模式下配合Hibernate来搭建项目的,所以本文从细节出发,详细介绍每一个步骤。。
需求:数据表结构:account表,用户账号表。book表,书籍信息表
项目结构: 

hibernate配置文件
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- 配置hibernate的基本属性 -->
<!-- 数据源配置到ioc容器中,所以在此不需要再配置 -->
<!-- 关联的.hbm.xml 也在ioc容器配置SessionFactory实例时进行配置 -->
<!-- 配置Hibernate的基本属性:方言,sql显示,格式化,自动建表,生成数据表的策略以及二级缓存等。。 -->
<!-- 使用的数据库方言 -->
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<!-- 自动创建表 -->
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<!-- 控制台打印sql语句 -->
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<!-- 格式化sql语句 -->
<property name="format_sql">true</property>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
数据库配置信息文件:db.properties
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql:///testspring
jdbc.initPoolSize=5
jdbc.maxPoolSize=10
Spring的配置文件
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<!-- 导入资源文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties" />
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"></property>
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"></property>
<property name="initialPoolSize" value="${jdbc.initPoolSize}"></property>
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="${jdbc.maxPoolSize}"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 自动扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.*"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 整合Hibernate的SessionFactory的实例:通过Spring提供的LocaltionSessionFactoryBean进行配置 -->
<bean id="sessionFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<!-- 配置数据源的属性 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
<!-- 配置hibernate配置文件的位置 -->
<!--
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml"></property>
-->
<!-- 使用HibernatePropites属性来配置Hibernate的基本配置 -->
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.format_sql">true</prop>
</props>
</property>
<!-- 自动扫描注解方式配置的hibernate类文件 -->
<property name="packagesToScan">
<list>
<value>com.entiy</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置Spring 的声明式事务 -->
<!-- 1.配置事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 2.配置事务属性,需要事务管理器 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 3.配置事务切点,并把切点和事务属性相关联起来 -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.service.*.*(..))" id="txPoincut"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPoincut"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
在ApplicationContext.xml文件中,我们可以引用Hibernate的配置文件来配置Hibernate的基本信息,也可以直接 使用HibernatePropites属性来配置Hibernate的基本配置,那么hibernate.cfg.xml就可以删除不用了,上文是直接在ioc容器使用HibernatePropites属性来配置的
接口 BookShopI.java:
public interface BookShopI {
/**
* 根据书的编号查找书的价格
* @param id 书的编号
* @return
*/
int findBookPriceById(String id);
/**
* 更新书的库存
* @param id 书的编号
*/
void updateBookStore(String id);
/**
* 更新用户的账户余额
* @param userName 用户名
* @param price 余额
*/
void updateUserAccount(String userName,int price);
}
接口的实现 BookShopImpl:
@Repository
public class BookShopImpl implements BookShopI {
@Autowired
private SessionFactory sessionFactory;
// 获取和当前线程绑定的session
private Session getSession() {
return sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
}
@Override
public int findBookPriceById(String id) {
String hql = "select b.price from Book b where b.bookId = :params ";
Query query = getSession().createQuery(hql).setParameter("params", id);
int price = (int) query.uniqueResult();
return price;
}
@Override
public void updateBookStore(String id) {
// 验证库存是否充足
String checkHql = "select b.store from Book b where b.bookId=:params ";
Query query = getSession().createQuery(checkHql).setParameter("params", id);
int store = (int) query.uniqueResult();
if (store == 0) {
throw new BookStoreException("库存不足");
}
String hql = "update Book b set b.store = b.store -1 where b.bookId=:params ";
getSession().createQuery(hql).setParameter("params", id).executeUpdate();
}
@Override
public void updateUserAccount(String userName, int price) {
// 验证余额是否充足
String checkHql = "select a.balance from Account a where a.userName=:params ";
Query query = getSession().createQuery(checkHql).setParameter("params", userName);
float balance = (float) query.uniqueResult();
if (balance < price) {
throw new UserPriceException("余额不足");
}
String hql = "update Account a set a.balance=a.balance - '" + price + "' where a.userName=:params ";
getSession().createQuery(hql).setParameter("params", userName).executeUpdate();
}
}
两个实体类:这里使用的是注解的方式
Account
@Entity
@Table(name="account")
public class Account implements Serializable {
private Long id;
private String userName;
private float balance;
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO)
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Column(name="username")
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
@Column(name="balance")
public float getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(float balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
}
**Book **
@Entity
@Table(name="book")
public class Book implements Serializable {
private Long id;
private String bookName;
private String bookId;
private int price;
private int store;
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO)
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Column(name="bookname")
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
@Column(name="bookid")
public String getBookId() {
return bookId;
}
public void setBookId(String bookId) {
this.bookId = bookId;
}
@Column(name="price")
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Column(name="store")
public int getStore() {
return store;
}
public void setStore(int store) {
this.store = store;
}
}
两个自定义异常:
BookStoreException
public class BookStoreException extends RuntimeException{
public BookStoreException() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public BookStoreException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) {
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public BookStoreException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public BookStoreException(String message) {
super(message);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public BookStoreException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
UserPriceException
public class UserPriceException extends RuntimeException {
public UserPriceException() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public UserPriceException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) {
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public UserPriceException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public UserPriceException(String message) {
super(message);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public UserPriceException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
service层:
** 接口:UserByBookServiceI**
public interface UserByBookServiceI {
/**
* 用户买书
*
* @param UserName
* 用户名
* @param bookId
* 书的编号
*/
void byBook(String userName, String bookId);
/**
* 用户买多本书
*
* @param userName
* 用户名
* @param bookIds
* 书的编号集合
*/
void byMoreBook(String userName, List<String> bookIds);
}
实现:UserByBookServiceImpl
@Service("userByBookService")
public class UserByBookServiceImpl implements UserByBookServiceI {
@Autowired
private BookShopI bookShopI;
@Override
public void byBook(String userName, String bookId) {
//获取书的价格
int price = bookShopI.findBookPriceById(bookId);
//使书的库存减1
bookShopI.updateBookStore(bookId);
//更新用户的账户余额
bookShopI.updateUserAccount(userName, price);
}
@Override
public void byMoreBook(String userName, List<String> bookIds) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
最后测试主方法:
public class Main {
private ApplicationContext ctx = null;
private UserByBookServiceI userByBookService=null;
{
ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext.xml");
userByBookService = (UserByBookServiceI) ctx.getBean("userByBookService");
}
@Test
public void testDataSource() throws SQLException {
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource) ctx.getBean("dataSource");
System.out.println(dataSource.getConnection());
}
@Test
public void byBook(){
userByBookService.byBook("admin", "1001");
}
}
运行前数据:
account表  book表:
book表: 
测试byBook()方法 控制台:

运行后数据 account表 
book表: 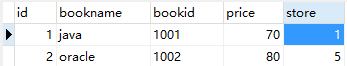
可以看到操作数据是成功的,同样的方法,byMoreBook方法也是可以运行通过的,并且事务的回滚也是可以成功的。






















 2018
2018

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








